chemia simr01 en - Leszek Niedzicki
... number is decreasing – they repel each other less – so they can fit in a smaller volume. Adding electrons (cation forming) increases ionic radius – more electrons are not fitting in the same volume due to repulsion. • + and – rule explains also why very big atoms (e.g. fblock elements) can form +2 t ...
... number is decreasing – they repel each other less – so they can fit in a smaller volume. Adding electrons (cation forming) increases ionic radius – more electrons are not fitting in the same volume due to repulsion. • + and – rule explains also why very big atoms (e.g. fblock elements) can form +2 t ...
Part a
... Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
... Electrical energy—results from movement of charged particles Mechanical energy—directly involved in moving matter Radiant or electromagnetic energy—exhibits wavelike properties (i.e., visible light, ultraviolet light, and X-rays) ...
ch14
... Carbon forms predominantly covalent bonds, but the larger members of the group form bonds with increasing ionic character. Elements of this group also exhibit multiple oxidation states. Lower oxidation states become more prominent down the group. Pb and Sn show more metallic character in their lower ...
... Carbon forms predominantly covalent bonds, but the larger members of the group form bonds with increasing ionic character. Elements of this group also exhibit multiple oxidation states. Lower oxidation states become more prominent down the group. Pb and Sn show more metallic character in their lower ...
Scientific Notation, Measurements, and
... o Gas – no fixed volume or shape, takes on shape of the container, highly compressible o Plasma – exists at extremely high temperatures as ions since electrons are striped away from the nucleus A mixture is two or more substances, combined in varying proportions - each retaining its own specific pro ...
... o Gas – no fixed volume or shape, takes on shape of the container, highly compressible o Plasma – exists at extremely high temperatures as ions since electrons are striped away from the nucleus A mixture is two or more substances, combined in varying proportions - each retaining its own specific pro ...
PIB and HH - Unit 4 - Chemical Names and Formulas
... The Periodic Table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in the mid-1800s. Mendeleev put all of the elements in order based on mass, and noticed a periodic reoccurance of chemical and physical properties. He arranged the elements in columns. Elements in each column have similar properties. Occasionally, ...
... The Periodic Table was developed by Dmitri Mendeleev in the mid-1800s. Mendeleev put all of the elements in order based on mass, and noticed a periodic reoccurance of chemical and physical properties. He arranged the elements in columns. Elements in each column have similar properties. Occasionally, ...
AP Chemistry Name: Ch.2 – The Nuclear Atom Date: Period:
... A component of washing powder mined in Death Valley. ...
... A component of washing powder mined in Death Valley. ...
Chapter 8
... A substance combines with oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light or heat. Hydrocarbons, when combined with oxygen in a combustion reaction, release carbon ...
... A substance combines with oxygen, releasing a large amount of energy in the form of light or heat. Hydrocarbons, when combined with oxygen in a combustion reaction, release carbon ...
The chemical elements are fundamental building materials of matter
... • 1.A: All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms: these are the elements. • 1.B: The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and nuclei. • 1.C: Elements display periodicity in their properties when the elements are orga ...
... • 1.A: All matter is made of atoms. There are a limited number of types of atoms: these are the elements. • 1.B: The atoms of each element have unique structures arising from interactions between electrons and nuclei. • 1.C: Elements display periodicity in their properties when the elements are orga ...
chemical bonds - geraldinescience
... Chemical Formulas • A chemical formula is a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound and the number of atoms of each element that are required to make a molecule of a compound. • In a chemical formula, the subscript that appears after the symbol for an element ...
... Chemical Formulas • A chemical formula is a combination of letters and numbers that shows which elements make up a compound and the number of atoms of each element that are required to make a molecule of a compound. • In a chemical formula, the subscript that appears after the symbol for an element ...
1-Three states of matter . A: density, volume and weight B: solid
... 19. Compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) on the other end are known as _______________ (Hint: They are the building blocks of proteins). A. nucleic acids B. amino acids C. carbohydrates D. lipids 20. ________________ are macromolecules that contain carbon, hyd ...
... 19. Compounds with an amino group (-NH2) on one end and a carboxyl group (COOH) on the other end are known as _______________ (Hint: They are the building blocks of proteins). A. nucleic acids B. amino acids C. carbohydrates D. lipids 20. ________________ are macromolecules that contain carbon, hyd ...
