PowerPoint 簡報
... the hydrogen atoms in water, HOH • alcohols form hydrogen bonds to other alcohol molecules, increasing boiling point, and to water, making them very soluble in water ...
... the hydrogen atoms in water, HOH • alcohols form hydrogen bonds to other alcohol molecules, increasing boiling point, and to water, making them very soluble in water ...
Reductive Elimination
... absence of excess phosphine and have found that there are three decomposition pathways, one for each of the different intermediates, 18e, 16e, and 14e, that can be formed. ...
... absence of excess phosphine and have found that there are three decomposition pathways, one for each of the different intermediates, 18e, 16e, and 14e, that can be formed. ...
A Crash Course In Organic Chemistry
... portion of a molecule that undergoes predictable reactions. All other organic compounds can be considered to be derivatives of hydrocarbons ...
... portion of a molecule that undergoes predictable reactions. All other organic compounds can be considered to be derivatives of hydrocarbons ...
Document
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
... 21.7: Preparation of Amines by Alkylation of Ammonia Ammonia and other alkylamines are good nucleophiles and react with 1° and 2° alkyl halides or tosylates via an SN2 reaction yielding alkyl amines. ...
Organic - UCLA Chemistry and Biochemistry
... the characteristic apparent quartet (J = 12 Hz) for Ha that is also seen in the spectrum of Id.' Likewise the stereochemistry of 9b was determined primarily from its highfield 'H NMR spectrum which showed the expected coupling constants for the conformation drawn, namely: Ha dd, J = 11.8, 6.8 Hz;Hb ...
... the characteristic apparent quartet (J = 12 Hz) for Ha that is also seen in the spectrum of Id.' Likewise the stereochemistry of 9b was determined primarily from its highfield 'H NMR spectrum which showed the expected coupling constants for the conformation drawn, namely: Ha dd, J = 11.8, 6.8 Hz;Hb ...
Ch. 11 Notes with Answers
... 3. PBr3 or HBr can convert an alcohol into RBr, capable of normal substitution and elimination reactions. Retrosynthesis Problems (In which you decide what to start from): Design syntheses for the following. Allowed starting materials include: Bromobenzene cyclopentanol any acyclic alcohol or alkene ...
... 3. PBr3 or HBr can convert an alcohol into RBr, capable of normal substitution and elimination reactions. Retrosynthesis Problems (In which you decide what to start from): Design syntheses for the following. Allowed starting materials include: Bromobenzene cyclopentanol any acyclic alcohol or alkene ...
Chapters E-18 review - Bakersfield College
... 10. How can we convert thé first compound into thé second compound? Détermine thé type of chemical reaction, catalyst (if it is necessary) and other necessary conditions: a) Benzène to Chlorobenzene ...
... 10. How can we convert thé first compound into thé second compound? Détermine thé type of chemical reaction, catalyst (if it is necessary) and other necessary conditions: a) Benzène to Chlorobenzene ...
Atom Transfer Radical Polymerization and
... The first such mechanism involves the reversible capture of the polymeric radical by some species to form a stable, persistent radical (Eq. 1). This mechanism was proposed in the aluminum/TEMPO-mediated (where TEMPO is the 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy free radical) as well as thephosphite-me ...
... The first such mechanism involves the reversible capture of the polymeric radical by some species to form a stable, persistent radical (Eq. 1). This mechanism was proposed in the aluminum/TEMPO-mediated (where TEMPO is the 2,2,6,6-tetramethyl-1-piperidinyloxy free radical) as well as thephosphite-me ...
CHM 222 - Jefferson State Community College
... Demonstrate an understanding of reactions involving aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives including nomenclature, synthesis and mechanisms. 1. Name and draw aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Propose a synthesis for each type of compound listed above. ...
... Demonstrate an understanding of reactions involving aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives including nomenclature, synthesis and mechanisms. 1. Name and draw aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and their derivatives. 2. Propose a synthesis for each type of compound listed above. ...
Addition/elimination under acidic conditions
... Predict the products of nucleophilic acyl substitutions Predict the direction of equilibrium and draw energy diagrams for the mechanisms of nucleophilic acyl substitution taking into account Le Chatlier’s principle ...
... Predict the products of nucleophilic acyl substitutions Predict the direction of equilibrium and draw energy diagrams for the mechanisms of nucleophilic acyl substitution taking into account Le Chatlier’s principle ...
