This is an official CDC HEALTH ADVISORY
... cases and 729 deaths (case fatality 55-60%) had been reported across the three affected countries. This is the largest outbreak of EVD ever documented and the first recorded in West Africa. EVD is characterized by sudden onset of fever and malaise, accompanied by other nonspecific signs and symptoms ...
... cases and 729 deaths (case fatality 55-60%) had been reported across the three affected countries. This is the largest outbreak of EVD ever documented and the first recorded in West Africa. EVD is characterized by sudden onset of fever and malaise, accompanied by other nonspecific signs and symptoms ...
(PDF, Unknown)
... The original source of the infection (the way the first victim became infected) is not known. It’s hypothesized that contact with an infected animal is how human infection begins. Health care workers and family members caring for Ebola victims are at extreme risk. Precautions such as masks, gowns, a ...
... The original source of the infection (the way the first victim became infected) is not known. It’s hypothesized that contact with an infected animal is how human infection begins. Health care workers and family members caring for Ebola victims are at extreme risk. Precautions such as masks, gowns, a ...
7-1 Infectious Disease Project 2016
... Research Questions: put the initials of who in your group is researching which questions ____ What is the specific disease Agent? (Type of infection: Virus, Bacteria, Parasite) ____ How the infection is transmitted (Vector) (include a diagram of transmission) ____ Where it occurs? (regions of ...
... Research Questions: put the initials of who in your group is researching which questions ____ What is the specific disease Agent? (Type of infection: Virus, Bacteria, Parasite) ____ How the infection is transmitted (Vector) (include a diagram of transmission) ____ Where it occurs? (regions of ...
Biosafety in Microbiological and Biomedical Laboratories, pp
... 1) Arboviruses are a large group of viruses that are spread by certain invertebrate animals (arthropods), most commonly blood-sucking insects (In USA. spread mainly by mosquitoes) T/F 2) Most people infected with arboviruses have few or no symptoms, but arboviruses can cause serious and potentially ...
... 1) Arboviruses are a large group of viruses that are spread by certain invertebrate animals (arthropods), most commonly blood-sucking insects (In USA. spread mainly by mosquitoes) T/F 2) Most people infected with arboviruses have few or no symptoms, but arboviruses can cause serious and potentially ...
viral_replication
... the upper respiratory tract and reproduces inside them, killing many cells in the process. • The dead cells increase the amount and thickness of the mucus produced which irritates the throat causing coughing. • Secondary bacterial infection is common ...
... the upper respiratory tract and reproduces inside them, killing many cells in the process. • The dead cells increase the amount and thickness of the mucus produced which irritates the throat causing coughing. • Secondary bacterial infection is common ...
Understanding and Controlling Ebola Exposure Risk in
... information reported by Ministries of Health in affected countries and the World Health Organization. By the end of September 2014, a total of 6,574 cases and 3,091 fatalities were reported. Guidance and frequent updates are issued by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). No spe ...
... information reported by Ministries of Health in affected countries and the World Health Organization. By the end of September 2014, a total of 6,574 cases and 3,091 fatalities were reported. Guidance and frequent updates are issued by the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). No spe ...
DNA viruses: Adeno-, Pox-Papilloma
... Merckel cell Polyomavirus (MCV) • Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) which is a rare skin cancer and highly aggressive. • Occur more frequently in immunosuppressed patients • MCC occurs most often on the face, head, and neck. • It usually appears as a firm, painless, nodule, or tumor. • These flesh-colore ...
... Merckel cell Polyomavirus (MCV) • Merkel cell carcinoma (MCC) which is a rare skin cancer and highly aggressive. • Occur more frequently in immunosuppressed patients • MCC occurs most often on the face, head, and neck. • It usually appears as a firm, painless, nodule, or tumor. • These flesh-colore ...
Zoonoses - USAID Natural Resource Management and
... • Pigs showed mild clinical signs of neurologic and respiratory disease • Human cases presented with fever, headache, signs consistent with encephalitis • 93% of human cases had occupational exposure to infected pigs suggesting transmission was via direct contact with pigs ...
... • Pigs showed mild clinical signs of neurologic and respiratory disease • Human cases presented with fever, headache, signs consistent with encephalitis • 93% of human cases had occupational exposure to infected pigs suggesting transmission was via direct contact with pigs ...
Emerging Infectious Disease, Zoonoses and the Human
... • Pigs showed mild clinical signs of neurologic and respiratory disease • Human cases presented with fever, headache, signs consistent with encephalitis • 93% of human cases had occupational exposure to infected pigs suggesting transmission was via direct contact with pigs ...
