![Homework Booklet [4,S]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/010355871_1-63c750e3d1b58eaaebbb3f5d45651c44-300x300.png)
Homework Booklet [4,S]
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
... 4. Explain the following in terms of bonding and structure ideas :. (i) Silicon dioxide and carbon dioxide both contain covalent bonds but the former melts at 1700oC whereas the latter is a gas at 0oC. (ii) Sodium oxide, carbon dioxide and silicon dioxide are all poor conductors of electricity ...
Chemistry 101: The Complete Notes
... Unfortunately, the safety guidelines for the seats are quoted in „metric‟ units. The label reads: “Do not exceed a 150 N load” and you must use this information to determine the maximum weight a child must not exceed in order to be protected during a collision at 55 mph. Can you do it? A child‟s lif ...
... Unfortunately, the safety guidelines for the seats are quoted in „metric‟ units. The label reads: “Do not exceed a 150 N load” and you must use this information to determine the maximum weight a child must not exceed in order to be protected during a collision at 55 mph. Can you do it? A child‟s lif ...
Spectroscopy in Organic Chemistry….
... But on the other Hand… • NMR is one of the least sensitive analytical methods • Characterized by long relaxation time constants, limiting experimental efficiency in real time • Sometimes too much information. Can be demanding on interpretation skill ...
... But on the other Hand… • NMR is one of the least sensitive analytical methods • Characterized by long relaxation time constants, limiting experimental efficiency in real time • Sometimes too much information. Can be demanding on interpretation skill ...
CHEM 30 REDOX
... Pd(s) + Pt (aq) → Pd (aq) + Pt(s) Pt2+(aq) + 2 e- → Pt(s) Pd2+(aq) + 2 e- → Pd(s) ...
... Pd(s) + Pt (aq) → Pd (aq) + Pt(s) Pt2+(aq) + 2 e- → Pt(s) Pd2+(aq) + 2 e- → Pd(s) ...
Introductary topics
... Naming Inorganic Compounds Names and Formulas of Binary Molecular Compounds Binary molecular compounds are composed of two nonmetallic elements. The element with the positive oxidation number (the one closest to the lower left corner on the periodic table) is usually written first. Exception: NH3. ...
... Naming Inorganic Compounds Names and Formulas of Binary Molecular Compounds Binary molecular compounds are composed of two nonmetallic elements. The element with the positive oxidation number (the one closest to the lower left corner on the periodic table) is usually written first. Exception: NH3. ...
Task 4 6 points - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... brown, extremely labile metal ozonide should be formed. Ionic ozonides are vigorously decomposed by water under the formation of oxygen. The resulting solution is alkaline. ...
... brown, extremely labile metal ozonide should be formed. Ionic ozonides are vigorously decomposed by water under the formation of oxygen. The resulting solution is alkaline. ...
Carbon Chemistry - North Allegheny School District
... Many compounds are made of only carbon and hydrogen. A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms is called a hydrocarbon. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, the primary component of natural gas. If you have a gas stove or gas furnace in your home, methane usually is the fuel that is bu ...
... Many compounds are made of only carbon and hydrogen. A compound that contains only carbon and hydrogen atoms is called a hydrocarbon. The simplest hydrocarbon is methane, the primary component of natural gas. If you have a gas stove or gas furnace in your home, methane usually is the fuel that is bu ...
Unit5C - OCCC.edu
... Example: Write the complete ionic and net ionic equations for the reaction. Which element is oxidized? What is the oxidizing ...
... Example: Write the complete ionic and net ionic equations for the reaction. Which element is oxidized? What is the oxidizing ...
Synthesis and Characterisation of N
... compounds containing low-valent main group elements. Recently, more work was put forth in the synthesis and study of molecules containing phosphorous in its +1 oxidation state (PI). One way of stabilizing the PI center is by using N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). Our group previously reported several ...
... compounds containing low-valent main group elements. Recently, more work was put forth in the synthesis and study of molecules containing phosphorous in its +1 oxidation state (PI). One way of stabilizing the PI center is by using N-heterocyclic carbenes (NHCs). Our group previously reported several ...
