In the Belly of the Beast
... atmosphere, it began to orbit the giant less quickly, drawing the two objects closer together. They now circle each other at a distance of only about 400,000 kilometers, or about the space between Earth and the moon. ...
... atmosphere, it began to orbit the giant less quickly, drawing the two objects closer together. They now circle each other at a distance of only about 400,000 kilometers, or about the space between Earth and the moon. ...
UK_Astronomy_in_Schools_Liverpool
... Sun and other stars. • the relative positions of the Earth, Sun and planets in the solar system. • about the movements of planets around the Sun and to relate these to gravitational forces • that the Sun and other stars are light sources and that the planets and other bodies are seen by reflected li ...
... Sun and other stars. • the relative positions of the Earth, Sun and planets in the solar system. • about the movements of planets around the Sun and to relate these to gravitational forces • that the Sun and other stars are light sources and that the planets and other bodies are seen by reflected li ...
The Liverpool Telescope
... Sun and other stars. • the relative positions of the Earth, Sun and planets in the solar system. • about the movements of planets around the Sun and to relate these to gravitational forces • that the Sun and other stars are light sources and that the planets and other bodies are seen by reflected li ...
... Sun and other stars. • the relative positions of the Earth, Sun and planets in the solar system. • about the movements of planets around the Sun and to relate these to gravitational forces • that the Sun and other stars are light sources and that the planets and other bodies are seen by reflected li ...
Magnetic Activity Cycles and the Solar
... Sun are bright in Mg II (UV) and Ca II (optical) • Measure ratio of total emission in line cores to flux in the wings Frohlich & Lean (2004) ...
... Sun are bright in Mg II (UV) and Ca II (optical) • Measure ratio of total emission in line cores to flux in the wings Frohlich & Lean (2004) ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... now, we wouldn't know about it for eight minutes because that is how long it would take for the light of the explosion to get here. ...
... now, we wouldn't know about it for eight minutes because that is how long it would take for the light of the explosion to get here. ...
Telescopes in History
... been seen before, and which surpass the old, previously known, stars in number more than ten times. But that which will excite the greatest astonishment by far . . . is this, namely, that I have discovered four planets, neither known nor observed by any one of the astronomers before my time. This mo ...
... been seen before, and which surpass the old, previously known, stars in number more than ten times. But that which will excite the greatest astonishment by far . . . is this, namely, that I have discovered four planets, neither known nor observed by any one of the astronomers before my time. This mo ...
NIE10x301Sponsor Thank You (Page 1)
... the aid of telescopes and the modern science of Astronomy. With even the smallest telescope, or possibly an ordinary pair of binoculars, you may be able to see the four largest moons of Jupiter. These moons have been called the Galilean Satellites in honour of Galileo. They appear as very faint star ...
... the aid of telescopes and the modern science of Astronomy. With even the smallest telescope, or possibly an ordinary pair of binoculars, you may be able to see the four largest moons of Jupiter. These moons have been called the Galilean Satellites in honour of Galileo. They appear as very faint star ...
Document
... The simple strategy to get ~10,000 detectors on the sky… • Use an optical design that has the largest possible focal plane area • Choose an aperture size that optimizes throughput/dollar • The Proposed Experiment: An array of 5-10 crossed-Dragone multifrequency telescopes, each with ~2-meter primar ...
... The simple strategy to get ~10,000 detectors on the sky… • Use an optical design that has the largest possible focal plane area • Choose an aperture size that optimizes throughput/dollar • The Proposed Experiment: An array of 5-10 crossed-Dragone multifrequency telescopes, each with ~2-meter primar ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • That the Earth was the center of the universe • That the celestial sphere was rotating around the Earth • However, there was two observations that caused problems with this idea ...
... • That the Earth was the center of the universe • That the celestial sphere was rotating around the Earth • However, there was two observations that caused problems with this idea ...
First evidence for water ice clouds found outside solar
... Brown dwarfs aren't quite very small stars, but they aren't quite giant planets either. They are too small to sustain the hydrogen fusion process that fuels stars. Their temperatures can range from nearly as hot as a star to as cool as a planet, and their masses also range between star-like and gian ...
... Brown dwarfs aren't quite very small stars, but they aren't quite giant planets either. They are too small to sustain the hydrogen fusion process that fuels stars. Their temperatures can range from nearly as hot as a star to as cool as a planet, and their masses also range between star-like and gian ...
The Imaging Chain in Optical Astronomy
... – CCD pixel reports a signal even when not exposed to light ...
... – CCD pixel reports a signal even when not exposed to light ...
Linking Asteroids and Meteorites through Reflectance
... • That the Earth was the center of the universe • That the celestial sphere was rotating around the Earth • However, there was two observations that caused problems with this idea ...
... • That the Earth was the center of the universe • That the celestial sphere was rotating around the Earth • However, there was two observations that caused problems with this idea ...
