Regents Unit 15b: Halides, Alcohols, & Ethers
... • Contain only carbon & hydrogen • But carbon can form strong covalent bonds to other elements, incl. O, N, F, Cl, Br, I, S, & P ...
... • Contain only carbon & hydrogen • But carbon can form strong covalent bonds to other elements, incl. O, N, F, Cl, Br, I, S, & P ...
C h e m g u id e –... ACID ANHYDRIDES: REACTIONS WITH WATER, ALCOHOLS AND PHENOLS
... and so the top group in your target molecule must come from an acid anhydride, but a bigger one than ethanoic anhydride. You can ignore the other group on the ring as just a distraction. You haven’t come across any reaction which would attach a group like this to a benzene ring, so it must have been ...
... and so the top group in your target molecule must come from an acid anhydride, but a bigger one than ethanoic anhydride. You can ignore the other group on the ring as just a distraction. You haven’t come across any reaction which would attach a group like this to a benzene ring, so it must have been ...
Carboxylic Acid Questions 1.-Arrange the following in order of (i
... (a) Thionyl chloride, SOCl2, is used to prepare acyl chlorides, the base removes the HCl by-product. (b) LiAlH4 is a hydride reducing agent, acids to primary alcohols. (c) An alcohol and a carboxylic acid give an ester. (d) Carboxylic acids react with bases to give carboxylates. ...
... (a) Thionyl chloride, SOCl2, is used to prepare acyl chlorides, the base removes the HCl by-product. (b) LiAlH4 is a hydride reducing agent, acids to primary alcohols. (c) An alcohol and a carboxylic acid give an ester. (d) Carboxylic acids react with bases to give carboxylates. ...
Chemistry of Nitrogen-containing Organic
... on reaction with KCN - what type of reaction is this? - what is significant about the length of the carbon chain? ...
... on reaction with KCN - what type of reaction is this? - what is significant about the length of the carbon chain? ...
Green synthesis of 2-amino-7-hydroxy-4-aryl-4H
... scaffolds are more privileged when they join with rigid hetero ring systems and/or other chemical functional groups. Obviously, functionalization of chromene derivatives has played an ever increasing role in the synthetic approaches to promising compounds in the field of medicinal chemistry. On the ...
... scaffolds are more privileged when they join with rigid hetero ring systems and/or other chemical functional groups. Obviously, functionalization of chromene derivatives has played an ever increasing role in the synthetic approaches to promising compounds in the field of medicinal chemistry. On the ...
this PDF file
... TMAFC was used for the oxidation of some alcohols and polycyclic arenes under microwave irradiation in CH2Cl2 as solvent. This method offers some advantages in term of simplicity of performance, simple operation condition, no side product formation, very low reaction time and a wide range of substra ...
... TMAFC was used for the oxidation of some alcohols and polycyclic arenes under microwave irradiation in CH2Cl2 as solvent. This method offers some advantages in term of simplicity of performance, simple operation condition, no side product formation, very low reaction time and a wide range of substra ...
Mechanisms of Alkenes
... • When working through a mechanism, the goal is NOT to memorize the steps of a mechanism OF A SPECIFIC MOLECULE– when you do that, typically you become too focused on the structures provided in one example. • When that happens, you get confused when the next mechanism problem has a DIFFERENT struct ...
... • When working through a mechanism, the goal is NOT to memorize the steps of a mechanism OF A SPECIFIC MOLECULE– when you do that, typically you become too focused on the structures provided in one example. • When that happens, you get confused when the next mechanism problem has a DIFFERENT struct ...
Slide 1
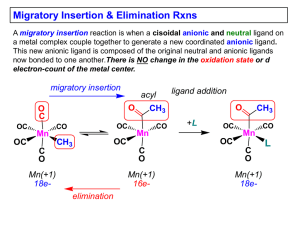
... 2) The two groups that react must be cisoidal to one another 3) A vacant coordination site is generated by the migratory insertion. Therefore, a vacant site is required for the back elimination reaction (e.g., b-hydride elimination). A trapping ligand is often needed to coordinate to the empty site ...
... 2) The two groups that react must be cisoidal to one another 3) A vacant coordination site is generated by the migratory insertion. Therefore, a vacant site is required for the back elimination reaction (e.g., b-hydride elimination). A trapping ligand is often needed to coordinate to the empty site ...
The Affinity of the Platinum Metals for Refractory Oxides
... oxides. Such reactions, which m a y start at temperatures as low as 6OO0C, occur because of the high a f i n i t y of the p l a t i n u m metals f o r the metal of the refractory oxide and result in the formation of intermetallic compounds or stable d i d solutions. T h i s account, based o n experi ...
... oxides. Such reactions, which m a y start at temperatures as low as 6OO0C, occur because of the high a f i n i t y of the p l a t i n u m metals f o r the metal of the refractory oxide and result in the formation of intermetallic compounds or stable d i d solutions. T h i s account, based o n experi ...
