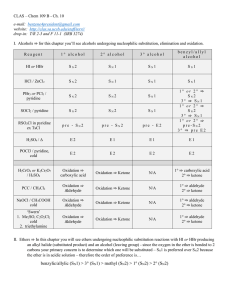
formic (methanoic) acid
... The most important acyl transfer agent in living organisms is acetyl coenzyme A. This compound is the ester of acetic acid and coenzyme A, a thiol. ...
... The most important acyl transfer agent in living organisms is acetyl coenzyme A. This compound is the ester of acetic acid and coenzyme A, a thiol. ...
Unit 4 Chemical Kinetics and Chemical Equilibrium
... Reactions of Alkenes Most reactions of alkenes are electrophilic addition reactions. Step 1: Attack of electrophile on pi bond forming a carbonium ion: ...
... Reactions of Alkenes Most reactions of alkenes are electrophilic addition reactions. Step 1: Attack of electrophile on pi bond forming a carbonium ion: ...
xes, except for the mono-complex which was regu
... Stepwise formation constants of the glycinato complexes decreased with the number of glycinato ions within the complexes. However, the stepwise formation reactions were more exothermic at a higher complex than a lower one in the case of nickel(II) and zinc(II) ions, except for the formation of Zn(gl ...
... Stepwise formation constants of the glycinato complexes decreased with the number of glycinato ions within the complexes. However, the stepwise formation reactions were more exothermic at a higher complex than a lower one in the case of nickel(II) and zinc(II) ions, except for the formation of Zn(gl ...
Document
... Ligand substitution in square planar complexes 21.3 The shape of the transition state Ligand substitution in octahedral complexes 21.5 Rate law and their interpretation 21.6 The activation of octahedral complexes ...
... Ligand substitution in square planar complexes 21.3 The shape of the transition state Ligand substitution in octahedral complexes 21.5 Rate law and their interpretation 21.6 The activation of octahedral complexes ...
Exam 4 - Chemistry Courses
... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12. A student measures the following in the process of collecting nitrogen gas by water displacement at STP: Vapor pressure of water at 0 °C: 4.58 mm Hg Volume of gas collected: 100 mL Assuming ideal gas behavior, ...
... --------------------------------------------------------------------------------------12. A student measures the following in the process of collecting nitrogen gas by water displacement at STP: Vapor pressure of water at 0 °C: 4.58 mm Hg Volume of gas collected: 100 mL Assuming ideal gas behavior, ...
Chem 51A Chapter 3 2014
... intermolecular forces present between covalent molecules. There are three types of intermolecular forces between covalent compounds: • van der Waals forces • dipole-dipole interactions • hydrogen bonding A. van der Waals Forces van der Waals forces are very weak interactions caused by momentary chan ...
... intermolecular forces present between covalent molecules. There are three types of intermolecular forces between covalent compounds: • van der Waals forces • dipole-dipole interactions • hydrogen bonding A. van der Waals Forces van der Waals forces are very weak interactions caused by momentary chan ...
A-Frame Complexes of Dirhodium Bridged by Dicarbene and
... diphosphines (usually dppm) bridge a pair of metals. Owing to the rotational freedom in the linking groups between the diphosphine or dicarbene ends of these bidentate ligands, complexes bridged by only one of these groups tend to adopt a skewed arrangement3a,7,11 in which the metals are quite widel ...
... diphosphines (usually dppm) bridge a pair of metals. Owing to the rotational freedom in the linking groups between the diphosphine or dicarbene ends of these bidentate ligands, complexes bridged by only one of these groups tend to adopt a skewed arrangement3a,7,11 in which the metals are quite widel ...
Microsoft Word
... mainly due to the steric and stereoelectronic differences between the substituents of the chiral sulfur atom: a lone pair of electrons, an oxygen atom and two different carbon ligands. It is well known that sulfoxides participate as neighbouring groups in a number of reactions. Sulfoxide group parti ...
... mainly due to the steric and stereoelectronic differences between the substituents of the chiral sulfur atom: a lone pair of electrons, an oxygen atom and two different carbon ligands. It is well known that sulfoxides participate as neighbouring groups in a number of reactions. Sulfoxide group parti ...
CHM 103 Lecture 22 S07
... Last Time: Cis-Trans Isomers In an alkene, the double bond • is rigid, i.e. NO ROTATION around the double bond! • holds attached groups in fixed positions. ...
... Last Time: Cis-Trans Isomers In an alkene, the double bond • is rigid, i.e. NO ROTATION around the double bond! • holds attached groups in fixed positions. ...
The Characteristic Properties of Acids and Bases
... 37 Which statement does not describe a property of a weak acid in solution? ...
... 37 Which statement does not describe a property of a weak acid in solution? ...
Key
... molecules move around, they will occasionally cluster in one place on an atom setting up a temporary, instantaneous dipole within the molecule. This electron cluster causes a repulsion of electrons in neighboring atoms such that another instantaneous dipole is formed. The interactions between this m ...
... molecules move around, they will occasionally cluster in one place on an atom setting up a temporary, instantaneous dipole within the molecule. This electron cluster causes a repulsion of electrons in neighboring atoms such that another instantaneous dipole is formed. The interactions between this m ...
reaction rate - davis.k12.ut.us
... Expressing Reaction Rates (cont.) • Reaction rates are determined experimentally (and always expressed as a positive value). • Average rate of reaction: the change in concentration of a reactant or product that occurs during a specific time interval. ...
