
B.Sc. Physical Sciences - Educational Multimedia Research Centre
... spin, spin quantum number (s) and magnetic spin quantum number (ms). Electronic configurations of the atoms. Concept of exchange energy. Relative energies of atomic orbitals, Anomalous electronic configurations. Unit 2: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bonding : Energy considerations i ...
... spin, spin quantum number (s) and magnetic spin quantum number (ms). Electronic configurations of the atoms. Concept of exchange energy. Relative energies of atomic orbitals, Anomalous electronic configurations. Unit 2: Chemical Bonding and Molecular Structure Ionic Bonding : Energy considerations i ...
Study Island Copyright © 2012 Study Island
... 15. Which of the following is true about a compound and its elements? A. The properties of a compound are the same as the properties of its elements. B. The elements all share identical properties, but their properties are different than the compound's properties. C. The properties of a compound are ...
... 15. Which of the following is true about a compound and its elements? A. The properties of a compound are the same as the properties of its elements. B. The elements all share identical properties, but their properties are different than the compound's properties. C. The properties of a compound are ...
Chemistry and Biochemistry - St. Mary`s University Academic Catalog
... This course is designed to provide a general overview of these two specific areas of chemistry for non- majors. It will provide the general basics of organic chemistry including basic carbon chemistry, nomenclature, structures of organic compounds, chemical characteristics and function,reactions, an ...
... This course is designed to provide a general overview of these two specific areas of chemistry for non- majors. It will provide the general basics of organic chemistry including basic carbon chemistry, nomenclature, structures of organic compounds, chemical characteristics and function,reactions, an ...
lecture slides of chap8
... the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but electron repulsion resulting from the additional electron enlarges the electron clouds ...
... the reduced electron repulsion resulting from removal of electrons make the electron clouds shrink. Anion is always larger than atom from which it is formed. This is because the nuclear charge remains the same but electron repulsion resulting from the additional electron enlarges the electron clouds ...
double-replacement reaction
... active metal displaces a less active metal according to the activity series. • In a double-replacement reaction, two aqueous solutions produce a precipitate of an insoluble compound. ...
... active metal displaces a less active metal according to the activity series. • In a double-replacement reaction, two aqueous solutions produce a precipitate of an insoluble compound. ...
Predicting Reactions • AP Chemistry CLASSIFYING REACTIONS
... the opposite of the reaction at the top of this 2. When you see a gaseous compound bubble through any solution, change the gas into the Lewis acid or base they become: CO2(g) + H2O H2CO3 NH3(g) + H2O NH4OH SO2(g) + H2O H2SO3 Some reactions involve industrial processes such as the formation of lime ( ...
... the opposite of the reaction at the top of this 2. When you see a gaseous compound bubble through any solution, change the gas into the Lewis acid or base they become: CO2(g) + H2O H2CO3 NH3(g) + H2O NH4OH SO2(g) + H2O H2SO3 Some reactions involve industrial processes such as the formation of lime ( ...
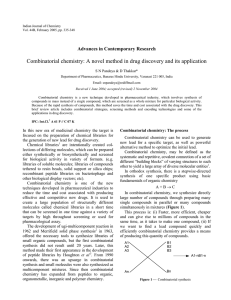
Combinatorial chemistry: A novel method in drug discovery and its
... light in the preceding step. The solution of amino acid is removed and the substrate is again illuminated through a second mask, activating a different region for reaction with a second protected building lock. The pattern of masks and sequence of reactance define the products and their location. Si ...
... light in the preceding step. The solution of amino acid is removed and the substrate is again illuminated through a second mask, activating a different region for reaction with a second protected building lock. The pattern of masks and sequence of reactance define the products and their location. Si ...
Unit B: Matter and Chemical Change
... Molecular Compounds Bonds are created by the sharing of electron Low melting point Not always form crystals Usually formed from only non-metallic elements Does not form ions in solution Usually does not conduct electricity Solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature. ...
... Molecular Compounds Bonds are created by the sharing of electron Low melting point Not always form crystals Usually formed from only non-metallic elements Does not form ions in solution Usually does not conduct electricity Solid, liquid, or gas at room temperature. ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus – Joliet Township High School
... 13. Classification of Molecules 14. Intermolecular Interactions 15. Dipole Moments 16. Dielectric Constants 17. Types of Compounds 18. Properties of Metallic, Molecular, Macromolecular and Ionic Compounds Student Activity – Students are given structures of various compounds and must explain why they ...
... 13. Classification of Molecules 14. Intermolecular Interactions 15. Dipole Moments 16. Dielectric Constants 17. Types of Compounds 18. Properties of Metallic, Molecular, Macromolecular and Ionic Compounds Student Activity – Students are given structures of various compounds and must explain why they ...
Second Semester Notes 09-10
... Nonmetals – everything to the right of the stairstep; includes hydrogen ...
... Nonmetals – everything to the right of the stairstep; includes hydrogen ...
synthesis-structure relationship in the aqueous ethylene glycol
... For the synthesis of the coordination compound, Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, EG (99%) and 1.5 M HNO3, all from “Reactivul” Bucharest, were used. The subsequent purification step applied to the coordination compound assures the removal of most reagent impurities and reaction byproducts, so the desired product is o ...
