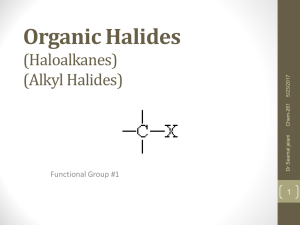Transition Metals
... number of donor atoms bonded to the central metal atom or ion in the complex ...
... number of donor atoms bonded to the central metal atom or ion in the complex ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Chemistry (IOSR-JAC)
... A study on Structural Aspects and Biological Activity of (E)-N'-[2- ydroxybenzylidene]benzohydrazide 1.2 Synthesis of ligand Ligand HBBH is synthesized by the reported procedure 5. 1.3 Synthesis of metal complexes The metal complexes of Cu (II), Ni (II), Co (II) and Mn(II) were prepared by mixing e ...
... A study on Structural Aspects and Biological Activity of (E)-N'-[2- ydroxybenzylidene]benzohydrazide 1.2 Synthesis of ligand Ligand HBBH is synthesized by the reported procedure 5. 1.3 Synthesis of metal complexes The metal complexes of Cu (II), Ni (II), Co (II) and Mn(II) were prepared by mixing e ...
Answers, Problem Set 12 (full)... “2,4
... (b) A saturated hydrocarbon is one that contains as many H’s per carbon as possible, and so you could say that it is saturated “with H’s”. It contains no double or triple bonds. Once a double bond or triple bond is formed, there will be less H’s because C only forms 4 bonds before its valence shell ...
... (b) A saturated hydrocarbon is one that contains as many H’s per carbon as possible, and so you could say that it is saturated “with H’s”. It contains no double or triple bonds. Once a double bond or triple bond is formed, there will be less H’s because C only forms 4 bonds before its valence shell ...
problem 18.33b Chapter 19: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... The reactivity of the acid derivative is related to it resonance stabilization. The C-N bond of amides is significantly stabilized through resonance and is consequently, the least reactive acid derivative. The C-Cl bond of acid chlorides is the least stabilized by resonance and is the most reactive ...
... The reactivity of the acid derivative is related to it resonance stabilization. The C-N bond of amides is significantly stabilized through resonance and is consequently, the least reactive acid derivative. The C-Cl bond of acid chlorides is the least stabilized by resonance and is the most reactive ...
AS Self Study Unit - Uses of Alkenes
... know that the alkenes can exhibit E-Z stereoisomerism be able to draw the structures of E and Z isomers understand that E-Z isomers exist due to restricted rotation about the C=C bond understand that the double bond in an alkene is a centre of high electron density understand the mechanism of electr ...
... know that the alkenes can exhibit E-Z stereoisomerism be able to draw the structures of E and Z isomers understand that E-Z isomers exist due to restricted rotation about the C=C bond understand that the double bond in an alkene is a centre of high electron density understand the mechanism of electr ...
Chapter 21: Carboxylic Acid Derivatives
... • Acid Halides, RCOX – Derived from the carboxylic acid name by replacing the -ic acid ending with -yl or the carboxylic acid ending with –carbonyl and specifying the halide ...
... • Acid Halides, RCOX – Derived from the carboxylic acid name by replacing the -ic acid ending with -yl or the carboxylic acid ending with –carbonyl and specifying the halide ...
Organic Halides (Haloalkanes) (Alkyl Halides)
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
... • The presence of a halide makes the molecule more polar. • Since water is also polar and “like dissolves like”, alkyl halides are soluble in water. The more halides connected to the parent chain, the more polar the molecule. • The polar nature of the molecule means that boiling and melting points o ...
TFG_QU Gonzálvez Noguera, Miguel Agustín
... Thiosemicarbazones (TSCs) have been considered of particular interest in medicinal chemistry due to their anticancer, antibacterial and antiviral activity.1 These compounds have a long history in medical studies, dating back to the 1950s, when they were discovered to be antileukemic agents, an effec ...
... Thiosemicarbazones (TSCs) have been considered of particular interest in medicinal chemistry due to their anticancer, antibacterial and antiviral activity.1 These compounds have a long history in medical studies, dating back to the 1950s, when they were discovered to be antileukemic agents, an effec ...
2 - Glow Blogs
... 0.315 g of an organic compound containing C, H and O was completely burned in oxygen and was found to produce 0.630 g of carbon dioxide and 0.258 g of water. Calculate the empirical formula for this compound. (4) ...
... 0.315 g of an organic compound containing C, H and O was completely burned in oxygen and was found to produce 0.630 g of carbon dioxide and 0.258 g of water. Calculate the empirical formula for this compound. (4) ...
Alkenes - Gadjah Mada University
... CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 Hydrogenation requires high temperatures and pressures as well as the presence of a catalyst (e.g. Ni). ...
... CH3CH=CHCH3 + H2 CH3CH2CH2CH3 Hydrogenation requires high temperatures and pressures as well as the presence of a catalyst (e.g. Ni). ...
CHAPTER 12. DECODING ORGANIC STRUCTURES: THE
... models give a somewhat clearer picture of the shapes of the molecules, but not the way the atoms can rotate around their bonds to form different shapes. For example, it makes no difference where the -OH is placed on the diagram of ethanol because all the positions are equivalent. This fact, which be ...
... models give a somewhat clearer picture of the shapes of the molecules, but not the way the atoms can rotate around their bonds to form different shapes. For example, it makes no difference where the -OH is placed on the diagram of ethanol because all the positions are equivalent. This fact, which be ...
Classes and Nomenclature of Halogen Compounds
... Reactions of Halogen Compounds C) Formation of organometallic compounds. Most organic chlorides, bromides, and iodides react with certain metals to give organometallic compounds, molecules with carbon-metal bonds. Grignard reagents are obtained by the reaction of alkyl or aryl halides with meta ...
... Reactions of Halogen Compounds C) Formation of organometallic compounds. Most organic chlorides, bromides, and iodides react with certain metals to give organometallic compounds, molecules with carbon-metal bonds. Grignard reagents are obtained by the reaction of alkyl or aryl halides with meta ...
Functional Groups III
... Amines have relatively high boiling points because they can form hydrogen bonds with each other as well as van der Waals ...
... Amines have relatively high boiling points because they can form hydrogen bonds with each other as well as van der Waals ...
Question number - Bethlehem College .::. Welcome
... Heating under reflux increases the rate of reaction and the condenser returns evaporated organic molecules to the reaction flask by condensing the vapour that is produced on heating. (iii) Sulfuric acid = catalyst (or dehydrating agent ) Anhydrous sodium sulfate = To remove last traces of water from ...
... Heating under reflux increases the rate of reaction and the condenser returns evaporated organic molecules to the reaction flask by condensing the vapour that is produced on heating. (iii) Sulfuric acid = catalyst (or dehydrating agent ) Anhydrous sodium sulfate = To remove last traces of water from ...
Revised organic chemistry
... 1) Dehydration of Alcohols: When an alcohol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 100oC or with phosphoric acid at 200oC or by passing alcohol vapour over alumina, P2O5 or anhydrous zinc chloride at 350-400oC a molecule of water is eliminated and alkene is formed. ...
... 1) Dehydration of Alcohols: When an alcohol is heated with concentrated sulphuric acid at 100oC or with phosphoric acid at 200oC or by passing alcohol vapour over alumina, P2O5 or anhydrous zinc chloride at 350-400oC a molecule of water is eliminated and alkene is formed. ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.