GRADE 11F: Chemistry 6
... Use the example of the substitution of halogenoalkanes by ammonia to identify the functional group amine. In a teacher-led session, outline the main rules for naming amines. Arrange students into pairs and give them a list of names of a variety of amines. Ask them to build models of them using ‘ball ...
... Use the example of the substitution of halogenoalkanes by ammonia to identify the functional group amine. In a teacher-led session, outline the main rules for naming amines. Arrange students into pairs and give them a list of names of a variety of amines. Ask them to build models of them using ‘ball ...
DuPont Tyzor Product Information - Tyzor
... not make any express or implied warranty that these products will continue to have these typical properties. ...
... not make any express or implied warranty that these products will continue to have these typical properties. ...
Chapter 10 Structure and Synthesis of Alcohols
... a. Aldehydes and ketones b. Esters and carboxylic acids c. Aldehydes, ketones, esters, and carboxylic acids d. Alkenes and alkynes e. Aldehydes, ketones, alkenes, and ...
... a. Aldehydes and ketones b. Esters and carboxylic acids c. Aldehydes, ketones, esters, and carboxylic acids d. Alkenes and alkynes e. Aldehydes, ketones, alkenes, and ...
Document
... C atoms are connected in a continuous non-branching chain. E.g. Butane: CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3 ...
... C atoms are connected in a continuous non-branching chain. E.g. Butane: CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH3 ...
Lecture 20 - U of L Class Index
... hence is best considered an organic derivative. Carbon suboxide is and evil-smelling gas, which is stable at low temperatures, but polymerizes when warmed to room temperature. The two important oxides are the monoxide and dioxide. CO is formed when carbon is burned in a deficiency of oxy gen. It is ...
... hence is best considered an organic derivative. Carbon suboxide is and evil-smelling gas, which is stable at low temperatures, but polymerizes when warmed to room temperature. The two important oxides are the monoxide and dioxide. CO is formed when carbon is burned in a deficiency of oxy gen. It is ...
06_chapter 1
... al. [8] on Ni/SiO2-Al2O3 catalysts. Two types of nickel sites were identified by temperature programmed reduction studies: one with no interaction with the support and the other having interaction with the support. They observed a direct correlation between hydrogenation activity and NiO with no int ...
... al. [8] on Ni/SiO2-Al2O3 catalysts. Two types of nickel sites were identified by temperature programmed reduction studies: one with no interaction with the support and the other having interaction with the support. They observed a direct correlation between hydrogenation activity and NiO with no int ...
Chap 24. Transition Metals and Coordination Compounds
... The oxidation state of the metal center is denoted by a Roman numeral If the complex is an anion, the ending -ate is attached to the name of the metal ...
... The oxidation state of the metal center is denoted by a Roman numeral If the complex is an anion, the ending -ate is attached to the name of the metal ...
main types and mechanisms of the reactions in organic chemistry
... Task №3. Give the mechanism of ethylene bromination reaction. Solution. Reactions which undergo -bonds fision, i.e., addition reactions, are typical for compounds which consist of carbon atoms in the state of sp2- or sphybridization. These reactions can pass on radical or onic mechanism depending o ...
... Task №3. Give the mechanism of ethylene bromination reaction. Solution. Reactions which undergo -bonds fision, i.e., addition reactions, are typical for compounds which consist of carbon atoms in the state of sp2- or sphybridization. These reactions can pass on radical or onic mechanism depending o ...
Module 2 Alcohols, halogenoalkanes and analysis
... Throughout the centuries, chemists have synthesised new substances and investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials. In the recent past, organic chemists have developed a broad range of original and exciting materials, such as pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, solvents and plas ...
... Throughout the centuries, chemists have synthesised new substances and investigated their properties in the search for more useful materials. In the recent past, organic chemists have developed a broad range of original and exciting materials, such as pharmaceuticals, refrigerants, solvents and plas ...
spectroscopic and antimicrobial studies of mixed ligand complexes
... stoichiometry of these complexes have been found to be [M (L1) (L2) (H2O)2] {where M = Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II)}. It is found that Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II) complexes exhibited octahedral geometry. The antimicrobial activities of ligands and their mixed ligand complexes were ...
... stoichiometry of these complexes have been found to be [M (L1) (L2) (H2O)2] {where M = Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II)}. It is found that Co (II), Ni (II), Cu (II) and Zn (II) complexes exhibited octahedral geometry. The antimicrobial activities of ligands and their mixed ligand complexes were ...
(PCP)Ir(O2)_BW_9-25.dot - Werner Kaminsky
... Organometallic reactivity is utilized in a range of organic transformations, but organometallic oxidation chemistry remains relatively under-developed.i Molecular oxygen is the most attractive terminal oxidant for chemical processes, in terms of cost, atom economy, and the potential for few byproduc ...
... Organometallic reactivity is utilized in a range of organic transformations, but organometallic oxidation chemistry remains relatively under-developed.i Molecular oxygen is the most attractive terminal oxidant for chemical processes, in terms of cost, atom economy, and the potential for few byproduc ...
Complexation Reactions
... B. Yes. The metal cation is the Lewis acid. C. No. Ammonia is a neutral molecule and cannot can not accept electron density from a Lewis base. D. No. The metal cation cannot accept electron density from a Lewis base. ...