VI. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) C
... minutes a few mL) through the stopcock using a syringe while N gas is flowing. Then break up all chunks of sodium and sodium salts using a very large spatula (you will have to flush with N again after that). Repeat until no further reaction occurs. Treat similarly with ethanol. Break up all chunks. ...
... minutes a few mL) through the stopcock using a syringe while N gas is flowing. Then break up all chunks of sodium and sodium salts using a very large spatula (you will have to flush with N again after that). Repeat until no further reaction occurs. Treat similarly with ethanol. Break up all chunks. ...
PPT File
... Compounds in which a hydrogen is replaced by an OH group. We distinguish three types: ...
... Compounds in which a hydrogen is replaced by an OH group. We distinguish three types: ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... However, because of carbon’s versatility, these few elements can be combined to build an inexhaustible variety of organic molecules. ...
... However, because of carbon’s versatility, these few elements can be combined to build an inexhaustible variety of organic molecules. ...
Chapter 4 Carbon and the Molecular Diversity of Life Lecture Outline
... However, because of carbon’s versatility, these few elements can be combined to build an inexhaustible variety of organic molecules. ...
... However, because of carbon’s versatility, these few elements can be combined to build an inexhaustible variety of organic molecules. ...
Microsoft Word - Final Exam Study Guide
... change in energy for reaction, Hammond’s postulate, nucleophile, leaving group, substitution reactions, SN1 mechanism, SN2 mechanism, alkene classifications, alkene stability, elimination reactions, Zaitsev’s rule, E1 mechanism, E2 mechanism, antiperiplanar, comparing substitution and elimination me ...
... change in energy for reaction, Hammond’s postulate, nucleophile, leaving group, substitution reactions, SN1 mechanism, SN2 mechanism, alkene classifications, alkene stability, elimination reactions, Zaitsev’s rule, E1 mechanism, E2 mechanism, antiperiplanar, comparing substitution and elimination me ...
I - Holland Public Schools
... In this case, 2 C2H2’s and 5 O2’s would need to collide in the same place at the same time VERY UNLIKELY * OK, so how does this work then? The chemical reaction is divided into a series of steps, each of which produces an intermediate, a product that is used as a reactant in a later step. Each step ...
... In this case, 2 C2H2’s and 5 O2’s would need to collide in the same place at the same time VERY UNLIKELY * OK, so how does this work then? The chemical reaction is divided into a series of steps, each of which produces an intermediate, a product that is used as a reactant in a later step. Each step ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT Paragraphs 3-1 through 3-18
... Amines result from the replacement of one or more of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia with hydrocarbons and have the general formula R-NH2. There are four classifications of amines: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Primary amines result from replacing one of the hydrogens of ammonia by a h ...
... Amines result from the replacement of one or more of the hydrogen atoms of ammonia with hydrocarbons and have the general formula R-NH2. There are four classifications of amines: primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary. Primary amines result from replacing one of the hydrogens of ammonia by a h ...
The 16 and 18 Electron Rule in Organometallic Chemistry and
... 2 Types of Organometallic Reactions Reactions of ligands which do not directly involve the transition metal are excluded from this classification.Some examples of such reactions are methanolysis of Ni(PF& to give Ni(PF,) ,[PF,-n(OMe)n], Friedel-Crafts acylation of ferrocene, and nucleophilic attack ...
... 2 Types of Organometallic Reactions Reactions of ligands which do not directly involve the transition metal are excluded from this classification.Some examples of such reactions are methanolysis of Ni(PF& to give Ni(PF,) ,[PF,-n(OMe)n], Friedel-Crafts acylation of ferrocene, and nucleophilic attack ...
Benzyne Mechanism
... Phenols and phenoxides are highly reactive. Only a weak catalyst (HF) required for FriedelCrafts reaction. Tribromination occurs without catalyst. Even reacts with CO2. O ...
... Phenols and phenoxides are highly reactive. Only a weak catalyst (HF) required for FriedelCrafts reaction. Tribromination occurs without catalyst. Even reacts with CO2. O ...
3(aq)
... more elements or new compounds. 1. It is the “opposite” of a synthesis reaction 2. Generically: AB A + B 3. Example: Ammonium nitrate is decomposed to produce dinitrogen monoxide and water. NH4NO3(s) N2O(g) + 2H2O(L) 4. One reactant will yield 2 or more products. ...
... more elements or new compounds. 1. It is the “opposite” of a synthesis reaction 2. Generically: AB A + B 3. Example: Ammonium nitrate is decomposed to produce dinitrogen monoxide and water. NH4NO3(s) N2O(g) + 2H2O(L) 4. One reactant will yield 2 or more products. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.