MECH 558 Combustion Class Notes
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen atoms (i.e. no mo ...
... Before learning how hydrocarbons react with oxygen in flames, we must first go over some nomenclature for the different classes of hydrocarbons. 2.1. Alkanes (paraffins): These molecules consist of carbon atoms which are all connected by single bonds and are saturated with hydrogen atoms (i.e. no mo ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry Unit 2: Organic
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
... The energy required to promote the electron would be more than offset by the formation of two extra covalent bonds. However, whereas the others would involve 2p orbitals. Spectroscopic measurements show that all four bonds in methane are identical. Let's look at an alkane, ethane for example. Each c ...
Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
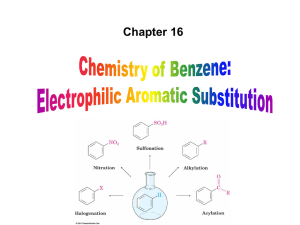
... – Aromatic nitration is useful in the pharmaceutical industry because the nitro-substituted product can be reduced by Fe or SnCl2 to yield arylamine ...
... – Aromatic nitration is useful in the pharmaceutical industry because the nitro-substituted product can be reduced by Fe or SnCl2 to yield arylamine ...
Sodium is an abundant metallic element with atomic number as 11
... -The reaction of sodium with alcohols is similar to the reaction of sodium with water, but slower. There are two general reactions with organic halides. One of them requires the condensation of two organic compounds, which form halogens when those are eliminated. The second type of reaction includes ...
... -The reaction of sodium with alcohols is similar to the reaction of sodium with water, but slower. There are two general reactions with organic halides. One of them requires the condensation of two organic compounds, which form halogens when those are eliminated. The second type of reaction includes ...
Fulltext PDF
... 3) The presence of sterically hindered groups bound to the Natoms facilitating the reductive elimination of the product from the metal during catalysis. Tolman in 1977 had devised a method for comparing the electrondonating ability of phosphine ligands [11]. This was determined by reacting one equiv ...
... 3) The presence of sterically hindered groups bound to the Natoms facilitating the reductive elimination of the product from the metal during catalysis. Tolman in 1977 had devised a method for comparing the electrondonating ability of phosphine ligands [11]. This was determined by reacting one equiv ...
Stereochemistry Tutorials: Assigning R/S and E/Z
... Assign priorities to the groups attached to the stereocenter. The four atoms directly attached to the stereocenter are hydrogen, carbon, carbon, and oxygen. Oxygen (Z = 8) has highest priority and hydrogen (Z = 1) has lowest priority. The two carbons (Z = 6) are tied in priority, so we move out to t ...
... Assign priorities to the groups attached to the stereocenter. The four atoms directly attached to the stereocenter are hydrogen, carbon, carbon, and oxygen. Oxygen (Z = 8) has highest priority and hydrogen (Z = 1) has lowest priority. The two carbons (Z = 6) are tied in priority, so we move out to t ...
10.4 Alcohols 10.4 Alcohols
... •Alcohols have the general formula: CnH2n+1OH •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •di ...
... •Alcohols have the general formula: CnH2n+1OH •The physical properties of alcohols are similar to those of both water and hydrocarbons •The shorter chain alcohols such as methanol and ethanol are similar to water, in general they •have higher boiling points than hydrocarbons but lower than water •di ...
© John Congleton, Orange Coast College Organic Chemistry 220
... What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to complete mechanisms that involeve hydride and methyl shifts. During E1 and E2 reactions what will b ...
... What makes a good nucleophile? What makes a good base? What makes a good leaving group? What is meant by high and low polarizability? Allylic bromination Understand, be able to predict, and be able to complete mechanisms that involeve hydride and methyl shifts. During E1 and E2 reactions what will b ...
Aromatic Compounds
... • In 1825 Michael Faraday isolated a compound which boils at 80o and had a H:C ratio of 1:1 • It was later synthesized from PhCO2H isolated from gum benzoin, it was found to have a MW of 78 amu (C6H6) and hence called benzene. • Numerous compounds related to benzene with low C:H ratio and pleasant a ...
... • In 1825 Michael Faraday isolated a compound which boils at 80o and had a H:C ratio of 1:1 • It was later synthesized from PhCO2H isolated from gum benzoin, it was found to have a MW of 78 amu (C6H6) and hence called benzene. • Numerous compounds related to benzene with low C:H ratio and pleasant a ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.