... B. Yes. The metal cation is the Lewis acid. C. No. Ammonia is a neutral molecule and cannot can not accept electron density from a Lewis base. D. No. The metal cation cannot accept electron density from a Lewis base. ...
Chem 4471 - Transition Metals and Catalysis
... Three in-class tests (15%, 15% and 20%); one final examination (50%). Term tests will be held during the regular lecture period on January 27, February 15 and March 17. If you miss a term test through illness, the weighting of marks will be revised appropriately. There is a three-hour final in the F ...
... Three in-class tests (15%, 15% and 20%); one final examination (50%). Term tests will be held during the regular lecture period on January 27, February 15 and March 17. If you miss a term test through illness, the weighting of marks will be revised appropriately. There is a three-hour final in the F ...
Organic Chemistry
... http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/organic/orgonaming5.htm http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/organic/orgonaming6.htm ...
... http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/organic/orgonaming5.htm http://www.kentchemistry.com/links/organic/orgonaming6.htm ...
week 4_carbohydrates
... in presence of oxidising agents, metal ions (Cu2+) and enzymes, monosacchs undergo several oxidation reactions e.g. Oxidation of aldehyde group (R-CHO) yields aldonic acid; of terminal CH2OH (alcohol) yields uronic acid; and of both the aldehyde and CH2OH gives aldaric acid. The carbonyl groups in b ...
... in presence of oxidising agents, metal ions (Cu2+) and enzymes, monosacchs undergo several oxidation reactions e.g. Oxidation of aldehyde group (R-CHO) yields aldonic acid; of terminal CH2OH (alcohol) yields uronic acid; and of both the aldehyde and CH2OH gives aldaric acid. The carbonyl groups in b ...
Alcohols phenols ethers
... (R–O/Ar–O) yields another class of compounds known as ‘ethers’, for example, CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether). ethers as compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group. Alcohols are organic compounds that have one or more hydroxy (-OH) ...
... (R–O/Ar–O) yields another class of compounds known as ‘ethers’, for example, CH3OCH3 (dimethyl ether). ethers as compounds formed by substituting the hydrogen atom of hydroxyl group of an alcohol or phenol by an alkyl or aryl group. Alcohols are organic compounds that have one or more hydroxy (-OH) ...
Complete the following equations
... Give THREE major uses of magnesium metal. (1) manufacture of light alloys for air-craft body; (2) reducing agent in isolation of B, Si, and Ti; (3) fire-work, flare and flash photography. ...
... Give THREE major uses of magnesium metal. (1) manufacture of light alloys for air-craft body; (2) reducing agent in isolation of B, Si, and Ti; (3) fire-work, flare and flash photography. ...
III B.Sc. Int.nanomaterials - E
... to the zinc salt solution, with the molar ratio of TAA and zinc ions being set to an initial value of either 4 or 8. In intervals, aliquots were collected from the reacting solution. 3. Describe about the Sol-gel process The sol-gel process, as the name implies, involves the evolution of inorganic n ...
... to the zinc salt solution, with the molar ratio of TAA and zinc ions being set to an initial value of either 4 or 8. In intervals, aliquots were collected from the reacting solution. 3. Describe about the Sol-gel process The sol-gel process, as the name implies, involves the evolution of inorganic n ...
1 R R 1Ch Ro_ R___ + ____ ____ + _+ S ___y → +
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 13. In a decomposition reaction, there is a single reactant. ________ 14. The activity series of metals can be used to predict products in doublereplacement reactions. ________ 15. Carbon dioxide an ...
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 13. In a decomposition reaction, there is a single reactant. ________ 14. The activity series of metals can be used to predict products in doublereplacement reactions. ________ 15. Carbon dioxide an ...
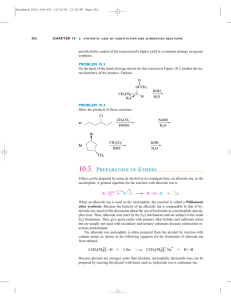
10.3 PREPARATION OF ETHERS
... However, this reaction is much less useful when ammonia is the nucleophile because the initial product, a primary amine, is a stronger base and a stronger nucleophile than is ammonia. Therefore, the primary amine preferentially reacts as the nucleophile, producing a secondary amine as a by-product ( ...
... However, this reaction is much less useful when ammonia is the nucleophile because the initial product, a primary amine, is a stronger base and a stronger nucleophile than is ammonia. Therefore, the primary amine preferentially reacts as the nucleophile, producing a secondary amine as a by-product ( ...
Document
... At higher temperatures, or in the absence of good nucleophiles, elimination becomes dominant. ...
... At higher temperatures, or in the absence of good nucleophiles, elimination becomes dominant. ...
Normal and abnormal carbene complexes derived
... been reached that, in general, very little M ? L p-backdonation occurs in known abnormal carbene complexes [13]. In most publications the metal–ligand bond in both normal and abnormal azolylidene or pyridylidene complexes is represented by a single line. The double bond description is used either to ...
... been reached that, in general, very little M ? L p-backdonation occurs in known abnormal carbene complexes [13]. In most publications the metal–ligand bond in both normal and abnormal azolylidene or pyridylidene complexes is represented by a single line. The double bond description is used either to ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.