dipole/induced-dipole and dipole/induced
... The reaction itself is strongly exothermic, but energy must be put into the system in order to get it going. This energy goes into breaking the weakest bond in the system, which we see from the bond dissociation energy data in Table 4.3, is the Cl-Cl bond with a bond dissociation energy of 242 kJ/mo ...
... The reaction itself is strongly exothermic, but energy must be put into the system in order to get it going. This energy goes into breaking the weakest bond in the system, which we see from the bond dissociation energy data in Table 4.3, is the Cl-Cl bond with a bond dissociation energy of 242 kJ/mo ...
Worked Example 19.1
... amino acid and can donate a proton from the —OH group on the side chain, functioning as an acid. The RO– remaining can interact with the substrate, initiating cleavage of the substrate. (c) Histidine is a basic amino acid and can accept a proton until needed to complete the cleavage reaction. In thi ...
... amino acid and can donate a proton from the —OH group on the side chain, functioning as an acid. The RO– remaining can interact with the substrate, initiating cleavage of the substrate. (c) Histidine is a basic amino acid and can accept a proton until needed to complete the cleavage reaction. In thi ...
chap 1 + 24 review
... o ie: 100.0 = 4 sig figs; .0002 = 1 sig fig; 200 = 1 sig fig o in addition/subtraction, count the place value (ie: tenths) for sig figs o in multiplication/division, count the actual number of sig figs Section 1.6: Dimensional analysis- use conversion factors to cancel out units to change measurem ...
... o ie: 100.0 = 4 sig figs; .0002 = 1 sig fig; 200 = 1 sig fig o in addition/subtraction, count the place value (ie: tenths) for sig figs o in multiplication/division, count the actual number of sig figs Section 1.6: Dimensional analysis- use conversion factors to cancel out units to change measurem ...
problems - chem.msu.su
... 3. What factors affect the solubility of K3[Co(NO2)6] in the mother solution after precipitate formation? Choose the right answers: a) stability constant of complex ion [Co(NO2)6]3–; b) solubility product of the precipitate; c) concentration of K+; d) concentration of Co(II); e) concentration of NO2 ...
... 3. What factors affect the solubility of K3[Co(NO2)6] in the mother solution after precipitate formation? Choose the right answers: a) stability constant of complex ion [Co(NO2)6]3–; b) solubility product of the precipitate; c) concentration of K+; d) concentration of Co(II); e) concentration of NO2 ...
File
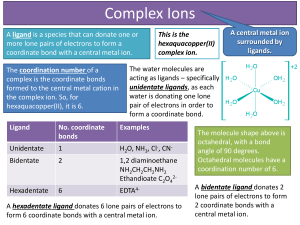
... Complex Ions A ligand is a species that can donate one or more lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. The coordination number of a complex is the coordinate bonds formed to the central metal cation in the complex ion. So, for hexaquacopper(II), it is 6. ...
... Complex Ions A ligand is a species that can donate one or more lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. The coordination number of a complex is the coordinate bonds formed to the central metal cation in the complex ion. So, for hexaquacopper(II), it is 6. ...
Chemical Reactions
... only C, H, (and maybe O) is reacted with oxygen – usually called “burning” If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. If the combustion is incomplete, the products will be CO (or possibly just C) and H2O. ...
... only C, H, (and maybe O) is reacted with oxygen – usually called “burning” If the combustion is complete, the products will be CO2 and H2O. If the combustion is incomplete, the products will be CO (or possibly just C) and H2O. ...
Exam 2
... worth studying. Also problems assigned for the text may also be helpful. Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical resu ...
... worth studying. Also problems assigned for the text may also be helpful. Chap 9 &10-- Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1 reactions. -Know the definitions of Sn2, Sn1, E2 and E1. -Be able to depict the reaction coordinate diagrams of each reaction -Be able to draw the mechanism, products and the stereochemical resu ...
Are You suprised ?
... B) Any proton donor is an acid. C) Solutions of highly charged metal ions are basic. D) For oxoacids of the same central atom, the greater the number of oxygen atoms the stronger the acid. ...
... B) Any proton donor is an acid. C) Solutions of highly charged metal ions are basic. D) For oxoacids of the same central atom, the greater the number of oxygen atoms the stronger the acid. ...
121. Acceptorless Dehydrogenation with Metal
... Efficiency of the Metal-ligand Cooperation catalysts are quite high. Catalysts load can be as high as 0.1%. Scope of the substrates are quite large. Aryl, alkyl, alkeyl(some examples) are both appropriate substituent groups of the substrates. Detailed studied about the operation pattern of cat ...
