name chemistry final review
... a. 200.0 g C3H6 and 200.0 g of O2 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2 O2 is the LR, C3H6 is in excess. There is 141.5g of C3H6 left over and 75.08g H2O and 183.4g CO2 produced. b. 45.9 g CuSO4 and 67.3 g of Fe(C2H3O2)3 3 CuSO4 + 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 → 3 Cu(C2H3O2)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 CuSO4 is the LR, Fe(C2H3O2)3 is in ...
... a. 200.0 g C3H6 and 200.0 g of O2 2 C3H6 + 9 O2 → 6 H2O + 6 CO2 O2 is the LR, C3H6 is in excess. There is 141.5g of C3H6 left over and 75.08g H2O and 183.4g CO2 produced. b. 45.9 g CuSO4 and 67.3 g of Fe(C2H3O2)3 3 CuSO4 + 2 Fe(C2H3O2)3 → 3 Cu(C2H3O2)2 + Fe2(SO4)3 CuSO4 is the LR, Fe(C2H3O2)3 is in ...
401
... breakthrough concerning the use of the antisymmetry principle is necessary to make these approaches applicable to larger molecules. Many people have accepted the antisymmetry rule that may be summarized as electronic wave functions must be prescribed to be antisymmetric for all exchanges of electron ...
... breakthrough concerning the use of the antisymmetry principle is necessary to make these approaches applicable to larger molecules. Many people have accepted the antisymmetry rule that may be summarized as electronic wave functions must be prescribed to be antisymmetric for all exchanges of electron ...
Honors Chemistry Semester 1 Exam Review
... amount of N2 produced if 100.0 g of NaN3 is decomposed using the following unbalanced equation: ...
... amount of N2 produced if 100.0 g of NaN3 is decomposed using the following unbalanced equation: ...
Elements, Compounds, and Chemical Equations
... Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. • Count the total number of each type of atom on the reactant (ingredient) side. • Count the total number of each type of atom in the product (what you make) side • If the number of each type of atom matches, the equation is balanced. If the numbers ...
... Count the atoms in the reactants and the products. • Count the total number of each type of atom on the reactant (ingredient) side. • Count the total number of each type of atom in the product (what you make) side • If the number of each type of atom matches, the equation is balanced. If the numbers ...
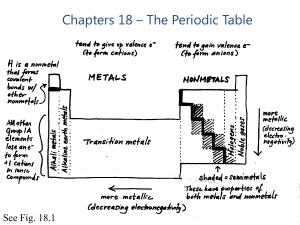
Chapters 18 – The Periodic Table
... element behaves like a true metal Common behavior: reaction with metal to become 2- ion in ionic compound; for most metals, most common minerals are oxides or sulfides Covalent bonds with other NMs; series of covalent hydrides (H2X) All but O have d orbitals available, so more than an octet is ...
... element behaves like a true metal Common behavior: reaction with metal to become 2- ion in ionic compound; for most metals, most common minerals are oxides or sulfides Covalent bonds with other NMs; series of covalent hydrides (H2X) All but O have d orbitals available, so more than an octet is ...
B. The Physical Properties of Matter
... space. (Matter is what makes up everything other than energy.) Hence, chemistry may be better described as the science concerned with the properties, composition, and behaviour of matter. ...
... space. (Matter is what makes up everything other than energy.) Hence, chemistry may be better described as the science concerned with the properties, composition, and behaviour of matter. ...
Question, hints, and answers. Look at hints if you need help. Look at
... Molecules in a sample of NH3(l) are held closely together by intermolecular forces *hint In the NH3 molecule, there is a covalent bond between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge ...
... Molecules in a sample of NH3(l) are held closely together by intermolecular forces *hint In the NH3 molecule, there is a covalent bond between N and H. But the N "wants" the electrons more than the H does, so it pulls them closer to itself. You end up with a little more than half the negative charge ...
National 5 Unit 1 Homework Booklet
... (a)What is the difference between a mixture and a compound? (b)Give 2 pieces of evidence that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. (c)Name the black solid. Is it an element or a compound? 7. Jennifer makes a salt solution by dissolving salt in water. (a)Which substance is the solute and ...
... (a)What is the difference between a mixture and a compound? (b)Give 2 pieces of evidence that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. (c)Name the black solid. Is it an element or a compound? 7. Jennifer makes a salt solution by dissolving salt in water. (a)Which substance is the solute and ...
Homework Booklet Unit 1 Feb14
... (a)What is the difference between a mixture and a compound? (b)Give 2 pieces of evidence that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. (c)Name the black solid. Is it an element or a compound? 7. Jennifer makes a salt solution by dissolving salt in water. (a)Which substance is the solute and ...
... (a)What is the difference between a mixture and a compound? (b)Give 2 pieces of evidence that suggest that a chemical reaction has taken place. (c)Name the black solid. Is it an element or a compound? 7. Jennifer makes a salt solution by dissolving salt in water. (a)Which substance is the solute and ...
File
... means moles need to be converted to grams. Also we will need to find out the molar ration between Fe2O3 and Al. With all chemistry problems and most scientific problems you arrive at the answer by using logical steps rather than guessing. It’s important to set out your work neatly, step wise so that ...