Standard Set 2 - Atascadero High School
... universe’s visible matter; that is, matter that emits or reflects light or some other electromagnetic radiation that is detectable on Earth. The presence of otherwise invisible matter can be inferred from the effect of its gravity on visible matter, and the mass of the invisible matter in the univer ...
... universe’s visible matter; that is, matter that emits or reflects light or some other electromagnetic radiation that is detectable on Earth. The presence of otherwise invisible matter can be inferred from the effect of its gravity on visible matter, and the mass of the invisible matter in the univer ...
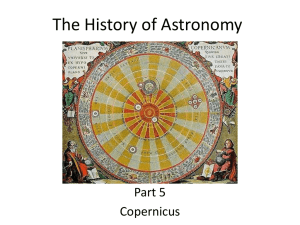
The History of Astronomy
... • He even got the relative distances from the sun correct (see chart on page 49). • Moon orbits Earth To avoid religious persecution he published his work “de revolutionibus orbium coelestium” posthumusly. ...
... • He even got the relative distances from the sun correct (see chart on page 49). • Moon orbits Earth To avoid religious persecution he published his work “de revolutionibus orbium coelestium” posthumusly. ...
Characteristics of Stars
... Use pages 793-799 in the textbook to find the answers to the questions below. Use the back of this page or a separate pieced of binder paper if you need more room. 1. How long would it take to travel to the Sun at light speed? How long would it take to travel to the nearest star if you could travel ...
... Use pages 793-799 in the textbook to find the answers to the questions below. Use the back of this page or a separate pieced of binder paper if you need more room. 1. How long would it take to travel to the Sun at light speed? How long would it take to travel to the nearest star if you could travel ...
01 - cloudfront.net
... from or toward our solar system. 26. the apparent shift in the wavelength of light emitted by a light source moving toward or away from an observer 27. that those galaxies are moving away from Earth 28. A 29. D 30. A 31. B 32. Parallax is the apparent shift in a star’s position when viewed from diff ...
... from or toward our solar system. 26. the apparent shift in the wavelength of light emitted by a light source moving toward or away from an observer 27. that those galaxies are moving away from Earth 28. A 29. D 30. A 31. B 32. Parallax is the apparent shift in a star’s position when viewed from diff ...
What does X-ray light show us?
... radio waves the size of buildings, to very short gamma-rays smaller than the size of the nucleus of an atom. ...
... radio waves the size of buildings, to very short gamma-rays smaller than the size of the nucleus of an atom. ...
Stars - Denbigh Baptist Christian School
... Scientist now believe a nova is when an existing star flares up to become 100’s or 1000’s times brighter. Outer layers gradually float off into space leaving smaller, dimmer star. Nova’s are not common. Nebula – cloud of interstellar gases and debris Supernovas – death explosion of a star. Star has ...
... Scientist now believe a nova is when an existing star flares up to become 100’s or 1000’s times brighter. Outer layers gradually float off into space leaving smaller, dimmer star. Nova’s are not common. Nebula – cloud of interstellar gases and debris Supernovas – death explosion of a star. Star has ...
Chapter Six: Astronomical Tools
... 1) The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum can be divided into seven color bands of Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet (from long to short wavelength). A single photon of which of these colors has the greatest amount of energy? a. red b. orange c. green d. blue e. violet 2) ...
... 1) The visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum can be divided into seven color bands of Red, Orange, Yellow, Green, Blue, Indigo and Violet (from long to short wavelength). A single photon of which of these colors has the greatest amount of energy? a. red b. orange c. green d. blue e. violet 2) ...
K - College of San Mateo
... SBIG Self Guiding Spectrograph (SGS) ___________________________________________________ ...
... SBIG Self Guiding Spectrograph (SGS) ___________________________________________________ ...
International Ultraviolet Explorer

The International Ultraviolet Explorer (IUE) was an astronomical observatory satellite primarily designed to take ultraviolet spectra. The satellite was a collaborative project between NASA, the UK Science Research Council and the European Space Agency (ESA). The mission was first proposed in early 1964, by a group of scientists in the United Kingdom, and was launched on January 26, 1978 aboard a NASA Delta rocket. The mission lifetime was initially set for 3 years, but in the end it lasted almost 18 years, with the satellite being shut down in 1996. The switch-off occurred for financial reasons, while the telescope was still functioning at near original efficiency.It was the first space observatory to be operated in real time by astronomers who visited the groundstations in the United States and Europe. Astronomers made over 104,000 observations using the IUE, of objects ranging from solar system bodies to distant quasars. Among the significant scientific results from IUE data were the first large scale studies of stellar winds, accurate measurements of the way interstellar dust absorbs light, and measurements of the supernova SN1987A which showed that it defied stellar evolution theories as they then stood. When the mission ended, it was considered the most successful astronomical satellite ever.