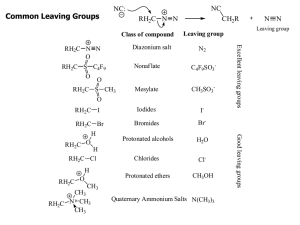
Common Leaving Groups
... Elimination Reactions Whenever substitution reactions are possible, we must also consider whether or not elimination reactions might occur under the same reaction conditions. In elimination reactions, a “neutral” molecule is „eliminated‟ from the substrate to form a π bond. The π bond is formed bet ...
... Elimination Reactions Whenever substitution reactions are possible, we must also consider whether or not elimination reactions might occur under the same reaction conditions. In elimination reactions, a “neutral” molecule is „eliminated‟ from the substrate to form a π bond. The π bond is formed bet ...
ppt
... • Stereoisomers: Isomers with the same connectivity between atoms but have a different arrangement of atoms. • We have already examined a form of stereoisomerism when we studied geometric isomers, that is, cis-trans isomers in disubstituted cycloalkanes and in alkenes. • In this chapter, we study is ...
... • Stereoisomers: Isomers with the same connectivity between atoms but have a different arrangement of atoms. • We have already examined a form of stereoisomerism when we studied geometric isomers, that is, cis-trans isomers in disubstituted cycloalkanes and in alkenes. • In this chapter, we study is ...
INTRODUCTION - Open Access Repository of Indian Theses
... 3. A Mild and Highly Efficient Synthesis of 3-Pyrrolyl-Indolinones and Pyrrolyl-Indeno[1,2-b]Quinoxalines using BiCl3 as a Catalyst An efficient synthesis of 3-pyrrolyl-indolinones and pyrrolyl-indeno[1,2-b] quinoxalines is described by the reaction of 4-hydroxyproline with isatin or indeno[1,2b]qui ...
... 3. A Mild and Highly Efficient Synthesis of 3-Pyrrolyl-Indolinones and Pyrrolyl-Indeno[1,2-b]Quinoxalines using BiCl3 as a Catalyst An efficient synthesis of 3-pyrrolyl-indolinones and pyrrolyl-indeno[1,2-b] quinoxalines is described by the reaction of 4-hydroxyproline with isatin or indeno[1,2b]qui ...
Acid-Catalyzed Hydration of Alkenes
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... transition state for attack of water on bromonium ion has carbocation character; more stable transition state (left) has positive charge on more highly substituted carbon ...
... the slow turnover rate hamper their potential utility. The second ones are the recently studied nickel complexes that provide enantioselectivities similar to those using titanium complexes but with low catalyst loadings (1 mol %). For the latter group, only Woodward and coworkers reported the succes ...
Rutgers...Ch17 Reactions of Aromatic Compounds
... In the case of toluene, ortho (and para) attack results in the positive charge being spread over two secondary carbons and one tertiary carbon atom (the one bearing the CH3 group). Since the sigma complexes for ortho (and para) attack have resonance forms with tertiary carbons, they are more stable ...
... In the case of toluene, ortho (and para) attack results in the positive charge being spread over two secondary carbons and one tertiary carbon atom (the one bearing the CH3 group). Since the sigma complexes for ortho (and para) attack have resonance forms with tertiary carbons, they are more stable ...
In the bachelor thesis of Esther Schippers, research is
... therefore also be soluble in aqueous solvents. To achieve this, for instance an ionic charge can be brought in the molecule. Ions are often good soluble in aqueous solutions. 3. The scaffold should have a part of the molecule that can easily be synthesized with another functional group. When differe ...
... therefore also be soluble in aqueous solvents. To achieve this, for instance an ionic charge can be brought in the molecule. Ions are often good soluble in aqueous solutions. 3. The scaffold should have a part of the molecule that can easily be synthesized with another functional group. When differe ...
Chapter 5
... determined. The gas phase Ni–C and C–O distances (which are directly comparable with our calculations) are 1.838 and 1.141 Å, respectively. We determined the Ni–C bond length to be 1.848 Å, 0.01 Å longer than the experimental value, whereas for the C–O bond our computed value is 1.164 Å (0.023 Å lon ...
... determined. The gas phase Ni–C and C–O distances (which are directly comparable with our calculations) are 1.838 and 1.141 Å, respectively. We determined the Ni–C bond length to be 1.848 Å, 0.01 Å longer than the experimental value, whereas for the C–O bond our computed value is 1.164 Å (0.023 Å lon ...
4 Reactions Alcohol Thiols GOB Structures
... Dehydration of Alcohols The dehydration of a secondary alcohol can result in the formation of a minor product and a major product. Saytzeff’s rule states that • the major product is the one that forms by removing the hydrogen from the carbon atom that has the smaller number of hydrogen atoms. • hyd ...