... • Pigs showed mild clinical signs of neurologic and respiratory disease • Human cases presented with fever, headache, signs consistent with encephalitis • 93% of human cases had occupational exposure to infected pigs suggesting transmission was via direct contact with pigs ...
2014 Ebola Outbreak Response West Africa
... Texas from Liberia, two healthcare workers who cared for the index patient, and one medical aid worker who traveled to New York City from Guinea Index patient – Symptoms developed on September 24, 2014 approximately four days after arrival, sought medical care at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital ...
... Texas from Liberia, two healthcare workers who cared for the index patient, and one medical aid worker who traveled to New York City from Guinea Index patient – Symptoms developed on September 24, 2014 approximately four days after arrival, sought medical care at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital ...
Ebola Virus Disease
... Texas from Liberia, two healthcare workers who cared for the index patient, and one medical aid worker who traveled to New York City from Guinea Index patient – Symptoms developed on September 24, 2014 approximately four days after arrival, sought medical care at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital ...
... Texas from Liberia, two healthcare workers who cared for the index patient, and one medical aid worker who traveled to New York City from Guinea Index patient – Symptoms developed on September 24, 2014 approximately four days after arrival, sought medical care at Texas Health Presbyterian Hospital ...
Slide 1
... 1968 – 1972 Outbreak of “Winter Vomiting Disease” in Norwalk, OH Acute gastroenteritis – “stomach flu” or “24 hour bug” Explosive vomiting, watery (non bloody) diarrhea, abd cramps, HA, body aches, low-grade fever. 24-60 hours #1 Cause of Foodborne Illness in US, causing about 2/3 of all foodborne i ...
... 1968 – 1972 Outbreak of “Winter Vomiting Disease” in Norwalk, OH Acute gastroenteritis – “stomach flu” or “24 hour bug” Explosive vomiting, watery (non bloody) diarrhea, abd cramps, HA, body aches, low-grade fever. 24-60 hours #1 Cause of Foodborne Illness in US, causing about 2/3 of all foodborne i ...
Approaches to the antimicrobial treatment of persistent Chlamydia
... (PALV) are tick-borne Arboviruses of the Bhanja antigenic group, one of seven groups of Bunyaviruses so far unassigned to any genus. These viruses have been isolated from India, various parts of Africa, former USSR and Europe. Confirmed vertebrate hosts are sheep, goat, cattle, African hedgehog Atel ...
... (PALV) are tick-borne Arboviruses of the Bhanja antigenic group, one of seven groups of Bunyaviruses so far unassigned to any genus. These viruses have been isolated from India, various parts of Africa, former USSR and Europe. Confirmed vertebrate hosts are sheep, goat, cattle, African hedgehog Atel ...
microbe
... -can live independently -prokaryotes (no nucleus or organelles) -have been on earth for at least 3.5 billion years -includes both true bacteria and archaea -they are adaptive (can adjust to different environments) ...
... -can live independently -prokaryotes (no nucleus or organelles) -have been on earth for at least 3.5 billion years -includes both true bacteria and archaea -they are adaptive (can adjust to different environments) ...
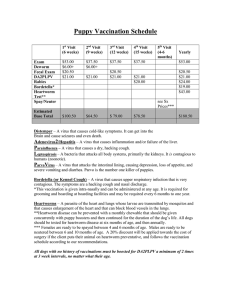
Kitten Vaccination Schedule
... ParvoVirus – A virus that attacks the intestinal lining, causing depression, loss of appetite, and severe vomiting and diarrhea. Parvo is the number one killer of puppies. Bordetella (or Kennel Cough) – A virus that causes upper respiratory infection that is very contagious. The symptoms are a hacki ...
... ParvoVirus – A virus that attacks the intestinal lining, causing depression, loss of appetite, and severe vomiting and diarrhea. Parvo is the number one killer of puppies. Bordetella (or Kennel Cough) – A virus that causes upper respiratory infection that is very contagious. The symptoms are a hacki ...
Virus and Bacteria
... and backaches. The initial toxemia phase lasted 4-5 days. On about the third or fourth day, the characteristic rash appeared. First, it appeared on the buccal and pharyngeal mucosa, the face, and the forearms. Within a day, it spread to the trunk and lower limbs. • The lesions usually protruded from ...
... and backaches. The initial toxemia phase lasted 4-5 days. On about the third or fourth day, the characteristic rash appeared. First, it appeared on the buccal and pharyngeal mucosa, the face, and the forearms. Within a day, it spread to the trunk and lower limbs. • The lesions usually protruded from ...
current scenario of therapeutics for ebola virus disease
... EHF and when it is possible for a patient ill with EHF to spread the virus to another human being. EHF is one of numerous viral hemorrhagic fevers. It is a severe, often fatal disease in humans and nonhuman primates (such as monkeys, gorillas and chimpanzees). EHF is caused by infection with a virus ...
