What Does a Positive Tuberculosis Blood Test Mean? What Doe
... A positive TB blood test tells us that at some stage you became infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the germ that causes TB. It is possible that you have been exposed to a person with disease caused by TB. What does a positive tuberculosis blood test mean? The TB blood test is a specialized te ...
... A positive TB blood test tells us that at some stage you became infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, the germ that causes TB. It is possible that you have been exposed to a person with disease caused by TB. What does a positive tuberculosis blood test mean? The TB blood test is a specialized te ...
Hand, Foot, Mouth Disease (HFMD)
... body for weeks after a person’s symptoms are gone. This means that infected people can still pass the infection to others even though they may appear well. How is HFMD diagnosed? A health care provider can diagnose HFMD by looking at the blisters on the body and the mouth sores in a person with a fe ...
... body for weeks after a person’s symptoms are gone. This means that infected people can still pass the infection to others even though they may appear well. How is HFMD diagnosed? A health care provider can diagnose HFMD by looking at the blisters on the body and the mouth sores in a person with a fe ...
Infectious Diseases Complied by Chaplain Larry W. Pope, M.Div
... Tuberculosis (TB) is a common and in many cases lethal infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis.[1] Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active ...
... Tuberculosis (TB) is a common and in many cases lethal infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis.[1] Tuberculosis usually attacks the lungs but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active ...
Engaging All Care Providers in TB Control:ISTC and Role of
... J.W. Lee, Director General, World Health Organization: March 24, 2006 ...
... J.W. Lee, Director General, World Health Organization: March 24, 2006 ...
OVERVIEW FOR INFECTION CONTROL BEST PRACTICES
... (infectious agent) typically found in acute care hospitals and nursing facilities where there is a susceptible host (compromised patient/resident) and a means of transmission. It is well known that the elderly population has a substantially increased incidence and severity of many infectious disease ...
... (infectious agent) typically found in acute care hospitals and nursing facilities where there is a susceptible host (compromised patient/resident) and a means of transmission. It is well known that the elderly population has a substantially increased incidence and severity of many infectious disease ...
Diapositiva 1
... Pediatric Drug-resistant Tuberculosis in Madrid: Family Matters Pediatr Infect Dis J 2014;33:345–350 Incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis disease in children: systematic review and global estimates. Lancet. ...
... Pediatric Drug-resistant Tuberculosis in Madrid: Family Matters Pediatr Infect Dis J 2014;33:345–350 Incidence of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis disease in children: systematic review and global estimates. Lancet. ...
Iowa Wing Bloodborne Pathogens
... – Touching the sore – Touching saliva that contains the virus ...
... – Touching the sore – Touching saliva that contains the virus ...
Diagnostic Testing Birds
... Blood testing Blood tests are used to look for problems with the internal organs (such as the liver and kidneys). The animal can be checked for things such as anaemia (not enough red blood cells) or changes with the white blood cells which can tell us useful information. These tests often need to b ...
... Blood testing Blood tests are used to look for problems with the internal organs (such as the liver and kidneys). The animal can be checked for things such as anaemia (not enough red blood cells) or changes with the white blood cells which can tell us useful information. These tests often need to b ...
doc
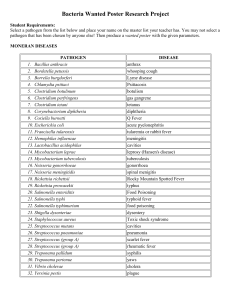
... 1) "Photo" (electron micrograph or microscopic picture/diagram) 2) Description - include Gram stain. 3) Organism's M.O. (police jargon for how the organism attacks and spreads). 4) Most common victims it preys upon. 5) Hide-out of the culprit (where it is most likely to be found). 6) Most common inj ...
... 1) "Photo" (electron micrograph or microscopic picture/diagram) 2) Description - include Gram stain. 3) Organism's M.O. (police jargon for how the organism attacks and spreads). 4) Most common victims it preys upon. 5) Hide-out of the culprit (where it is most likely to be found). 6) Most common inj ...
