More Reaction Information
... • For reactions that are not metal + nonmetal, or do not involve O2, we need a method for determining how the electrons are transferred. • Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an oxidation state that allows them to determine the electron flow in the reaction. – Even though t ...
... • For reactions that are not metal + nonmetal, or do not involve O2, we need a method for determining how the electrons are transferred. • Chemists assign a number to each element in a reaction called an oxidation state that allows them to determine the electron flow in the reaction. – Even though t ...
Study Guide for Final #1
... 1.) Know the parts of the scientific method and how they relate to each other. 2.) Know the difference between pure (basic) and applied chemistry and how they both contribute to the knowledge base in chemistry. 3.) What is the difference between the macroscopic view and the microscopic view? ...
... 1.) Know the parts of the scientific method and how they relate to each other. 2.) Know the difference between pure (basic) and applied chemistry and how they both contribute to the knowledge base in chemistry. 3.) What is the difference between the macroscopic view and the microscopic view? ...
Chem 110 2014 - University of KwaZulu
... -elements present in such samples have same proportion by mass at the end of a chemical process as before the process took place. Law of Multiple Proportions -if 2 elements (C & O) can combine to form 2 or more different compounds (CO & CO2), the different masses of one element (O) combining with a ...
... -elements present in such samples have same proportion by mass at the end of a chemical process as before the process took place. Law of Multiple Proportions -if 2 elements (C & O) can combine to form 2 or more different compounds (CO & CO2), the different masses of one element (O) combining with a ...
Types of reactions: redox reactions
... As a reactant, chlorine has an oxidation number of zero, but as part of the product magnesium chloride, the element has an oxidation number of -1. Each chlorine atom has gained an electron and the element has therefore been reduced. The half-reaction for this change is: ...
... As a reactant, chlorine has an oxidation number of zero, but as part of the product magnesium chloride, the element has an oxidation number of -1. Each chlorine atom has gained an electron and the element has therefore been reduced. The half-reaction for this change is: ...
Practice Problem - HCC Southeast Commons
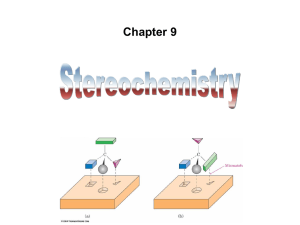
... into two pieces that are exact mirror images – If an object has a plane of symmetry it is necessarily the same as its mirror image – An achiral molecule is a molecule with a plane of symmetry and is the same as its mirror image ...
... into two pieces that are exact mirror images – If an object has a plane of symmetry it is necessarily the same as its mirror image – An achiral molecule is a molecule with a plane of symmetry and is the same as its mirror image ...
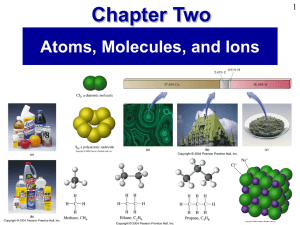
Prentice Hall Ch 02 Atoms Molecules Ions
... General Chemistry 4th edition, Hill, Petrucci, McCreary, Perry ...
... General Chemistry 4th edition, Hill, Petrucci, McCreary, Perry ...
lecture ch1-3 chem161pikul
... – Do not conduct electricity in solid state – Do conduct electricity in liquid and aqueous states where ions are free to move Molecular compounds: – Do not conduct electricity in any state – Molecules are comprised of uncharged particles Jesperson, Brady, Hyslop. Chemistry: The Molecular Nature ...
... – Do not conduct electricity in solid state – Do conduct electricity in liquid and aqueous states where ions are free to move Molecular compounds: – Do not conduct electricity in any state – Molecules are comprised of uncharged particles Jesperson, Brady, Hyslop. Chemistry: The Molecular Nature ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... The fourth state of matter is plasma. Plasma is an ionized gas, a gas into which sufficient energy is provided to free electrons from atoms or molecules and to allow species, ions and electrons, to coexist. In effect plasma is a cloud of protons, neutrons and electrons where all the electrons have c ...
... The fourth state of matter is plasma. Plasma is an ionized gas, a gas into which sufficient energy is provided to free electrons from atoms or molecules and to allow species, ions and electrons, to coexist. In effect plasma is a cloud of protons, neutrons and electrons where all the electrons have c ...
Powerpoints - Holy Cross Collegiate
... • If a precipitate is collected by filtration, some of it may remain dissolved in the filtrate. • When a precipitate is rinsed to remove traces of the reactants, some of the precipitate may dissolve in the rinsing solvent. • Mechanical losses are the small amount of product that are lost when they r ...
... • If a precipitate is collected by filtration, some of it may remain dissolved in the filtrate. • When a precipitate is rinsed to remove traces of the reactants, some of the precipitate may dissolve in the rinsing solvent. • Mechanical losses are the small amount of product that are lost when they r ...