... Efficiency of the Metal-ligand Cooperation catalysts are quite high. Catalysts load can be as high as 0.1%. Scope of the substrates are quite large. Aryl, alkyl, alkeyl(some examples) are both appropriate substituent groups of the substrates. Detailed studied about the operation pattern of cat ...
Handout
... 20. If the lipid above was a triglyceride, how many fatty acids would be linked to the glycerol? 21. If the lipid above was a phospholipid, how many fatty acids would be linked to the glycerol and what additional group(s) would be present in the molecule? 22. What type of reaction would occur to lin ...
... 20. If the lipid above was a triglyceride, how many fatty acids would be linked to the glycerol? 21. If the lipid above was a phospholipid, how many fatty acids would be linked to the glycerol and what additional group(s) would be present in the molecule? 22. What type of reaction would occur to lin ...
Name - Clydebank High School
... 3. Complete the following sentences by filling in the missing words. Sodium chloride is a salt made when sodium hydroxide is neutralised using ……………………………………….. acid. Calcium sulphate is a salt made by reacting …………………………. hydroxide with sulphuric acid. When potassium hydroxide reacts with nitric ac ...
... 3. Complete the following sentences by filling in the missing words. Sodium chloride is a salt made when sodium hydroxide is neutralised using ……………………………………….. acid. Calcium sulphate is a salt made by reacting …………………………. hydroxide with sulphuric acid. When potassium hydroxide reacts with nitric ac ...
CI 12.4 - Sackville School
... this page Add the reaction types to the arrows Click here to go to the Key words and definitions for help Click here to check ...
... this page Add the reaction types to the arrows Click here to go to the Key words and definitions for help Click here to check ...
Demonstrate understanding of the properties of organic compounds
... products are formed? • But-2-ene and HBr and … But-1-ene • Markovnikov’s rule “The rich get richer, poor get poorer” • Hydrogen is eliminated from the C with least H’s already • But-2-ene is the major product and But-1-ene the minor ...
... products are formed? • But-2-ene and HBr and … But-1-ene • Markovnikov’s rule “The rich get richer, poor get poorer” • Hydrogen is eliminated from the C with least H’s already • But-2-ene is the major product and But-1-ene the minor ...
Document
... hardest to break, whereas the C-I bond is relatively weaker (228 kJmol-1) and therefore easier to break. C-Hal bonds get weaker, and so more reactive, down group 7. Chloro compounds are fairly unreactive and remain in the troposphere long enough to reach the stratosphere, where they react with and ...
... hardest to break, whereas the C-I bond is relatively weaker (228 kJmol-1) and therefore easier to break. C-Hal bonds get weaker, and so more reactive, down group 7. Chloro compounds are fairly unreactive and remain in the troposphere long enough to reach the stratosphere, where they react with and ...
organic revision nots
... substitution and (ii) it directs the incoming substituents to ortho and para positions in benzene ring.. 33. Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. 34. O=C=O is nonpolar while R-O-R is polar. 35. Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synt ...
... substitution and (ii) it directs the incoming substituents to ortho and para positions in benzene ring.. 33. Preparation of ethers by acid dehydration of secondary or tertiary alcohols is not a suitable method. 34. O=C=O is nonpolar while R-O-R is polar. 35. Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synt ...
Chapter 13: EDTA titrations
... Sometimes there is not a strong reaction between EBT and the metal. This can be overcome by a displacement titration. The solution begins with the Mg2+ complexed with EDTA. The analyte is added (assuming higher binding constant and lower concentration) and the Mg2+ is displaced. The Mg2+ is titrate ...
... Sometimes there is not a strong reaction between EBT and the metal. This can be overcome by a displacement titration. The solution begins with the Mg2+ complexed with EDTA. The analyte is added (assuming higher binding constant and lower concentration) and the Mg2+ is displaced. The Mg2+ is titrate ...
Chemical Equations
... • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compounds. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction Types: Combustion •Combustion, at its mos ...
... • Synthesis are, at this introductory level, almost always the reverse of a decomposition reaction. That means that two pieces join together to produce one, a more complex compounds. These pieces can be elements or simpler compounds. • A + B ---> AB Reaction Types: Combustion •Combustion, at its mos ...
Chapter 18 lectures as pdf
... catalysis leads to loss of water, acetal isolated if water removed (protecting group) • Primary amines – imines if water removed • Secondary amines – enamines if water removed ...
... catalysis leads to loss of water, acetal isolated if water removed (protecting group) • Primary amines – imines if water removed • Secondary amines – enamines if water removed ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.