Salmonella Infections
... Con firmed cases and carriers of Salmonella bacteria should pay special attention to personal hygiene. Hands should always be washed using soap and warm water immediately after using the toilet and before handling or preparing food. Infected individuals should not share towels or bathwater, and care ...
... Con firmed cases and carriers of Salmonella bacteria should pay special attention to personal hygiene. Hands should always be washed using soap and warm water immediately after using the toilet and before handling or preparing food. Infected individuals should not share towels or bathwater, and care ...
Beyond Borders: The Emerging Threat of Infectious Diseases
... "The idea is that there's a global effort all on the same track," he said. "In the former Soviet Union, and also in areas of Central and Eastern Europe, we need to concentrate on making it through this transition period by ensuring vaccine delivery and basic sanitation. When you're seeing cholera, a ...
... "The idea is that there's a global effort all on the same track," he said. "In the former Soviet Union, and also in areas of Central and Eastern Europe, we need to concentrate on making it through this transition period by ensuring vaccine delivery and basic sanitation. When you're seeing cholera, a ...
Respiratory Tract Infections
... Cilia if functioning will move material up the respiratory tract, but if damaged this physical defence is impaired The lungs also have a resident macrophage population (alveolar macrophages) but they are of limited use against several respiratory pathogens that possess a capsule some organisms ...
... Cilia if functioning will move material up the respiratory tract, but if damaged this physical defence is impaired The lungs also have a resident macrophage population (alveolar macrophages) but they are of limited use against several respiratory pathogens that possess a capsule some organisms ...
Diapositive 1 - ISR Radiology
... mycobacterial infection -False negative : technical error in injection or in the induration measurement, viral infection, immunodepression, anergic time (+/- 40 days)… ...
... mycobacterial infection -False negative : technical error in injection or in the induration measurement, viral infection, immunodepression, anergic time (+/- 40 days)… ...
group a streptococcal (gas) disease
... for example, through open mouth kissing, mouth-tomouth resuscitation or through direct contact with infected sores on the skin. Can Group A Strep infections be serious? In rare cases, the same strep bacteria can cause a severe form of illness called invasive GAS disease. This happens when bacteria g ...
... for example, through open mouth kissing, mouth-tomouth resuscitation or through direct contact with infected sores on the skin. Can Group A Strep infections be serious? In rare cases, the same strep bacteria can cause a severe form of illness called invasive GAS disease. This happens when bacteria g ...
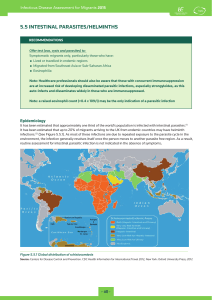
5.5 INTESTINAL PARASITES/HELMINTHS
... = Migrated from Southeast Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa = Eosinophilia ...
... = Migrated from Southeast Asia or Sub-Saharan Africa = Eosinophilia ...
Chapter 4: BASIC FACTS ABOUT TUBERCULOSIS (TB)
... Aerobic Slow-growing (divide once every 15 to 20 hours) ...
... Aerobic Slow-growing (divide once every 15 to 20 hours) ...
Slides 3
... Cell-free vs cell-associated virus Relative contributions of each are not determined May depend on the particular route of transmission ...
... Cell-free vs cell-associated virus Relative contributions of each are not determined May depend on the particular route of transmission ...
M. tuberculosis
... baseline tuberculin skin test is advisable in order to compare with retesting after return. If the skin reaction to tuberculin suggests recent infection, the traveller should receive, or be referred for, treatment for latent infection”. ...
... baseline tuberculin skin test is advisable in order to compare with retesting after return. If the skin reaction to tuberculin suggests recent infection, the traveller should receive, or be referred for, treatment for latent infection”. ...
chapter 22 - Medical and Public Health Law Site
... the provisions of chapter 36-4 and chapter 36-9, any person performing specific health services under federal, state, and local programs affecting the public health, shall carry out such services through medically accepted procedures approved by the State Board of Medical and Osteopathic Examiners a ...
