Exercise #5_Chpt 2
... Copper (II) sulfate is found as a hydrated salt, CuSO4.xH2O. A technician carefully heats 2.50g of the salt to a constant mass of 1.60g. a) What is meant by constant mass? b) How many moles of copper sulfate are there in 1.60g of anhydrous copper (II) sulfate? c) How many moles of water were lost? ...
... Copper (II) sulfate is found as a hydrated salt, CuSO4.xH2O. A technician carefully heats 2.50g of the salt to a constant mass of 1.60g. a) What is meant by constant mass? b) How many moles of copper sulfate are there in 1.60g of anhydrous copper (II) sulfate? c) How many moles of water were lost? ...
Chemistry
... JOHN MCMURRY, educated at Harvard and Columbia, has taught approximately 17,000 students in general and organic chemistry over a 30-year period. A Professor of Chemistry at Cornell University since 1980, Dr. McMurry previously spent 13 years on the faculty at the University of California at Santa Cr ...
... JOHN MCMURRY, educated at Harvard and Columbia, has taught approximately 17,000 students in general and organic chemistry over a 30-year period. A Professor of Chemistry at Cornell University since 1980, Dr. McMurry previously spent 13 years on the faculty at the University of California at Santa Cr ...
The 2016 AP Chemistry Exam will be Monday
... - Zeros after the last non-zero are significant ONLY IF there is a decimal point 3. Element Names & Symbols: Memorize elements 1 to 38 and Ag, Cd, Sn, I, Xe, Cs, Ba, W, Hg, Pb, Sn, Rn, Fr, U, Th, Pu, and Am written correctly (Co, not CO)! Students should be able to locate these elements quickly on t ...
... - Zeros after the last non-zero are significant ONLY IF there is a decimal point 3. Element Names & Symbols: Memorize elements 1 to 38 and Ag, Cd, Sn, I, Xe, Cs, Ba, W, Hg, Pb, Sn, Rn, Fr, U, Th, Pu, and Am written correctly (Co, not CO)! Students should be able to locate these elements quickly on t ...
Chapter 1
... a) rice pudding Heterogeneous mixture b) seawater Homogeneous mixture unless there are undissolved particles such as sand, then heterogeneous c) magnesium Element d) gasoline Homogeneous mixture ...
... a) rice pudding Heterogeneous mixture b) seawater Homogeneous mixture unless there are undissolved particles such as sand, then heterogeneous c) magnesium Element d) gasoline Homogeneous mixture ...
Ch 4 Review
... a. in order of atomic charge c. in order of subatomic particles b. in order of atomic number d. in alphabetical order ____ 18. The attractive force between oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as a. a covalent bond. c. an atomic bond. b ...
... a. in order of atomic charge c. in order of subatomic particles b. in order of atomic number d. in alphabetical order ____ 18. The attractive force between oppositely charged ions that result from the transfer of electrons from one atom to another is known as a. a covalent bond. c. an atomic bond. b ...
SMU: Transferring as a Chemistry Major
... degree will take longer than two years. with scientists who are experts in their • B.A. in Chemistry • If a course is part of a two-course fields and who take pride in providing • B.S. in Biochemistry sequence, finish the sequence at the a quality education. same institution. The traditional degree ...
... degree will take longer than two years. with scientists who are experts in their • B.A. in Chemistry • If a course is part of a two-course fields and who take pride in providing • B.S. in Biochemistry sequence, finish the sequence at the a quality education. same institution. The traditional degree ...
Notes
... Electrochemistry is the study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Reactions with electron transfers are commonly called oxidation-reduction reactions (redox reactions) Not all reactions involve an electron transfer – these reactions are referred to as metathesis reactions Oxida ...
... Electrochemistry is the study of the interchange of chemical and electrical energy. Reactions with electron transfers are commonly called oxidation-reduction reactions (redox reactions) Not all reactions involve an electron transfer – these reactions are referred to as metathesis reactions Oxida ...
No Slide Title
... The metals in these two groups have similar outer electron configurations, with one electron in the outermost s orbital. Chemical properties are quite different due to difference in the ionization energy. ...
... The metals in these two groups have similar outer electron configurations, with one electron in the outermost s orbital. Chemical properties are quite different due to difference in the ionization energy. ...
Chapter 7 Chemical Reactions
... Rules for Balancing equations Write equation with correct formulas for reactants and products Count the number of each atom on each side of the equation (polyatomic unchanged count as one unit) Balance the elements one at a time by using coefficients, start with elements that appear only once on eac ...
... Rules for Balancing equations Write equation with correct formulas for reactants and products Count the number of each atom on each side of the equation (polyatomic unchanged count as one unit) Balance the elements one at a time by using coefficients, start with elements that appear only once on eac ...
wahideh chemistry eportfolio hw
... There is only one naturally occurring isotope of sodium: sodium-23. Sixteen radioactive isotopes of sodium with measured half lives are also known. Two radioactive isotopes of sodium—sodium-22 and sodium-24— are used in medicine and other applications. They can be used as tracers to follow sodium in ...
... There is only one naturally occurring isotope of sodium: sodium-23. Sixteen radioactive isotopes of sodium with measured half lives are also known. Two radioactive isotopes of sodium—sodium-22 and sodium-24— are used in medicine and other applications. They can be used as tracers to follow sodium in ...
CH 4 Notes
... Oxidation numbers (or oxidation states) help us keep track of electrons during chemical reactions. Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms using specific rules. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the char ...
... Oxidation numbers (or oxidation states) help us keep track of electrons during chemical reactions. Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms using specific rules. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the char ...
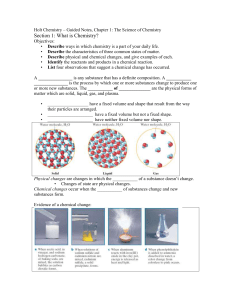
Holt Chemistry – Guided Notes, Chapter 1
... 6. Give three examples each of physical and chemical changes. Physical – change of state, same substance remains before and after Chemical – one or more new substances forms, chemical reaction ...
... 6. Give three examples each of physical and chemical changes. Physical – change of state, same substance remains before and after Chemical – one or more new substances forms, chemical reaction ...
Reactions (The Basics)
... Generally take place between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution Generally 3 things happen: ...
... Generally take place between two ionic compounds in aqueous solution Generally 3 things happen: ...
AP Chemistry: Aqueous Reactions and Solution Stoichiometry
... Oxidation numbers (or oxidation states) help us keep track of electrons during chemical reactions. Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms using specific rules. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the charge on th ...
... Oxidation numbers (or oxidation states) help us keep track of electrons during chemical reactions. Oxidation numbers are assigned to atoms using specific rules. For an atom in its elemental form, the oxidation number is always zero. For any monatomic ion, the oxidation number equals the charge on th ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.