... means moles need to be converted to grams. Also we will need to find out the molar ration between Fe2O3 and Al. With all chemistry problems and most scientific problems you arrive at the answer by using logical steps rather than guessing. It’s important to set out your work neatly, step wise so that ...
Physical and Chemical Changes Worksheet
... Can you recognize the chemical and physical changes that happen all around us? If you change the way something looks, but haven’t made a new substance, a physical change (P) has occurred. If the substance has been changes into another substance, a chemical change (C) has occurred. ...
... Can you recognize the chemical and physical changes that happen all around us? If you change the way something looks, but haven’t made a new substance, a physical change (P) has occurred. If the substance has been changes into another substance, a chemical change (C) has occurred. ...
5073 Chemistry IGCSE ordinary level for 2016
... For over 2000 years, people have wondered about the fundamental building blocks of matter. As far back as 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth ce ...
... For over 2000 years, people have wondered about the fundamental building blocks of matter. As far back as 440 BC, the Greek Leucippus and his pupil Democritus coined the term atomos to describe the smallest particle of matter. It translates to mean something that is indivisible. In the eighteenth ce ...
Revised Syllabus - M. Sc. First Year - Chemistry
... fugacity and determination of fugacity by graphical method, numericals. Non-ideal systems: Activity, activity coefficient, Debye-Huckel theory for activity coefficient of electrolytic solutions, determination of activity and activity coefficients, ionic strength, numerical on ionic strength and Deb ...
... fugacity and determination of fugacity by graphical method, numericals. Non-ideal systems: Activity, activity coefficient, Debye-Huckel theory for activity coefficient of electrolytic solutions, determination of activity and activity coefficients, ionic strength, numerical on ionic strength and Deb ...
Chapter 2
... • The common charge on Mg is +2 (or Mg2+). • The common charge on N is –3 (or N3-). • Since we want to make a neutral (uncharged) compound, the total charges from the cations and anions must cancel-out (or sum to zero). • Therefore, Mg needs to lose 6 electrons (3 2+) and N gain those 6 electrons ...
... • The common charge on Mg is +2 (or Mg2+). • The common charge on N is –3 (or N3-). • Since we want to make a neutral (uncharged) compound, the total charges from the cations and anions must cancel-out (or sum to zero). • Therefore, Mg needs to lose 6 electrons (3 2+) and N gain those 6 electrons ...
Identify the following properties as either - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... not make careful observations make-up data ...
... not make careful observations make-up data ...
St. Xavier`s College – Autonomous Mumbai Syllabus for 3 Semester
... 1. To understand some more concepts of thermodynamics from a chemist’s viewpoint. 2. To predict the feasibility of a reaction. 3. To understand concepts involved in electrolytic cells and their applications. 4. To motivate students to solve numerical problems with different systems of units which il ...
... 1. To understand some more concepts of thermodynamics from a chemist’s viewpoint. 2. To predict the feasibility of a reaction. 3. To understand concepts involved in electrolytic cells and their applications. 4. To motivate students to solve numerical problems with different systems of units which il ...
01.CN_Other pages/p1-9
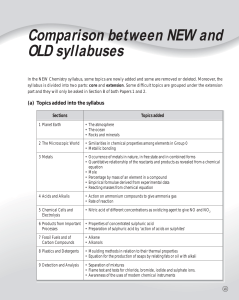
... In the NEW Chemistry syllabus, some topics are newly added and some are removed or deleted. Moreover, the syllabus is divided into two parts: core and extension. Some difficult topics are grouped under the extension part and they will only be asked in Section B of both Papers 1 and 2. ...
... In the NEW Chemistry syllabus, some topics are newly added and some are removed or deleted. Moreover, the syllabus is divided into two parts: core and extension. Some difficult topics are grouped under the extension part and they will only be asked in Section B of both Papers 1 and 2. ...
Lecture 9
... 0 = 2(1) + 2(O.N. of C) 0 - (2(1)) = 2(O.N. of C) -2÷2 = O.N. of C O.N. of C = -1 The key is remembering the oxidation number is a property of a single atom and not forgetting to divide by the number of atoms in the molecule or ion as indicated by the subscript. ...
... 0 = 2(1) + 2(O.N. of C) 0 - (2(1)) = 2(O.N. of C) -2÷2 = O.N. of C O.N. of C = -1 The key is remembering the oxidation number is a property of a single atom and not forgetting to divide by the number of atoms in the molecule or ion as indicated by the subscript. ...
Topic 4 Chemistry of the Elements of the Main Group
... electricity. Metals make crystal lattice structures in which electrons can flow freely. Metalloids or semi-metals show intermediate conduction properties (they are semiconductors). Their electronegativity values are close to 2. The valence electrons of metalloids are localised around the nucleus but ...
... electricity. Metals make crystal lattice structures in which electrons can flow freely. Metalloids or semi-metals show intermediate conduction properties (they are semiconductors). Their electronegativity values are close to 2. The valence electrons of metalloids are localised around the nucleus but ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.