+ (aq)
... 1. d-block metal atoms are small in size and closely packed in the metallic lattice. All Group I metals and some Group II metals do not have close-packed structures 2. Both 3d and 4s electrons of d-block metals participate in metallic bonding by delocalizing into the electron sea, and thus the metal ...
... 1. d-block metal atoms are small in size and closely packed in the metallic lattice. All Group I metals and some Group II metals do not have close-packed structures 2. Both 3d and 4s electrons of d-block metals participate in metallic bonding by delocalizing into the electron sea, and thus the metal ...
Notes
... or identity of a substance • Physical change - produces a recognizable difference in the appearance of a substance without causing any change in its composition or identity - conversion from one physical state to another - melting an ice cube ...
... or identity of a substance • Physical change - produces a recognizable difference in the appearance of a substance without causing any change in its composition or identity - conversion from one physical state to another - melting an ice cube ...
Chemistry
... Group 17 elements: General introduction, occurrence, electronic configuration, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties, anomalous behaviour of fluorine with reasons, reactivity towards hydrogen and oxygen. Chlorine: preparation– from HCl with KMnO4, properties – reaction with Al ...
... Group 17 elements: General introduction, occurrence, electronic configuration, oxidation states, trends in physical and chemical properties, anomalous behaviour of fluorine with reasons, reactivity towards hydrogen and oxygen. Chlorine: preparation– from HCl with KMnO4, properties – reaction with Al ...
N Goalby chemrevise.org 1 2.5 Transition Metals Substitution
... If visible light of increasing frequency is passed through a sample of a coloured complex ion, some of the light is absorbed. The amount of light absorbed is proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species (and to the distance travelled through the solution). Some complexes have only pale ...
... If visible light of increasing frequency is passed through a sample of a coloured complex ion, some of the light is absorbed. The amount of light absorbed is proportional to the concentration of the absorbing species (and to the distance travelled through the solution). Some complexes have only pale ...
Chapter 1: Matter and Change
... A change in a substance that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance is called a physical change. Examples of physical changes include grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling a material. These types of changes do not change the identity of the substance present. Melting and boilin ...
... A change in a substance that does not involve a change in the identity of the substance is called a physical change. Examples of physical changes include grinding, cutting, melting, and boiling a material. These types of changes do not change the identity of the substance present. Melting and boilin ...
Elements Of Physical Chemistry 4th Edition Laidler
... chemistry 4th edition laidler rar tinyurl com l82qsmh redding area wls atlas of pediatric physical diagnosis expert consult online and print 6e pdf, physical chemistry with c d and solutions manual fourth - physical chemistry with c d and solutions manual fourth edition by laidler the elements jigsa ...
... chemistry 4th edition laidler rar tinyurl com l82qsmh redding area wls atlas of pediatric physical diagnosis expert consult online and print 6e pdf, physical chemistry with c d and solutions manual fourth - physical chemistry with c d and solutions manual fourth edition by laidler the elements jigsa ...
Classifying Chemical Reactions by What Atoms Do
... must gain or lose electrons (of course, if one atom loses electrons, another must accept them). Atoms that lose electrons are being oxidized, atoms that gain electrons are being reduced. ...
... must gain or lose electrons (of course, if one atom loses electrons, another must accept them). Atoms that lose electrons are being oxidized, atoms that gain electrons are being reduced. ...
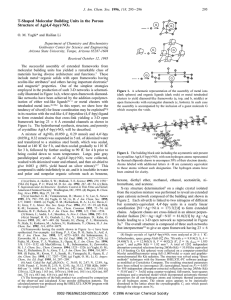
T-Shaped Molecular Building Units in the Porous Structure of Ag(4,4
... materials having diverse architecture and functions.1 These include metal-organic solids with open frameworks having zeolite-like attributes2 and others having important electronic3 and magnetic4 properties. One of the simplest strategies employed in the production of such 3-D networks is schematica ...
... materials having diverse architecture and functions.1 These include metal-organic solids with open frameworks having zeolite-like attributes2 and others having important electronic3 and magnetic4 properties. One of the simplest strategies employed in the production of such 3-D networks is schematica ...
WIPO IPC: Internet Publication
... In still other cases, the pure chemical aspect is covered by section C and the applied chemical aspect by another section, such as A, B or F, e.g., the use of a substance or composition for: treatment of plants or animals, covered by subclass A01N; foodstuffs, covered by class A23; ammunition ...
... In still other cases, the pure chemical aspect is covered by section C and the applied chemical aspect by another section, such as A, B or F, e.g., the use of a substance or composition for: treatment of plants or animals, covered by subclass A01N; foodstuffs, covered by class A23; ammunition ...
Oxidation Numbers
... reduction: a decrease in the oxidation number Cl2(g) + 2e− → 2Cl−(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2e− → Sn2+(aq) (oxidation # becoming less positive or ...
... reduction: a decrease in the oxidation number Cl2(g) + 2e− → 2Cl−(aq) Sn4+(aq) + 2e− → Sn2+(aq) (oxidation # becoming less positive or ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.