* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
Physical cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Chinese astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Astrobiology wikipedia , lookup
Tropical year wikipedia , lookup
Formation and evolution of the Solar System wikipedia , lookup
History of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Outer space wikipedia , lookup
Geocentric model wikipedia , lookup
Spitzer Space Telescope wikipedia , lookup
Non-standard cosmology wikipedia , lookup
Hubble Deep Field wikipedia , lookup
Doctor Light (Kimiyo Hoshi) wikipedia , lookup
Extraterrestrial life wikipedia , lookup
Astrophotography wikipedia , lookup
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Future of an expanding universe wikipedia , lookup
Expansion of the universe wikipedia , lookup
International Ultraviolet Explorer wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
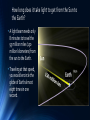
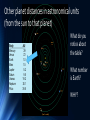
Unit Overview: Understanding the Universe S TA R T ING WIT H E A R T H A ND B E YO ND Our solar system – examining size and scale in space 6.11B UNDERSTAND THAT GRAVITY IS THE FORCE THAT GOVERNS MOTION IN OUR SOLAR SYSTEM 8.8 D MODEL AND DESCRIBE HOW LIGHT YEARS ARE USED TO MEASURE DISTANCES AND SIZES IN THE UNIVERSE Why do the planets revolve around the Sun? • Define gravity: Any object with mass exerts a force of attraction on other objects with mass. • The Earth, Sun and planets are not the only objects that exert gravity. Everything with mass exerts a force a gravity including us! • Our mass is very small relative to the mass of the Earth and so the force of attraction we exert on the objects around us is very small; too small to overcome friction. • The Sun exerts a large force of gravity because it is so massive and that is what keeps the planets in orbit around it. Solar system in the Milky Way galaxy The Milky Way • The Milky Way is a cluster of stars, known as a galaxy • It contains hundreds of billions of stars • If you traveled at the speed of light for about 2 million years, you would reach the next galaxy – the Andromeda Galaxy • There are billions of galaxies in the universe and they are VERY far apart from each other! Distance in Space • A light-year is how astronomers measure distance in space. It’s defined by how far a beam of light travels in one year – a distance of six trillion miles. • Astronomers use light-years and astronomical units to measure distance • To repeat - A light-year is the distance that light travels in one year Light Years Explained To put it in perspective… • Have you ever been on your way to meet some friends and, while en route, called to tell them you’re running late? • If you’re like me, you might tell them “I’m about ten minutes away”. You’re using how long it will take you to get there as a substitute for how far away you are. • Astronomers do the same thing when figuring out the distance to a star or galaxy, but instead of relying on how fast they could drive or walk, they use a beam of light as their reference. How long does it take light to get from the Sun to the Earth? • A light beam needs only 8 minutes to travel the 93 million miles (150 million kilometers) from the sun to the Earth. • Traveling at that speed, you would encircle the globe of Earth almost eight times in one second. Distances to other places • Impressive! Certainly faster than traveling by airplane. So if you were to travel off the Earth in a straight line at light speed, you’d get pretty far in the same amount of time, right? • Actually, since space is so vast, you wouldn’t have even made it to the moon. Travel to the moon takes about a second-and-a-half, at light speed. • Travel to the sun at light speed takes about eight minutes. Can you even imagine? • Traveling at a speed where you cross nearly 200,000 miles every second for eight full minutes would only get you to the center of our solar system. • The fact that light takes time to get anywhere has an interesting side effect. If light from the sun takes eight minutes to get to us, then we’re actually seeing the sun as it was eight minutes ago. We’re looking into the past! How about even larger distances? The Milky Way Galaxy is about 100,000 light years across, we are about 26,000 light years away from the center of it. Powersof10.com Even further - Our closest neighbor • Moving beyond our galaxy, it’s just over two million light years to our nearest galactic neighbor, the Andromeda galaxy. The light we currently see from that galaxy left there about the same time the ancestors of modern humans were first discovering stone tools. Astronomers measure the distance to the Andromeda galaxy using lightyears. One light-year equals about 6 trillion miles. This galaxy is over 2 million light-years from Earth Another measurement in space: Astronomical Unit • The distance of the Sun to the Earth is called an Astronomical Unit (AU) and is sometimes used to denote large distances that are less than a light year • Distances within our universe are measured in light years and AU A light year = about 63,241 astronomical units Sun to Earth Distance 1 Astronomical Unit (AU) 93,000,000 Miles • The Sun is at an average distance of about 93,000,000 miles (150 million kilometers) away from Earth. • Like all of the other planets in our Solar System, Earth does not travel around the Sun in a perfect circle. Instead its orbit is elliptical. • This means that the distance between Earth and the Sun changes during a year. • At its closest, the Sun is 91.4 million miles and at its farthest, the Sun is 94.5 million miles (152.1 million km) away. • The Earth is closest to the Sun during winter in the northern hemisphere. Other planet distances in astronomical units (from the sun to that planet) Body Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Pluto AU .39 .72 1.0 1.5 5.2 9.5 19.2 30.1 39.5 What do you notice about the table? What number is Earth? WHY? Check for understanding: #1 • If the nearest star is 4 light years away how many miles away is it? A light year means 6 trillion miles. Think about that for a moment. If you go outside tonight and shine a flash light at the sky, in the next year that light will travel 6 trillion miles. 