
2006 Practice Final Exam - Department of Chemistry | Oregon State
... Galactose is an aldohexose Galactose has 5 chiral carbons It can form a ring structure It is a carbohydrate ...
... Galactose is an aldohexose Galactose has 5 chiral carbons It can form a ring structure It is a carbohydrate ...
Document
... Organic reactions can convert simple organic molecules into large, complex ones. TAXOL is an anti-cancer drug that chemists can synthesize. ...
... Organic reactions can convert simple organic molecules into large, complex ones. TAXOL is an anti-cancer drug that chemists can synthesize. ...
Sodium Borohydride Reduction of Vanillin
... drugs as L-dopa, which is used for treating Parkinson's disease. At one time synthetic vanillin was made mostly from isoeugenol, a naturally occurring and widely used perfume ingredient. Most vanillin is now synthesized using lignin derived from wood pulp. Lignin is a complex polymer that gives rigi ...
... drugs as L-dopa, which is used for treating Parkinson's disease. At one time synthetic vanillin was made mostly from isoeugenol, a naturally occurring and widely used perfume ingredient. Most vanillin is now synthesized using lignin derived from wood pulp. Lignin is a complex polymer that gives rigi ...
Reactions of 2, 6-cycloheptadienone and 2, 7
... aldehyde and acetonedicarboxylic acid, Robinson' also noted '(that tropinone might result.. .by the addition of methylamine to a cycloheptadienone. . . . I ' Yearly 10 years ago, Hor&k2reported the characterization by paper chromatography of tropinone prepared from a large excess of methylamine and ...
... aldehyde and acetonedicarboxylic acid, Robinson' also noted '(that tropinone might result.. .by the addition of methylamine to a cycloheptadienone. . . . I ' Yearly 10 years ago, Hor&k2reported the characterization by paper chromatography of tropinone prepared from a large excess of methylamine and ...
Hydroxyl Compounds
... EFFECTS OF Acidity • The acidity decreases as the substitution on the alkyl group increase. - Reason: a more highly substituted alkyl group inhibits solvation of the alkoxide ion and drives the dissociation equilibrium to the left. - For example: methanol is more acidic than t-butyl alcohol. • The ...
... EFFECTS OF Acidity • The acidity decreases as the substitution on the alkyl group increase. - Reason: a more highly substituted alkyl group inhibits solvation of the alkoxide ion and drives the dissociation equilibrium to the left. - For example: methanol is more acidic than t-butyl alcohol. • The ...
Reactions of Alcohols
... The ZnCl2 coordinates to the hydroxyl oxygen, and this generates a far superior leaving group. Primary alcohols react in a similar fashion except the free cation is not generated, and the substitution is of S N2 ...
... The ZnCl2 coordinates to the hydroxyl oxygen, and this generates a far superior leaving group. Primary alcohols react in a similar fashion except the free cation is not generated, and the substitution is of S N2 ...
chapter 6-hydroxyl compounds
... EFFECTS OF Acidity • The acidity decreases as the substitution on the alkyl group increase. - Reason: a more highly substituted alkyl group inhibits solvation of the alkoxide ion and drives the dissociation equilibrium to the left. - For example: methanol is more acidic than t-butyl alcohol. • The ...
... EFFECTS OF Acidity • The acidity decreases as the substitution on the alkyl group increase. - Reason: a more highly substituted alkyl group inhibits solvation of the alkoxide ion and drives the dissociation equilibrium to the left. - For example: methanol is more acidic than t-butyl alcohol. • The ...
Chemistry of Carbon
... Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons are the simplest type of carbon-based compounds. Nonetheless, they can vary greatly in size. The smallest hydrocarbons have just one or two carbon atoms, but large hydrocarbons may have hundreds. The size of hydrocarbon m ...
... Hydrocarbons are compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen. Hydrocarbons are the simplest type of carbon-based compounds. Nonetheless, they can vary greatly in size. The smallest hydrocarbons have just one or two carbon atoms, but large hydrocarbons may have hundreds. The size of hydrocarbon m ...
cape chemistry unit ii module i
... Tertiary alcohol Tertiary alcohol: -OH on C with 0 hydrogen attached [-OH on C attached to 3 other C] No oxidation except under extreme conditions ...
... Tertiary alcohol Tertiary alcohol: -OH on C with 0 hydrogen attached [-OH on C attached to 3 other C] No oxidation except under extreme conditions ...
Organic Chemistry Fifth Edition
... • Hydroxide cleaves epoxides at elevated temperatures to give trans 1,2-diols ...
... • Hydroxide cleaves epoxides at elevated temperatures to give trans 1,2-diols ...
Alcohols, Phenols , Phenols and Ethers Alcohols
... a manner that the boron atom gets attached to the sp carbon carrying greater number of hydrogen atoms. The alcohol so formed looks as if it has been formed by the addition of water to the alkene in a way opposite to the Markovnikov’s rule. In this reaction, alcohol is obtained in excellent yield. 2. ...
... a manner that the boron atom gets attached to the sp carbon carrying greater number of hydrogen atoms. The alcohol so formed looks as if it has been formed by the addition of water to the alkene in a way opposite to the Markovnikov’s rule. In this reaction, alcohol is obtained in excellent yield. 2. ...
Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... When ethylbenzene or propylbenzene react under radical conditions, halogenation occurs primarily at the benzylic position Chapter 15 ...
... When ethylbenzene or propylbenzene react under radical conditions, halogenation occurs primarily at the benzylic position Chapter 15 ...