... Expressing Reaction Rates (cont.) • Reaction rates are determined experimentally (and always expressed as a positive value). • Average rate of reaction: the change in concentration of a reactant or product that occurs during a specific time interval. ...
unit 6 alcohols
... HOCH2CH2CH2CH2Br + 2Li do NOT produce HOCH2CH2CH2CH2Li. The H from the –OH reacts immediately: HOCH2CH2CH2CH2Br + 2Li Li+ -OCH2CH2CH2CH3 + LiBr ...
... HOCH2CH2CH2CH2Br + 2Li do NOT produce HOCH2CH2CH2CH2Li. The H from the –OH reacts immediately: HOCH2CH2CH2CH2Br + 2Li Li+ -OCH2CH2CH2CH3 + LiBr ...
Practical Problem I - Scheikundeolympiade
... i) Determination of bromide in the unknown sample solution Fill the 250 mL volumetric flask containing the bromide sample solution to the mark with water. Transfer three 25.00 mL portions (pipette) of the sample solution to three erlenmeyer flasks. Add about 5 mL of 6 M nitric acid (measuring cylin ...
... i) Determination of bromide in the unknown sample solution Fill the 250 mL volumetric flask containing the bromide sample solution to the mark with water. Transfer three 25.00 mL portions (pipette) of the sample solution to three erlenmeyer flasks. Add about 5 mL of 6 M nitric acid (measuring cylin ...
today in chemistry history
... © COMPOUND INTEREST 2016 - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM | @COMPOUNDCHEM Shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence. ...
... © COMPOUND INTEREST 2016 - WWW.COMPOUNDCHEM.COM | @COMPOUNDCHEM Shared under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives licence. ...
naming of ethers
... Solubility in water – low molecular mass ethers are soluble in water. As the mass of a molecule (size of the alkyl group) increases, the solubility decreases. Melting and Boiling points – the melting and boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols. Flammability – like alcohols, ethers ...
... Solubility in water – low molecular mass ethers are soluble in water. As the mass of a molecule (size of the alkyl group) increases, the solubility decreases. Melting and Boiling points – the melting and boiling points of ethers are lower than isomeric alcohols. Flammability – like alcohols, ethers ...
Equilibrium
... b. If raising the temperature of the reaction results in an equilibrium with a higher concentration of C than A, how will the value of Keq change? 12. The following reaction occurs when steam is passed over hot carbon. The mixture of gases it generates is called water gas and is useful as an indust ...
... b. If raising the temperature of the reaction results in an equilibrium with a higher concentration of C than A, how will the value of Keq change? 12. The following reaction occurs when steam is passed over hot carbon. The mixture of gases it generates is called water gas and is useful as an indust ...
Document
... Stability and Coordination Complexes ([MLn]x+) Typically expressed in terms of an overall formation or stability constant. (This is Kst on the Chemistry Data sheet you receive with exams) [M]x+ + nL ...
... Stability and Coordination Complexes ([MLn]x+) Typically expressed in terms of an overall formation or stability constant. (This is Kst on the Chemistry Data sheet you receive with exams) [M]x+ + nL ...
Chapter 10 - UCSB CLAS
... II. Ethers ⇒ In this chapter you will see ethers undergoing nucleophilic substitution reactions with HI or HBr producing an alkyl halide (substituted product) and an alcohol (leaving group) - since the oxygen in the ether is bonded to 2 carbons your primary concern is to determine which one will be ...
... II. Ethers ⇒ In this chapter you will see ethers undergoing nucleophilic substitution reactions with HI or HBr producing an alkyl halide (substituted product) and an alcohol (leaving group) - since the oxygen in the ether is bonded to 2 carbons your primary concern is to determine which one will be ...
Experiment 1
... information before you can draw the Lewis structure. 3- Complete the octets of the atoms bonded to the central atom. (Remember, however, that hydrogen can have only two electrons). 4- Place any leftover electrons on the central atom, even if doing so results in more than an octet. 5- If there are no ...
... information before you can draw the Lewis structure. 3- Complete the octets of the atoms bonded to the central atom. (Remember, however, that hydrogen can have only two electrons). 4- Place any leftover electrons on the central atom, even if doing so results in more than an octet. 5- If there are no ...
Hydroformylation

Hydroformylation, also known as oxo synthesis or oxo process, is an important homogeneously catalyzed industrial process for the production of aldehydes from alkenes. This chemical reaction entails the addition of a formyl group (CHO) and a hydrogen atom to a carbon-carbon double bond. This process has undergone continuous growth since its invention in 1938: Production capacity reached 6.6×106 tons in 1995. It is important because the resulting aldehydes are easily converted into many secondary products. For example, the resulting aldehydes are hydrogenated to alcohols that are converted to plasticizers or detergents. Hydroformylation is also used in specialty chemicals, relevant to the organic synthesis of fragrances and natural products. The development of hydroformylation, which originated within the German coal-based industry, is considered one of the premier achievements of 20th-century industrial chemistry.The process typically entails treatment of an alkene with high pressures (between 10 to 100 atmospheres) of carbon monoxide and hydrogen at temperatures between 40 and 200 °C. Transition metal catalysts are required.













![[Ru(Triphos)H2(CO)] Characterisation - Durham e](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/017676948_1-4352644236c53cc416f065328f560d26-300x300.png)