... For the synthesis of the coordination compound, Fe(NO3)3·9H2O, EG (99%) and 1.5 M HNO3, all from “Reactivul” Bucharest, were used. The subsequent purification step applied to the coordination compound assures the removal of most reagent impurities and reaction byproducts, so the desired product is o ...
Document
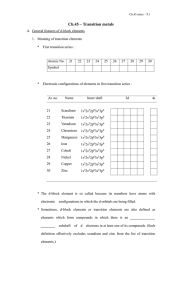
... first transition series react to form compounds, they can form ions of roughly the ___________________ by losing different numbers of electrons. * The higher oxidation states arise through ____________ bonding with more electronegative elements such as fluorine, chlorine and oxygen, as in TiCl4 , ...
... first transition series react to form compounds, they can form ions of roughly the ___________________ by losing different numbers of electrons. * The higher oxidation states arise through ____________ bonding with more electronegative elements such as fluorine, chlorine and oxygen, as in TiCl4 , ...
The Cool Balancing Chemical Reactions Presentation
... Yes! The law of conservation of mass was established in 1789 by French Chemist Antoine Lavoisier. The law states that matter cannot be destroyed or created in any ordinary chemical reaction. This simply means that the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the product. This is the reaso ...
... Yes! The law of conservation of mass was established in 1789 by French Chemist Antoine Lavoisier. The law states that matter cannot be destroyed or created in any ordinary chemical reaction. This simply means that the mass of the reactants must be equal to the mass of the product. This is the reaso ...
Department of Chemistry
... This course will focus on introductory chemical principles, including periodicity, chemical bonding, molecular structure, organic functional groups, equilibrium and the relationship between structure and properties. Students will explore stoichiometric relationships in solution and gas systems which ...
... This course will focus on introductory chemical principles, including periodicity, chemical bonding, molecular structure, organic functional groups, equilibrium and the relationship between structure and properties. Students will explore stoichiometric relationships in solution and gas systems which ...
Chapter 4 - profpaz.com
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
... This relationship is valid because the product of molarity times volume on each side equals the moles of solute, which remains constant during dilution. Molarity and volume, however, are inversely proportional during the dilution process. ...
Reactions of Metals and Their Compounds
... Because the metal atoms loses electrons to the sea, they are positively charged (why?). The positive metal IONS are attracted to the negative electrons = METALLIC BONDING. ...
... Because the metal atoms loses electrons to the sea, they are positively charged (why?). The positive metal IONS are attracted to the negative electrons = METALLIC BONDING. ...
Chemistry: Introduction to Chemical Reactions Guided Inquiry What
... Why do methane molecules (natural gas) collide with oxygen molecules in the air harmlessly until there is a spark or flame, and then they cause an explosion? Why do iron atoms react with oxygen molecules in the air to form rust, but gold molecules do not react with air? The Collision theory is the b ...
... Why do methane molecules (natural gas) collide with oxygen molecules in the air harmlessly until there is a spark or flame, and then they cause an explosion? Why do iron atoms react with oxygen molecules in the air to form rust, but gold molecules do not react with air? The Collision theory is the b ...
Chemistry
... states of matter and changes between the physical states of matter. 2. Determine rates of chemical reactions and the variables that affect chemical reaction rates. 3. Assess experimental data for mechanistic features of a chemical reaction. 4. Identify the constituents of a system at chemical equili ...
... states of matter and changes between the physical states of matter. 2. Determine rates of chemical reactions and the variables that affect chemical reaction rates. 3. Assess experimental data for mechanistic features of a chemical reaction. 4. Identify the constituents of a system at chemical equili ...
Precipitate Lab Report Power Point with Answers
... If the results of putting 2 aqueous solutions together results in the formation of 2 new aqueous solutions, without a precipitate forming, no reaction really occurred. Rather you just mixed the two solutions together, making a homogenous mixture (the same throughout, mixed with no new properties). W ...
... If the results of putting 2 aqueous solutions together results in the formation of 2 new aqueous solutions, without a precipitate forming, no reaction really occurred. Rather you just mixed the two solutions together, making a homogenous mixture (the same throughout, mixed with no new properties). W ...
C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Ionic bonding
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
... increases number of collisions and increases rate Temperature: Particles have more energy and move faster and collide more often. More particles have energy greater than the activation energy so more successful collisions Catalyst: Catalysts change the rate of chemical reactions but are not used up ...
Atoms, Ions and Molecules
... All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements comb ...
... All atoms of a given element show the same chemical properties. 2. Atoms of different elements have different properties. In an ordinary chemical reaction, no atom of any element disappears or is changed into an atom of another element. 3. Compounds are formed when atoms of two or more elements comb ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.


















![C2_revision_slides_V3_+_questions_+_MS_-_H[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000092833_1-97fb33725e7f1ef12029ed42751d3dca-300x300.png)