+ H 2 O
... bent shape and ability to hydrogen bond gives it many special properties. Water molecules are attracted to one another by dipole interactions This hydrogen bonding gives water: a) its high surface tension, b) its Water’s ...
... bent shape and ability to hydrogen bond gives it many special properties. Water molecules are attracted to one another by dipole interactions This hydrogen bonding gives water: a) its high surface tension, b) its Water’s ...
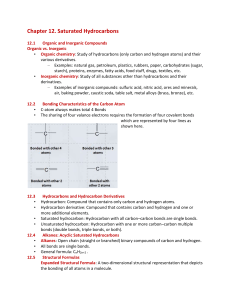
Notes-C12-121
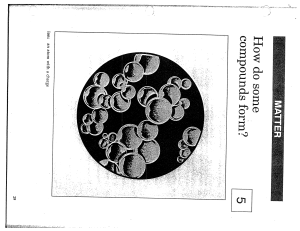
... starch), proteins, enzymes, fatty acids, food stuff, drugs, textiles, etc. • Inorganic chemistry: Study of all substances other than hydrocarbons and their derivatives. – Examples of inorganic compounds: sulfuric acid, nitric acid, ores and minerals, air, baking powder, caustic soda, table salt, met ...
... starch), proteins, enzymes, fatty acids, food stuff, drugs, textiles, etc. • Inorganic chemistry: Study of all substances other than hydrocarbons and their derivatives. – Examples of inorganic compounds: sulfuric acid, nitric acid, ores and minerals, air, baking powder, caustic soda, table salt, met ...
Document
... This process is called electrolysis and the substance that is broken down is called the electrolyte. During electrolysis, positively charged ions move to the negative electrode, and negatively charged ions move to the positive electrode. Electrolysis is used to electroplate objects. This maybe for a ...
... This process is called electrolysis and the substance that is broken down is called the electrolyte. During electrolysis, positively charged ions move to the negative electrode, and negatively charged ions move to the positive electrode. Electrolysis is used to electroplate objects. This maybe for a ...
Chapter 4 Packet
... neutralization and precipitation reactions) and write balanced molecular and net ionic equations for them. I will also be able identify spectator ions. 6. be able to choose which type of equation is most appropriate (molecular, ionic or net ionic) equation for specific situations. 7. recognize react ...
... neutralization and precipitation reactions) and write balanced molecular and net ionic equations for them. I will also be able identify spectator ions. 6. be able to choose which type of equation is most appropriate (molecular, ionic or net ionic) equation for specific situations. 7. recognize react ...
Learning objectives C8.2 Chemical Reactions Reactivity of Metals
... Acid + metal Acid + metal oxide Acid + metal carbonate Acid + alkali Be able to produce word and symbol equations for these reactions and work out the name of the salt produced from the reactants used ...
... Acid + metal Acid + metal oxide Acid + metal carbonate Acid + alkali Be able to produce word and symbol equations for these reactions and work out the name of the salt produced from the reactants used ...
RES8_chemcontentchecklist
... Explain in terms of van der Waals’ forces the variations in the boiling points of alkanes with different carbon-chain length and branching. Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion o ...
... Explain in terms of van der Waals’ forces the variations in the boiling points of alkanes with different carbon-chain length and branching. Describe the combustion of alkanes, leading to their use as fuels in industry, in the home and in transport. Explain using equations the incomplete combustion o ...
Inorganic chemistry

Inorganic chemistry deals with the synthesis and behavior of inorganic and organometallic compounds. This field covers all chemical compounds except the myriad organic compounds (carbon based compounds, usually containing C-H bonds), which are the subjects of organic chemistry. The distinction between the two disciplines is far from absolute, and there is much overlap, most importantly in the sub-discipline of organometallic chemistry. It has applications in every aspect of the chemical industry–including catalysis, materials science, pigments, surfactants, coatings, medicine, fuel, and agriculture.