... EHF and when it is possible for a patient ill with EHF to spread the virus to another human being. EHF is one of numerous viral hemorrhagic fevers. It is a severe, often fatal disease in humans and nonhuman primates (such as monkeys, gorillas and chimpanzees). EHF is caused by infection with a virus ...
Blood Semen Vaginal fluid Breast milk
... Get tested regularly and get your test result. If you test negative, you may in fact be HIV-positive, but your immune system has not yet developed detectible antibodies. Stop all risk behavior and get retested in 6 months. Most people will develop detectable antibodies within 3 months after infectio ...
... Get tested regularly and get your test result. If you test negative, you may in fact be HIV-positive, but your immune system has not yet developed detectible antibodies. Stop all risk behavior and get retested in 6 months. Most people will develop detectable antibodies within 3 months after infectio ...
Viruses Virus • Microscopic particle that invades and
... o Virus attaches itself to the host cell o The virus injects its genetic material into the host cell o The genetic material takes over the host cell and instructs the cell to make new virus parts o The virus parts join to make new viruses which burst out of the host, killing the host cell. o The cyc ...
... o Virus attaches itself to the host cell o The virus injects its genetic material into the host cell o The genetic material takes over the host cell and instructs the cell to make new virus parts o The virus parts join to make new viruses which burst out of the host, killing the host cell. o The cyc ...
Protective Measures For Prevention Of SARS Infection
... • After the virus enters the body, it requires 310 days incubation period before the disease appears. • According to current data, infected people do not pass on the virus to others during the incubation period. • They become infectious only when the first symptoms appear: cough, sneezing – which sp ...
... • After the virus enters the body, it requires 310 days incubation period before the disease appears. • According to current data, infected people do not pass on the virus to others during the incubation period. • They become infectious only when the first symptoms appear: cough, sneezing – which sp ...
Ebola virus disease

Ebola virus disease (EVD; also Ebola hemorrhagic fever, or EHF), or simply Ebola, is a disease of humans and other primates caused by ebolaviruses. Signs and symptoms typically start between two days and three weeks after contracting the virus with a fever, sore throat, muscular pain, and headaches. Then, vomiting, diarrhea and rash usually follow, along with decreased function of the liver and kidneys. At this time some people begin to bleed both internally and externally. The disease has a high risk of death, killing between 25 and 90 percent of those infected, with an average of about 50 percent. This is often due to low blood pressure from fluid loss, and typically follows six to sixteen days after symptoms appear.The virus spreads by direct contact with body fluids, such as blood, of an infected human or other animals. This may also occur through contact with an item recently contaminated with bodily fluids. Spread of the disease through the air between primates, including humans, has not been documented in either laboratory or natural conditions. Semen or breast milk of a person after recovery from EVD may still carry the virus for several weeks to months. Fruit bats are believed to be the normal carrier in nature, able to spread the virus without being affected by it. Other diseases such as malaria, cholera, typhoid fever, meningitis and other viral hemorrhagic fevers may resemble EVD. Blood samples are tested for viral RNA, viral antibodies or for the virus itself to confirm the diagnosis.Control of outbreaks requires coordinated medical services, alongside a certain level of community engagement. The medical services include rapid detection of cases of disease, contact tracing of those who have come into contact with infected individuals, quick access to laboratory services, proper healthcare for those who are infected, and proper disposal of the dead through cremation or burial. Samples of body fluids and tissues from people with the disease should be handled with special caution. Prevention includes limiting the spread of disease from infected animals to humans. This may be done by handling potentially infected bush meat only while wearing protective clothing and by thoroughly cooking it before eating it. It also includes wearing proper protective clothing and washing hands when around a person with the disease. No specific treatment or vaccine for the virus is available, although a number of potential treatments are being studied. Supportive efforts, however, improve outcomes. This includes either oral rehydration therapy (drinking slightly sweetened and salty water) or giving intravenous fluids as well as treating symptoms.The disease was first identified in 1976 in two simultaneous outbreaks, one in Nzara, and the other in Yambuku, a village near the Ebola River from which the disease takes its name. EVD outbreaks occur intermittently in tropical regions of sub-Saharan Africa. Between 1976 and 2013, the World Health Organization reports a total of 24 outbreaks involving 1,716 cases. The largest outbreak is the ongoing epidemic in West Africa, still affecting Guinea and Sierra Leone. {{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|casesasof}}, this outbreak has {{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|cases}} reported cases resulting in {{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|deaths}} deaths.{{#section:Ebola virus epidemic in West Africa|caserefs}}