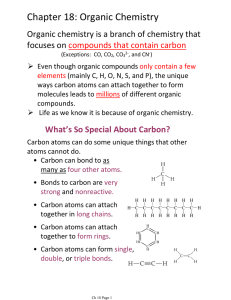
Chapter 18: Organic Chemistry
... bond - this is the parent chain. Name the parent chain like an alkane, but drop the 'ane' ending and add 'ene'. 2) Number the parent chain starting from the end closer to the double bond and designate the location of the first carbon in the double bond as a number in front of the parent chain. 3) Na ...
... bond - this is the parent chain. Name the parent chain like an alkane, but drop the 'ane' ending and add 'ene'. 2) Number the parent chain starting from the end closer to the double bond and designate the location of the first carbon in the double bond as a number in front of the parent chain. 3) Na ...
ch13[1].
... The Carbonyl Group • In this and several following chapters, we study the physical and chemical properties of classes of compounds containing the carbonyl group, C=O. • aldehydes and ketones (Chapter 13) • carboxylic acids (Chapter 14) • acid halides, acid anhydrides, esters, and amides ...
... The Carbonyl Group • In this and several following chapters, we study the physical and chemical properties of classes of compounds containing the carbonyl group, C=O. • aldehydes and ketones (Chapter 13) • carboxylic acids (Chapter 14) • acid halides, acid anhydrides, esters, and amides ...
T_AllylCF3paperBM[5]
... CF3-substituted allyl alcohols 1 promoted by Bronsted or Lewis acids were investigated (Scheme 1, нет ее). Dehydroxylation of 1 can lead to allyl cation having resonance forms A and B. However, due to strong electron-withdrawing character of CF3-group form A is destabilized significantly. As a resul ...
... CF3-substituted allyl alcohols 1 promoted by Bronsted or Lewis acids were investigated (Scheme 1, нет ее). Dehydroxylation of 1 can lead to allyl cation having resonance forms A and B. However, due to strong electron-withdrawing character of CF3-group form A is destabilized significantly. As a resul ...
Reductive Deoxygenation of Ketones and Secondary Alcohols by
... Friedel-Crafts alkylation products of the toluene by the (8) Structure 5, representing an aluminoxane dimer, is only exemplary of the wide variety of oligomers possibly formed. (9) (a) An AI-H bond either was initially present in the organoaluminum reagents employed or was potentially available from ...
... Friedel-Crafts alkylation products of the toluene by the (8) Structure 5, representing an aluminoxane dimer, is only exemplary of the wide variety of oligomers possibly formed. (9) (a) An AI-H bond either was initially present in the organoaluminum reagents employed or was potentially available from ...
Identification of Alcohols
... Finally if no precipitate is formed after the 10 minutes- standing period, dilute the solution with an equal volume of distilled water to obtain the iodoform precipitate. It is important to proceed through all these steps so that only at the final step you can say that the test is negative. Bot ...
... Finally if no precipitate is formed after the 10 minutes- standing period, dilute the solution with an equal volume of distilled water to obtain the iodoform precipitate. It is important to proceed through all these steps so that only at the final step you can say that the test is negative. Bot ...
Porphyrin Complex - Center for Biomimetic Systems
... by 2, triphenylmethanol was yielded as the only detected product. When the triphenylmethane hydroxylation was carried out in the presence of H218O, 50% of the oxygen atom in the triphenylmethanol product derived from the labeled water (Scheme 1A). Furthermore, when the triphenylmethane hydroxylation ...
... by 2, triphenylmethanol was yielded as the only detected product. When the triphenylmethane hydroxylation was carried out in the presence of H218O, 50% of the oxygen atom in the triphenylmethanol product derived from the labeled water (Scheme 1A). Furthermore, when the triphenylmethane hydroxylation ...
OCR A Level Chemistry B (Salters) Multiple Choice Questions Quiz
... We’d like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you. If you do not currently offer this ...
... We’d like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ you can help us to ensure that our resources work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click ‘Send’. Thank you. If you do not currently offer this ...
Week # 3 Homework doc
... and nitrogen, and has a negative partial charge. The hydrogen, which has a partial positive charge tries to find another atom of oxygen or nitrogen with excess electrons to share and is attracted to the partial negative charge. This forms the basis for the hydrogen bond. Hydrogen Bond Definition: Th ...
... and nitrogen, and has a negative partial charge. The hydrogen, which has a partial positive charge tries to find another atom of oxygen or nitrogen with excess electrons to share and is attracted to the partial negative charge. This forms the basis for the hydrogen bond. Hydrogen Bond Definition: Th ...
Materials Seminar Professor Carsten Sievers Georgia Institute of Technology
... higher alcohols. HDO is a promising route for converting complex mixtures of oxygenates in bio-oils to biofuels. The process provides oils with reduced reactivity and corrosiveness and increases the energy density of the product. In HDO, oxygen-containing functional groups are replaced by hydrogen, ...
... higher alcohols. HDO is a promising route for converting complex mixtures of oxygenates in bio-oils to biofuels. The process provides oils with reduced reactivity and corrosiveness and increases the energy density of the product. In HDO, oxygen-containing functional groups are replaced by hydrogen, ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.












![ch13[1].](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008194698_1-d188c504eac7b7806e762a2340484910-300x300.png)
![T_AllylCF3paperBM[5]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003584459_1-3decab572f7fca68901a941affab18ea-300x300.png)








