Scope and Limitations - Organic Reactions Wiki
... Osmium tetroxide has since established itself as the reagent of choice for the syndihydroxylation of olefins, primarily because of its inertness toward other functional groups and lack of over-oxidation products.4 Researchers from the UpJohn company reported a convenient and reliable procedure for ...
... Osmium tetroxide has since established itself as the reagent of choice for the syndihydroxylation of olefins, primarily because of its inertness toward other functional groups and lack of over-oxidation products.4 Researchers from the UpJohn company reported a convenient and reliable procedure for ...
SULFONATION OF BY SO3
... The sulfonation process relates to the sulfur trioxide sulfonation of long chain and branched chain aliphatic alcohols such as fatty alcohols, and to the sulfonation of the aromatic nucleus of alkyl aromatic compounds. The reaction of sulfur trioxide is with an alkyl benzene whereby the sulfonated a ...
... The sulfonation process relates to the sulfur trioxide sulfonation of long chain and branched chain aliphatic alcohols such as fatty alcohols, and to the sulfonation of the aromatic nucleus of alkyl aromatic compounds. The reaction of sulfur trioxide is with an alkyl benzene whereby the sulfonated a ...
course outline - Clackamas Community College
... Describe how amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to make a protein molecule and know the kinds of reactions involved in making and breaking these bonds. Define and recognize descriptions of the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein. Know the four major classes of ...
... Describe how amino acids are joined by peptide bonds to make a protein molecule and know the kinds of reactions involved in making and breaking these bonds. Define and recognize descriptions of the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of a protein. Know the four major classes of ...
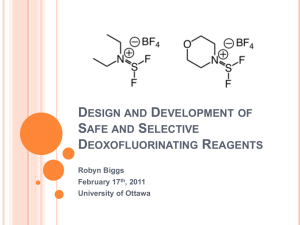
Design and Development of Safe and Selective Deoxofluorinating
... Umemoto, T.; Singh, R. P.; Xu, Y.; Saito, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18199. ...
... Umemoto, T.; Singh, R. P.; Xu, Y.; Saito, N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2010, 132, 18199. ...
Organic compounds containing Nitrogen
... **6. Explain with asuitable example how benzene sulphonyl chloride can distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines? Ans. Hinsberg’s reagent i.e. benzene sulphonyl chloride ( C6H5SO2Cl) reacts with primary, secondary and tertiary amines in a different manner. This is used for the distinction o ...
... **6. Explain with asuitable example how benzene sulphonyl chloride can distinguish primary, secondary and tertiary amines? Ans. Hinsberg’s reagent i.e. benzene sulphonyl chloride ( C6H5SO2Cl) reacts with primary, secondary and tertiary amines in a different manner. This is used for the distinction o ...
Lecture8
... Electrophilic carbenes are prone to nucleophilic attack. The reactivity is similar to that of carbonyl derivatives in organic chemistry. ...
... Electrophilic carbenes are prone to nucleophilic attack. The reactivity is similar to that of carbonyl derivatives in organic chemistry. ...
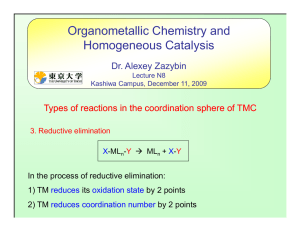
Catalysis by main-group metal - Université Paris-Sud
... The discovery of simple processes and reactions for the formation of C-N bonds represents an important challenge for synthetic chemists.1 Substituted amines have wide applications in the synthesis of drugs, dyes, detergents, fragrances, pharmaceuticals, and crop protection agents. Among the various ...
... The discovery of simple processes and reactions for the formation of C-N bonds represents an important challenge for synthetic chemists.1 Substituted amines have wide applications in the synthesis of drugs, dyes, detergents, fragrances, pharmaceuticals, and crop protection agents. Among the various ...
New L-Serine Derivative Ligands as Cocatalysts for Diels
... effect of AlCl3 and FeCl3 (entries 2 and 4, Table 1) being totally suppressed. This suggests that the cation coordinates to the basic amine group of 6 and the resulting complex is not sufficiently acidic to catalyze the Diels-Alder reaction. The Boc-protection of serine 8 led to serine ligand 4. The ...
... effect of AlCl3 and FeCl3 (entries 2 and 4, Table 1) being totally suppressed. This suggests that the cation coordinates to the basic amine group of 6 and the resulting complex is not sufficiently acidic to catalyze the Diels-Alder reaction. The Boc-protection of serine 8 led to serine ligand 4. The ...
Mannich Reaction - SUST Repository
... suitably activated saturated derivatives ,and NH substrates may be amine ,amides,hetrocycles,etc.Out of OH substrate alcohol are mainly able to give stable Mannich products5.C-,N-,O- and SMannich bases are known. C- Mannich bases such as : R-(C=O)-C-CH2N ,Z-C (Z= carboxy ,Nitro,N-hetroaryl,etc),Z=C ...