... Dehydration of Alcohols The dehydration of a secondary alcohol can result in the formation of a minor product and a major product. Saytzeff’s rule states that • the major product is the one that forms by removing the hydrogen from the carbon atom that has the smaller number of hydrogen atoms. • hyd ...
Perspective and prospects for pincer ligand chemistry
... to introduce chirality in the arms. These ligands impose a C2 symmetry at the metal center, allowing for investigations of chiral induction in reactive substrates. One interesting class of pincers can be prepared by chloropalladation of difunctional alkynes, giving N−C−S and N−C−O derivatives in whi ...
... to introduce chirality in the arms. These ligands impose a C2 symmetry at the metal center, allowing for investigations of chiral induction in reactive substrates. One interesting class of pincers can be prepared by chloropalladation of difunctional alkynes, giving N−C−S and N−C−O derivatives in whi ...
Reaction of orthoesters with alcohols in the presence of acidic
... as stated before, this reaction is found to be general with regard to various orthoesters but selective with respect to various primary allylic and benzylic alcohols. However, when SiO2 is used as the catalyst, we could isolate corresponding O-acetylated compound 3 as major product (in case of prima ...
... as stated before, this reaction is found to be general with regard to various orthoesters but selective with respect to various primary allylic and benzylic alcohols. However, when SiO2 is used as the catalyst, we could isolate corresponding O-acetylated compound 3 as major product (in case of prima ...
Final Sc. Ed. 423. Chemistry II
... as acids and bases, reaction with phosphorus halides, thionyl chlorides, sulphuric acid, carboxylic acids, oxidation, reduction) Introduction, nomenclature, classification structure methods of preparation (Dehydration of alcohols, Williamson synthesis) Physical properties Chemical properties (Haloge ...
... as acids and bases, reaction with phosphorus halides, thionyl chlorides, sulphuric acid, carboxylic acids, oxidation, reduction) Introduction, nomenclature, classification structure methods of preparation (Dehydration of alcohols, Williamson synthesis) Physical properties Chemical properties (Haloge ...
Reactions of alcohols File
... -CH2OH -C-CH(OH)-Calcohols! NB Oxidant = hot acidified Cr2O72- [dichromate(VI)] ion] Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
... -CH2OH -C-CH(OH)-Calcohols! NB Oxidant = hot acidified Cr2O72- [dichromate(VI)] ion] Provided by mixture of potassium dichromate(VI), K2Cr2O7, and excess dilute sulphuric acid, H2SO4. Oxidant is represented by : [O] ...
Topic 16 notes - A
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
... Optical isomers are often found together in a mixture in equal quantities. The opposite effect they have on the rotation of plane polarised light will thus result in no overall rotation. An equimolar mixture of two optical isomers will thus have no effect on plane polarised light and is thus not opt ...
Air-Stable Trialkylphosphonium Salts
... A. F.; Fu, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6989-7000. Shaughnessy, K. H.; Kim, P.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 2123-2132. (d) Stille reaction: Littke, A. F.; Fu, G. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2411-2413. Littke, A. F.; Schwarz, L.; Fu, G. C. Manuscript in preparation. (e) ...
... A. F.; Fu, G. C. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 6989-7000. Shaughnessy, K. H.; Kim, P.; Hartwig, J. F. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1999, 121, 2123-2132. (d) Stille reaction: Littke, A. F.; Fu, G. C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 1999, 38, 2411-2413. Littke, A. F.; Schwarz, L.; Fu, G. C. Manuscript in preparation. (e) ...
Final Exam Review Sheet Chemistry 110a/1998
... Be able to explain how a kinetic isotope effect can be used to determine the rate-determining step of this oxidation process. c. Explain why 1° alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids. d. Explain how 1° alcohols can be converted to aldehydes when PDC is used as the reagent in anhydrous dichlorome ...
... Be able to explain how a kinetic isotope effect can be used to determine the rate-determining step of this oxidation process. c. Explain why 1° alcohols are converted to carboxylic acids. d. Explain how 1° alcohols can be converted to aldehydes when PDC is used as the reagent in anhydrous dichlorome ...
Nucleophilic Substitution and b
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol, discussed earlier as reverse of hydration Secondary and tertiary alcohols, carbocations Protonation, establishing of good leaving group. Elimination of water to yield carbocation in rate determining step. ...
... Acid Catalyzed Dehydration of an Alcohol, discussed earlier as reverse of hydration Secondary and tertiary alcohols, carbocations Protonation, establishing of good leaving group. Elimination of water to yield carbocation in rate determining step. ...
