Document
... Introduction • The discovery of pharmacologic agents by modern pharmaceutical companies and universities often involves the use of receptor-ligand binding techniques. Following the synthesis of a series of new chemically related compounds, which can constitute hundreds to thousands of compounds, th ...
... Introduction • The discovery of pharmacologic agents by modern pharmaceutical companies and universities often involves the use of receptor-ligand binding techniques. Following the synthesis of a series of new chemically related compounds, which can constitute hundreds to thousands of compounds, th ...
Routes of drug Adminstration
... • Many drugs are not administered orally because of drug instability in the gastrointestinal tract or drug degradation by the digestive enzymes in the intestine. • erythropoietin and human growth hormone are administered IM, and insulin is administered SC or IM, because of the potential for degrada ...
... • Many drugs are not administered orally because of drug instability in the gastrointestinal tract or drug degradation by the digestive enzymes in the intestine. • erythropoietin and human growth hormone are administered IM, and insulin is administered SC or IM, because of the potential for degrada ...
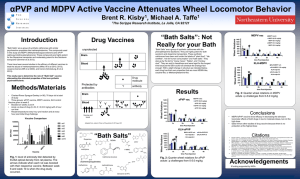
αPVP and MDPV Active Vaccine Attenuates Wheel Locomotor Behavior Introduction
... phenylethylamine backbone. They are highly potent for both serotonin and dopamine transporters. These synthetic cathinones have been sold under the labels of “plant food”, “lab certified”, “not for human consumption” and “bath salts”. They also go by the terms “meow meow”, “flakka”, and “monkey dust ...
... phenylethylamine backbone. They are highly potent for both serotonin and dopamine transporters. These synthetic cathinones have been sold under the labels of “plant food”, “lab certified”, “not for human consumption” and “bath salts”. They also go by the terms “meow meow”, “flakka”, and “monkey dust ...
Matter- Types and Changes
... • CO2 contains 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen all chemically linked. • H2SO4 contains 2 hydrogen, 1 sulfur, and 4 oxygen atoms. • (NH4)2C2O4 - A subscript outside parentheses applies to everything within the parentheses; ...
... • CO2 contains 1 atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen all chemically linked. • H2SO4 contains 2 hydrogen, 1 sulfur, and 4 oxygen atoms. • (NH4)2C2O4 - A subscript outside parentheses applies to everything within the parentheses; ...
club drugs - Florida Alcohol and Drug Abuse Association
... But in the past few years, these drugs have been found increasingly in more mainstream settings. Due to the uncertainty of their sources (i.e. pharmacological agents, chemicals used to manufacture them, and contaminants) it is often difficult to determine symptoms, toxicity, and consequences of usin ...
... But in the past few years, these drugs have been found increasingly in more mainstream settings. Due to the uncertainty of their sources (i.e. pharmacological agents, chemicals used to manufacture them, and contaminants) it is often difficult to determine symptoms, toxicity, and consequences of usin ...
351 Pharmacology 3rd sf
... Receptor/Binding site “A specific protein in either the plasma membrane or interior of a target cell with which a ligand/drug combines” It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must ...
... Receptor/Binding site “A specific protein in either the plasma membrane or interior of a target cell with which a ligand/drug combines” It must be selective in choosing ligands/drugs to bind To avoid constant activation of the receptor by promiscuous binding of many different ligands It must ...
presentation
... transported or distributed across state lines • When a sponsor screens a new molecule for pharmacological activity and toxicity in animals and wants to test the drugs diagnostic or therapeutic potential on humans – At this point, the molecule changes in legal status – Under Federal Food, Drug, and C ...
... transported or distributed across state lines • When a sponsor screens a new molecule for pharmacological activity and toxicity in animals and wants to test the drugs diagnostic or therapeutic potential on humans – At this point, the molecule changes in legal status – Under Federal Food, Drug, and C ...
Biological Methods of Stress Management
... One way that effectiveness is assessed is through comparing outcomes e.g. One group is given a drug and another is given a placebo This enables us to determine whether the effectiveness of a drug is due to pharmacological properties or something psychological ...
... One way that effectiveness is assessed is through comparing outcomes e.g. One group is given a drug and another is given a placebo This enables us to determine whether the effectiveness of a drug is due to pharmacological properties or something psychological ...
October 1 AP Biology - John D. O`Bryant School of Math & Science
... Do Now (Quiz) 2. Several seriously epidemic viral diseases of earlier centuries were then incurable because they resulted in severe dehydration due to vomiting and diarrhea. Today they are usually not fatal because we have developed which of the following? ...
... Do Now (Quiz) 2. Several seriously epidemic viral diseases of earlier centuries were then incurable because they resulted in severe dehydration due to vomiting and diarrhea. Today they are usually not fatal because we have developed which of the following? ...
Chapter 14 Drugs - Ozark R
... • These results can be permanent and severe – Can effect a person’s ability to walk, talk, or think. – Can kill the user instantly – Even a person experimenting with inhalants for the first time can die from choking, suffocation or a heart attack. ...
... • These results can be permanent and severe – Can effect a person’s ability to walk, talk, or think. – Can kill the user instantly – Even a person experimenting with inhalants for the first time can die from choking, suffocation or a heart attack. ...
document
... – Sulfonamides: MPE, SJS/TEN, DRESS – SJS/TEN to various drugs is 500 fold more frequent ...
... – Sulfonamides: MPE, SJS/TEN, DRESS – SJS/TEN to various drugs is 500 fold more frequent ...
The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occured is
... A covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally is What happens when an acid reacts with a base? ____ is a compound that increases the number of hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. Which of the following would taste sour? When all the molecules of a compound break apart in water to m ...