6 trillion x 4 light years = 24 trillion miles! Check for understanding: question 2 • How long will it take for the light from that star (that is 4 light years away) to travel to the Earth? Four years. Remember, a light year is the distance that light can travel IN A YEAR! Light Year and Time • Using a light year as a distance measurement has another advantage -- it helps you determine age. • Let's say that a star is 1 million light years away. The light from that star has traveled at the speed of light to reach us. Therefore, it has taken the star's light 1 million years to get here, and the light we are seeing was created 1 million years ago. • So the star we are seeing is really how the star looked a million years ago, not how it looks today. In the same way, our sun is 8 or so light minutes away. If the sun were to suddenly explode right now, we wouldn't know about it for eight minutes because that is how long it would take for the light of the explosion to get here. Origin of the Universe 8 . 8 D – MO DE L A ND D E S CR IB E HO W L I G HT Y E A R S A R E U S E D TO ME A SURE DISTA NCES A ND S I Z E S I N T HE U NI VE R SE How the universe began • What evidence supports scientific theories on the origin of the universe? • Video: The beginning of everything (6 min) Scientific Theories about the Beginning: • Astronomers combine mathematical models with observations to develop workable theories of how the Universe came to be. • The mathematical underpinnings of the Big Bang theory include Albert Einstein's general theory of relativity along with standard theories of fundamental particles such as quantum mechanics. • Today NASA spacecraft such as the Hubble Space Telescope and the Spitzer Space Telescope continue measuring the expansion of the Universe. • One of the goals has long been to decide whether the Universe will expand forever, or whether it will someday stop, turn around, and collapse in a "Big Crunch?" Big Bang Theory • Once it was understood that the Universe had a beginning, scientists began to ask “how did it come into existence, and what existed before it?” • Most scientists now believe that the answer to the first part of the question is that the Universe sprang into existence from a singularity - a term physicists use to describe regions of space that defy the laws of physics. We know very little about singularities, but we believe that others probably exist in the cores of black holes. • The second part of the question, as to what existed before the Big Bang, has scientists baffled. By definition, nothing existed prior to the beginning, but that fact creates more questions than answers. For instance, if nothing existed prior to the Big Bang, what caused the singularity to be created in the first place? The growing universe: • Once the singularity was created (however it happened), it began to expand through a process called inflation. The Universe went from very small, very dense, and very hot to the cool expanse that we see today. • This theory is now referred to as the Big Bang, a term first coined by Fred Hoyle during a British Broadcasting Corporation (BBC) radio broadcast in 1950. • Interestingly, there really wasn’t any sort of explosion (or bang) as the name suggests, but rather the rapid expansion of space and time. • It is like blowing up a balloon, as you blow air in, the exterior of the balloon expands outward. Evidence Gathered from the Hubble Telescope • The Hubble Space Telescope is one of the most powerful and prolific science instruments ever made, earning a place as one of the technical wonders of the modern world. From its lofty perch 350 miles above Earth, Hubble sees farther and sharper than any previous telescope. • By witnessing bursts of light from faraway exploding stars, Hubble helped astronomers discover dark energy, which pervades our universe. This mysterious energy exerts a repulsive force that works against gravity. • One of Hubble’s key duties was to help astronomers determine a precise age for the universe. The telescope’s keen vision helped astronomers accomplish that goal by measuring the brightness of dozens of pulsating stars • By knowing their brightness, astronomers then calculated the stars’ distance from Earth. • Astronomers determined the universe’s age - it is about 13.75 billion years old. Famous Hubble Images Famous Hubble Images Famous Hubble Images Famous Hubble Images HW Assignment: • Read pages 328-332 in your textbook on evidence of the big bang theory • Then watch this video: “The Beginning of Everything” (posted on my website) • You will go to the google form also posted and answer the questions.