... suitably activated saturated derivatives ,and NH substrates may be amine ,amides,hetrocycles,etc.Out of OH substrate alcohol are mainly able to give stable Mannich products5.C-,N-,O- and SMannich bases are known. C- Mannich bases such as : R-(C=O)-C-CH2N ,Z-C (Z= carboxy ,Nitro,N-hetroaryl,etc),Z=C ...
Fluorinated Alcohols Enable Olefin Epoxidation by H2O2
... 6-311G**, which was abandoned in favor of the more extended basis set. The reaction critical points for the epoxidation pathways in Scheme 1 were studied by gradient optimization. All the TSs were verified by frequency calculations. The reaction mechanisms for the smaller systems, (e,n) and (e,F3) w ...
... 6-311G**, which was abandoned in favor of the more extended basis set. The reaction critical points for the epoxidation pathways in Scheme 1 were studied by gradient optimization. All the TSs were verified by frequency calculations. The reaction mechanisms for the smaller systems, (e,n) and (e,F3) w ...
Synthesis of enantiopure alcohols
... Previously we have reported that the enantioselectivity (E) decreased during esterifications of a range of secondary alcohols (1-4) catalyzed by immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) and that addition of enantiopure (R)alcohols, (R)-1, (R)-2, (R)-5, (R)-6 and (R)-7, induced incr ...
... Previously we have reported that the enantioselectivity (E) decreased during esterifications of a range of secondary alcohols (1-4) catalyzed by immobilized lipase B from Candida antarctica (Novozym 435) and that addition of enantiopure (R)alcohols, (R)-1, (R)-2, (R)-5, (R)-6 and (R)-7, induced incr ...
When 1°, 2°, aromatic amines or aryl amines . (Rand
... Thus the chief problem encountered in electrophilic substitution with aromatlf amines is that are hightly reactive. For example, ...
... Thus the chief problem encountered in electrophilic substitution with aromatlf amines is that are hightly reactive. For example, ...
Diphenylsilene - American Chemical Society
... least squares analyses of the expression k d m y = ko + kq[Q]. b2,3Dimethyl-l,3-butadiene. Not determined. well as several other products which have not yet been rigorously identified. At least one of these is the product of addition of the solvent to 2, according to G C / M S analysis of the crude ...
... least squares analyses of the expression k d m y = ko + kq[Q]. b2,3Dimethyl-l,3-butadiene. Not determined. well as several other products which have not yet been rigorously identified. At least one of these is the product of addition of the solvent to 2, according to G C / M S analysis of the crude ...
215-216 HH W12-notes
... As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
... As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
Chapter 13. Alcohols, Diols, and Ethers
... As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
... As HOCl is not stable, it has to be generated in situ in the reaction medium. ...
Chapter 16
... Due to this polarization, the orbitals are no longer symmetrical for an aldehyde or ketone as they are for an alkene – there is more electron density on oxygen in HOMO and more electron density on carbon in LUMO ...
... Due to this polarization, the orbitals are no longer symmetrical for an aldehyde or ketone as they are for an alkene – there is more electron density on oxygen in HOMO and more electron density on carbon in LUMO ...
12-Nucleophilic Reactions
... The addition of salts to nucleophilic reactions also indicated situations beyond the limiting mechanisms, remember the example discussed earlier concerning common ion salts ...
... The addition of salts to nucleophilic reactions also indicated situations beyond the limiting mechanisms, remember the example discussed earlier concerning common ion salts ...
RES15_c2_wp
... 2. The structures of phenol and other phenols 3. The acidic properties of phenol, i.e. with sodium and sodium hydroxide 4. The explanation of the acidic properties of phenol – in terms of the delocalisation of oxygen’s lone pairs 5. The reaction of phenol with bromine 6. The explanation of phenol’s ...
... 2. The structures of phenol and other phenols 3. The acidic properties of phenol, i.e. with sodium and sodium hydroxide 4. The explanation of the acidic properties of phenol – in terms of the delocalisation of oxygen’s lone pairs 5. The reaction of phenol with bromine 6. The explanation of phenol’s ...
Organic Compounds - 2012 Book Archive
... Carbon is unique among the elements in its ability to catenate, to form a wide variety of compounds that contain long chains and/or rings of carbon atoms. (For more information on carbon, see Chapter 12 "Solids", Section 12.8 "Polymeric Solids", and Chapter 22 "The ", Section 22.2 "The Elements of G ...
... Carbon is unique among the elements in its ability to catenate, to form a wide variety of compounds that contain long chains and/or rings of carbon atoms. (For more information on carbon, see Chapter 12 "Solids", Section 12.8 "Polymeric Solids", and Chapter 22 "The ", Section 22.2 "The Elements of G ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.