... A covalent bond in which electrons are shared unequally is What happens when an acid reacts with a base? ____ is a compound that increases the number of hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. Which of the following would taste sour? When all the molecules of a compound break apart in water to m ...
to free sample
... combines the terms “pharmacology” and “therapeutics.” Disease management refers to a collective management of all aspects of the patient’s disease, not just pharmacotherapy. ...
... combines the terms “pharmacology” and “therapeutics.” Disease management refers to a collective management of all aspects of the patient’s disease, not just pharmacotherapy. ...
full text pdf
... structure and/or function. Metals can perform functions that cannot otherwise be achieved, such as electrolyte balance (important for processes that include the firing of neurons), as well as oxygen transport, electron transfer, and catalysis. The importance of metals to health is made clear by the ...
... structure and/or function. Metals can perform functions that cannot otherwise be achieved, such as electrolyte balance (important for processes that include the firing of neurons), as well as oxygen transport, electron transfer, and catalysis. The importance of metals to health is made clear by the ...
Light">CHAPTER
... combines the terms “pharmacology” and “therapeutics.” Disease management refers to a collective management of all aspects of the patient’s disease, not just pharmacotherapy. ...
... combines the terms “pharmacology” and “therapeutics.” Disease management refers to a collective management of all aspects of the patient’s disease, not just pharmacotherapy. ...
Adulteration and Evaluation of Crude drugs
... period which provide suitable atmosphere for hydrolysis of ...
... period which provide suitable atmosphere for hydrolysis of ...
Pre-Lecture Quiz
... 2. Topiramate (Topamax) may be used as monotherapy in the treatment of primary generalized tonic–clonic seizures. ...
... 2. Topiramate (Topamax) may be used as monotherapy in the treatment of primary generalized tonic–clonic seizures. ...
Name: _____________________ Mods: ______________ Unit
... 2. Atoms in a compound are held together by _________________ bonds. ...
... 2. Atoms in a compound are held together by _________________ bonds. ...
DRUG INTERACTIONS AND ANESTHESIA
... TERMINOLOGY Pharmacology - study of how chemical agents affect living processes Pharmacokinetics - what the body does to the drug (absorption, distribution and elimination) Pharmacodynamics - what the drug does to the body (dose – response relationship) ...
... TERMINOLOGY Pharmacology - study of how chemical agents affect living processes Pharmacokinetics - what the body does to the drug (absorption, distribution and elimination) Pharmacodynamics - what the drug does to the body (dose – response relationship) ...
Drug Education
... Coke, Cane Cocaine was first used in the 1800's as an anesthetic. Extracted from the leaves of the Erythroxylon Coca Bush grown in South America, it is the most potent stimulant of a natural origin. Abuse and adverse side affects caused the drug to be restricted in ...
... Coke, Cane Cocaine was first used in the 1800's as an anesthetic. Extracted from the leaves of the Erythroxylon Coca Bush grown in South America, it is the most potent stimulant of a natural origin. Abuse and adverse side affects caused the drug to be restricted in ...
Drug Metabolism
... readily excretable products. The liver is the major site for drug metabolism, but specific drugs may undergo biotransformation in other tissues, such as the kidney and the intestines. [Note: Some agents are initially administered as inactive compounds (prodrugs) and must be metabolized to their acti ...
... readily excretable products. The liver is the major site for drug metabolism, but specific drugs may undergo biotransformation in other tissues, such as the kidney and the intestines. [Note: Some agents are initially administered as inactive compounds (prodrugs) and must be metabolized to their acti ...
Drug discovery
In the fields of medicine, biotechnology and pharmacology, drug discovery is the process by which new candidate medications are discovered. Historically, drugs were discovered through identifying the active ingredient from traditional remedies or by serendipitous discovery. Later chemical libraries of synthetic small molecules, natural products or extracts were screened in intact cells or whole organisms to identify substances that have a desirable therapeutic effect in a process known as classical pharmacology. Since sequencing of the human genome which allowed rapid cloning and synthesis of large quantities of purified proteins, it has become common practice to use high throughput screening of large compounds libraries against isolated biological targets which are hypothesized to be disease modifying in a process known as reverse pharmacology. Hits from these screens are then tested in cells and then in animals for efficacy.Modern drug discovery involves the identification of screening hits, medicinal chemistry and optimization of those hits to increase the affinity, selectivity (to reduce the potential of side effects), efficacy/potency, metabolic stability (to increase the half-life), and oral bioavailability. Once a compound that fulfills all of these requirements has been identified, it will begin the process of drug development prior to clinical trials. One or more of these steps may, but not necessarily, involve computer-aided drug design. Modern drug discovery is thus usually a capital-intensive process that involves large investments by pharmaceutical industry corporations as well as national governments (who provide grants and loan guarantees). Despite advances in technology and understanding of biological systems, drug discovery is still a lengthy, ""expensive, difficult, and inefficient process"" with low rate of new therapeutic discovery. In 2010, the research and development cost of each new molecular entity (NME) was approximately US$1.8 billion. Drug discovery is done by pharmaceutical companies, with research assistance from universities. The ""final product"" of drug discovery is a patent on the potential drug. The drug requires very expensive Phase I, II and III clinical trials, and most of them fail. Small companies have a critical role, often then selling the rights to larger companies that have the resources to run the clinical trials.Discovering drugs that may be a commercial success, or a public health success, involves a complex interaction between investors, industry, academia, patent laws, regulatory exclusivity, marketing and the need to balance secrecy with communication. Meanwhile, for disorders whose rarity means that no large commercial success or public health effect can be expected, the orphan drug funding process ensures that people who experience those disorders can have some hope of pharmacotherapeutic advances.