CH - YSU.edu
... 3. (10 pts) Draw a Newman projection that depicts looking down the C-2 – C-3 bond of n-pentane. Rotate around the C-2 – C-3 bond axis and draw Newman projections for the most stable staggered conformation, the least stable eclipsed conformation and one of the gauche forms. ...
... 3. (10 pts) Draw a Newman projection that depicts looking down the C-2 – C-3 bond of n-pentane. Rotate around the C-2 – C-3 bond axis and draw Newman projections for the most stable staggered conformation, the least stable eclipsed conformation and one of the gauche forms. ...
ppt
... 22.12: Reaction of Amines with Alkyl Halides. Amines react with alkyl halides and tosylates by nucleophilic substitution (SN2). Products from multiple alkylation often results. 22.13: The Hoffmann Elimination. 1° amine react with excess methyl iodide yield quarternary (4°) ammonium salts. E2 elimin ...
... 22.12: Reaction of Amines with Alkyl Halides. Amines react with alkyl halides and tosylates by nucleophilic substitution (SN2). Products from multiple alkylation often results. 22.13: The Hoffmann Elimination. 1° amine react with excess methyl iodide yield quarternary (4°) ammonium salts. E2 elimin ...
104 Chapter 22: Amines. Organic derivatives of ammonia, NH3
... 22.12: Reaction of Amines with Alkyl Halides. Amines react with alkyl halides and tosylates by nucleophilic substitution (SN2). Products from multiple alkylation often results. 22.13: The Hoffmann Elimination. 1° amine react with excess methyl iodide yield quarternary (4°) ammonium salts. E2 elimin ...
... 22.12: Reaction of Amines with Alkyl Halides. Amines react with alkyl halides and tosylates by nucleophilic substitution (SN2). Products from multiple alkylation often results. 22.13: The Hoffmann Elimination. 1° amine react with excess methyl iodide yield quarternary (4°) ammonium salts. E2 elimin ...
Chapter 14: Alcohols, Phenols, and Ethers This chapter is the first of
... This chapter is the first of three that consider hydrocarbon derivatives with oxygen. This chapter is the first of three that consider hydrocarbon derivatives with o containing functional groups. Many biochemically important molecules contain carbon atoms bonded to oxygen atoms. In this chapter we c ...
... This chapter is the first of three that consider hydrocarbon derivatives with oxygen. This chapter is the first of three that consider hydrocarbon derivatives with o containing functional groups. Many biochemically important molecules contain carbon atoms bonded to oxygen atoms. In this chapter we c ...
Faculteit der Natuurwetenschappen, Wiskunde en Informatica
... a [2+2] photocycloaddition. A challenging part of this approach is to obtain enantiomerically pure β-hydroxy-ketones (17, figure 1), which are required for the synthesis of the photo substrate (1). Chiral acetals are used to obtain β-hydroxy-ketones via diastereoselective addition of Grignard reagen ...
... a [2+2] photocycloaddition. A challenging part of this approach is to obtain enantiomerically pure β-hydroxy-ketones (17, figure 1), which are required for the synthesis of the photo substrate (1). Chiral acetals are used to obtain β-hydroxy-ketones via diastereoselective addition of Grignard reagen ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Two substituents on a benzene ring could have three possible relationships: – ortho-: On adjacent carbons. – meta-: With one carbon between them. – para-: On opposite sides of ring. ...
... • Two substituents on a benzene ring could have three possible relationships: – ortho-: On adjacent carbons. – meta-: With one carbon between them. – para-: On opposite sides of ring. ...
Chapter 25 Organic and Biological Chemistry
... • Two substituents on a benzene ring could have three possible relationships: – ortho-: On adjacent carbons. – meta-: With one carbon between them. – para-: On opposite sides of ring. ...
... • Two substituents on a benzene ring could have three possible relationships: – ortho-: On adjacent carbons. – meta-: With one carbon between them. – para-: On opposite sides of ring. ...
Alkene

In organic chemistry, an alkene is an unsaturated hydrocarbon that contains at least one carbon–carbon double bond. Alkene, olefin, and olefine are used often interchangeably (see nomenclature section below). Acyclic alkenes, with only one double bond and no other functional groups, known as mono-enes, form a homologous series of hydrocarbons with the general formula CnH2n. Alkenes have two hydrogen atoms less than the corresponding alkane (with the same number of carbon atoms). The simplest alkene, ethylene (C2H4), which has the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry (IUPAC) name ethene is the organic compound produced on the largest scale industrially. Aromatic compounds are often drawn as cyclic alkenes, but their structure and properties are different and they are not considered to be alkenes.