Directed Reading
... a. Helium does not react with other substances but does form new substances. b. Helium reacts with other substances but does not form new substances. c. Helium reacts with other substances to form new substances. d. Helium does not react with other substances to form new substances. ______ 9. A subs ...
... a. Helium does not react with other substances but does form new substances. b. Helium reacts with other substances but does not form new substances. c. Helium reacts with other substances to form new substances. d. Helium does not react with other substances to form new substances. ______ 9. A subs ...
AP Chemistry
... What is the percentage of water in a sample of Epsom salts when its mass was 2.25 g before dehydration, and 1.07 g after? ...
... What is the percentage of water in a sample of Epsom salts when its mass was 2.25 g before dehydration, and 1.07 g after? ...
Quarterly 1 Review Trupia - Trupia
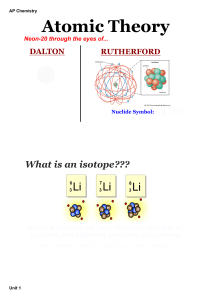
... What conclusion about the internal structure of the atom did this evidence show? c In the same experiment, some of the alpha particles returned toward the source. What does this evidence indicate about the charge of the atom’s nucleus? ...
... What conclusion about the internal structure of the atom did this evidence show? c In the same experiment, some of the alpha particles returned toward the source. What does this evidence indicate about the charge of the atom’s nucleus? ...
naming-and-formulas-chem-1-ab
... Molecular Formulas: A formula that specifies the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of the substance. ...
... Molecular Formulas: A formula that specifies the actual number of atoms of each element in one molecule of the substance. ...
Chemistry-5th-Edition-Brady-Solution-Manual
... The heavy line separates the metals from the nonmetals, and the metalloids border the line. ...
... The heavy line separates the metals from the nonmetals, and the metalloids border the line. ...
Honors Chemistry
... a. The formation of HCl and H2 from H2 and Cl2 b. The color change when NO is exposed to air c. The formation of steam from burning H2 and O2 d. The solidification of corn oil at low temperatures e. the odor of NH3 when NH4Cl is rubbed together with Ca(OH)2 powder? ...
... a. The formation of HCl and H2 from H2 and Cl2 b. The color change when NO is exposed to air c. The formation of steam from burning H2 and O2 d. The solidification of corn oil at low temperatures e. the odor of NH3 when NH4Cl is rubbed together with Ca(OH)2 powder? ...
서울대학교 일반화학실험
... the number of neutrons could differ in a given element leading to isotopes of the same element. Changes in the number of electrons lead to ions of different charge; however, identity of the element remains unchanged. Changes in the number of protons deep in the atomic nucleus results in the creation ...
... the number of neutrons could differ in a given element leading to isotopes of the same element. Changes in the number of electrons lead to ions of different charge; however, identity of the element remains unchanged. Changes in the number of protons deep in the atomic nucleus results in the creation ...
Biology\Ch 2 Chemistry
... Ions are atoms that have become charged (usually in a solution) by gaining or losing electrons. Ex: NaCl sometimes breaks into separate Na+ and Cl- ions in solution. Chlorine gains an electron (it already had 7 electrons in its outer energy level so it needed 1 to complete the level) and becomes neg ...
... Ions are atoms that have become charged (usually in a solution) by gaining or losing electrons. Ex: NaCl sometimes breaks into separate Na+ and Cl- ions in solution. Chlorine gains an electron (it already had 7 electrons in its outer energy level so it needed 1 to complete the level) and becomes neg ...
Midterm Review Questions and Answers
... 11. Lavoisier performed a similar experiment to the one described below. A strip of magnesium metal is wrapped around a nichrome wire and placed into a flask. The flask is then closed with the ends of the wire coming out of the flask. Next, a battery is connected to the nichrome wire. This connectio ...
... 11. Lavoisier performed a similar experiment to the one described below. A strip of magnesium metal is wrapped around a nichrome wire and placed into a flask. The flask is then closed with the ends of the wire coming out of the flask. Next, a battery is connected to the nichrome wire. This connectio ...
Unit 11: The Mole
... MOLAR MASS The molar mass of an element is the mass in grams of one mole of any pure substance. ...
... MOLAR MASS The molar mass of an element is the mass in grams of one mole of any pure substance. ...