... the provisions of chapter 36-4 and chapter 36-9, any person performing specific health services under federal, state, and local programs affecting the public health, shall carry out such services through medically accepted procedures approved by the State Board of Medical and Osteopathic Examiners a ...
Johne`s Disease in Goats - Langford Veterinary Services
... Johne’s is a disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium paratuberculosis avium, a similar pathogen to that causing TB. What does it look like? ...
... Johne’s is a disease caused by the bacteria Mycobacterium paratuberculosis avium, a similar pathogen to that causing TB. What does it look like? ...
infection prevention and control
... Susceptibility (Resistance to infection) Factors which influence susceptible: Age Nutritional status Chronic disease history Trauma Smoking ...
... Susceptibility (Resistance to infection) Factors which influence susceptible: Age Nutritional status Chronic disease history Trauma Smoking ...
Mikrobiology - GEOCITIES.ws
... transcient flora - periodically occurs in organism, but as patogen act just in some special locations - S. pneumoniae Infectious disease - caused by microorganism or by it´s toxin Factors of developement infectious disease: 1. Virulence - adaptability of the patogen to cause disease 2. Resistence of ...
... transcient flora - periodically occurs in organism, but as patogen act just in some special locations - S. pneumoniae Infectious disease - caused by microorganism or by it´s toxin Factors of developement infectious disease: 1. Virulence - adaptability of the patogen to cause disease 2. Resistence of ...
6-0 Notes- Infectious Diseases 6-0 Notes-Infectious
... Tuberculosis (TB) – bacteria; transmitted by infected person sneezing, coughing even speaking; symptoms- persistent cough, coughing up blood, fever, chills, appetite loss; control/treatment- antibiotics; vaccine available for at-risk children/infants but not widely used in U.S.; where occurs/# of ca ...
... Tuberculosis (TB) – bacteria; transmitted by infected person sneezing, coughing even speaking; symptoms- persistent cough, coughing up blood, fever, chills, appetite loss; control/treatment- antibiotics; vaccine available for at-risk children/infants but not widely used in U.S.; where occurs/# of ca ...
Tuberculosis

Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (short for tubercle bacillus), in the past also called phthisis, phthisis pulmonalis, or consumption, is a widespread, infectious disease caused by various strains of mycobacteria, usually Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Tuberculosis typically attacks the lungs, but can also affect other parts of the body. It is spread through the air when people who have an active TB infection cough, sneeze, or otherwise transmit respiratory fluids through the air. Most infections do not have symptoms, known as latent tuberculosis. About one in ten latent infections eventually progresses to active disease which, if left untreated, kills more than 50% of those so infected.The classic symptoms of active TB infection are a chronic cough with blood-tinged sputum, fever, night sweats, and weight loss (the last of these giving rise to the formerly common term for the disease, ""consumption""). Infection of other organs causes a wide range of symptoms. Diagnosis of active TB relies on radiology (commonly chest X-rays), as well as microscopic examination and microbiological culture of body fluids. Diagnosis of latent TB relies on the tuberculin skin test (TST) and/or blood tests. Treatment is difficult and requires administration of multiple antibiotics over a long period of time. Household, workplace and social contacts are also screened and treated if necessary. Antibiotic resistance is a growing problem in multiple drug-resistant tuberculosis (MDR-TB) infections. Prevention relies on early detection and treatment of cases and on screening programs and vaccination with the bacillus Calmette-Guérin vaccine.One-third of the world's population is thought to have been infected with M. tuberculosis, and new infections occur in about 1% of the population each year. In 2007, an estimated 13.7 million chronic cases were active globally, while in 2013, an estimated 9 million new cases occurred. In 2013 there were between 1.3 and 1.5 million associated deaths, most of which occurred in developing countries. The total number of tuberculosis cases has been decreasing since 2006, and new cases have decreased since 2002. The rate of tuberculosis in different areas varies across the globe; about 80% of the population in many Asian and African countries tests positive in tuberculin tests, while only 5–10% of the United States population tests positive. More people in the developing world contract tuberculosis because of a poor immune system, largely due to high rates of HIV infection and the corresponding development of AIDS.