GCE Chemistry Teachers` Guide (A2) Word Document
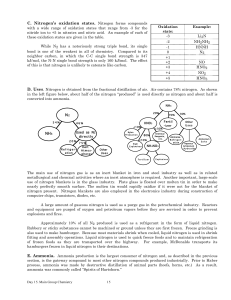
... The new QCA criteria have necessitated the introduction of this topic. The topic is treated in such a way as to keep recall to a minimum. There is a useful analogy with enthalpy which will help to explain the examiners' intentions here. Students may not be able to offer a definition of enthalpy or f ...
... The new QCA criteria have necessitated the introduction of this topic. The topic is treated in such a way as to keep recall to a minimum. There is a useful analogy with enthalpy which will help to explain the examiners' intentions here. Students may not be able to offer a definition of enthalpy or f ...
Introduction to Computational Chemistry Laboratory
... on the size of the basis set used, however because of the mean field approximation, the energies from HF calculations are always greater than the exact energy and tend, with increasing basis size, to a limiting value called the Hartree-Fock limit. An additional issue that affects the accuracy of the ...
... on the size of the basis set used, however because of the mean field approximation, the energies from HF calculations are always greater than the exact energy and tend, with increasing basis size, to a limiting value called the Hartree-Fock limit. An additional issue that affects the accuracy of the ...
CHAPTER 1 CHEMICAL FOUNDATIONS 1 CHAPTER ONE
... a. Distillation separates components of a mixture, so the orange liquid is a mixture (has an average color of the yellow liquid and the red solid). Distillation utilizes boiling point differences to separate out the components of a mixture. Distillation is a physical change because the components of ...
... a. Distillation separates components of a mixture, so the orange liquid is a mixture (has an average color of the yellow liquid and the red solid). Distillation utilizes boiling point differences to separate out the components of a mixture. Distillation is a physical change because the components of ...
Chapter1 - WilsonChemWiki
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus. In the neutral atom the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Mass number: the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Atomic symbols for is ...
... Atomic number: the number of protons in the nucleus. In the neutral atom the number of electrons equals the number of protons. Mass number: the sum of the number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus. Isotopes: atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons. Atomic symbols for is ...
chemistry of living things
... • Defined as the study of the structure of matter and the composition of substances, their properties, and their chemical reactions • Biochemistry is the study of chemical reactions of living things © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ...
... • Defined as the study of the structure of matter and the composition of substances, their properties, and their chemical reactions • Biochemistry is the study of chemical reactions of living things © 2004 Delmar Learning, a Division of Thomson Learning, Inc. ...
Unit 1: Sig. Figs, Compounds, Elements, Homo/Hetero mixtures
... 1. Which of the following gases does not exist in nature as a diatomic molecule? a. Nitrogen b. Helium c. Hydrogen d. oxygen 2. Ionic compounds generally form: a. Liquids b. Gases c. Crystals d. molecules 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all atoms are shared in: a. A nonpolar covalen ...
... 1. Which of the following gases does not exist in nature as a diatomic molecule? a. Nitrogen b. Helium c. Hydrogen d. oxygen 2. Ionic compounds generally form: a. Liquids b. Gases c. Crystals d. molecules 3. In metallic bonding, the valence electrons of all atoms are shared in: a. A nonpolar covalen ...
C1a Revision notes - Calthorpe Park Moodle
... smaller and smaller units, and eventually there would be a tiny particle that could not be divided any further - an atom. This was remarkable because there was no way ancient Greeks could support this theory by observation or experiment. John Dalton ...
... smaller and smaller units, and eventually there would be a tiny particle that could not be divided any further - an atom. This was remarkable because there was no way ancient Greeks could support this theory by observation or experiment. John Dalton ...
physical setting chemistry
... discoveries important to science today. According to a legend, Hiero, the king of Syracuse, commanded Archimedes to find out if the royal crown was made of gold, only. The king suspected that the crown consisted of a mixture of gold, tin, and copper. Archimedes measured the mass of the crown and the ...
... discoveries important to science today. According to a legend, Hiero, the king of Syracuse, commanded Archimedes to find out if the royal crown was made of gold, only. The king suspected that the crown consisted of a mixture of gold, tin, and copper. Archimedes measured the mass of the crown and the ...
Introduction to Chemistry and the Metric System
... 3. What mass of iron (D = 7.87 g/mL) would displace 34.0 cm of water? ...
... 3. What mass of iron (D = 7.87 g/mL) would displace 34.0 cm of water? ...
The Atomic Molecular Theory
... These statements are summaries of many observations, which required a tremendous amount of experimentation to achieve and even more creative thinking to systematize as we have written them here. By making these assumptions, we can proceed directly with the experiments which led to the development of ...
... These statements are summaries of many observations, which required a tremendous amount of experimentation to achieve and even more creative thinking to systematize as we have written them here. By making these assumptions, we can proceed directly with the experiments which led to the development of ...
Atomic emission spectrum
... element. Each atom's atomic emission spectrum is unique and can be used to determine if that element is part of an unknown compound. Light consists of Electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths. Therefore, when the elements or their compounds are heated either on a flame or by an electric ...
... element. Each atom's atomic emission spectrum is unique and can be used to determine if that element is part of an unknown compound. Light consists of Electromagnetic radiation of different wavelengths. Therefore, when the elements or their compounds are heated either on a flame or by an electric ...
Unit 8 Powerpoint
... 4. Balance the elements one at a time by using coefficients. Begin by balancing elements that appear only once on each side of the equation. Unwritten coefficients are assumed to be 1 Once you are certain you have the correct chemical ...
... 4. Balance the elements one at a time by using coefficients. Begin by balancing elements that appear only once on each side of the equation. Unwritten coefficients are assumed to be 1 Once you are certain you have the correct chemical ...
Test - Regents
... (1) moving from a higher to a lower principal energy level (2) moving from a lower to a higher principal energy level (3) being lost by the Ne(g) atoms (4) being gained by the Ne(g) atoms ...
... (1) moving from a higher to a lower principal energy level (2) moving from a lower to a higher principal energy level (3) being lost by the Ne(g) atoms (4) being gained by the Ne(g) atoms ...
ch22 lecture 7e
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43– to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43– into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
... – The inorganic cycle involves slow weathering of phosphatecontaining rocks, which causes PO43– to leach into the rivers and seas. – The land-based biological cycle involves incorporation of PO43– into organisms and its release through excretion and ...
Chemical Formulas and Formula Weight Calculations
... It must then be admitted that very simple relations also exist between the volumes of gaseous substances and the numbers of simple or compound molecules which form them. The first h th i to ...
... It must then be admitted that very simple relations also exist between the volumes of gaseous substances and the numbers of simple or compound molecules which form them. The first h th i to ...
TEST on Atomic Structure
... _D__ 26) Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons have no charge and have almost no mass. b. Protons are negatively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have a negative charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. Electrons have almost no mass ...
... _D__ 26) Which of the following is true about subatomic particles? a. Electrons have no charge and have almost no mass. b. Protons are negatively charged and the lightest subatomic particle. c. Neutrons have a negative charge and are the lightest subatomic particle. d. Electrons have almost no mass ...
Multivalent Ionic Compounds
... Periodic Table. If the element does not form an ion simply state “no ion”. The first two are done for you as an example. Hint: Ions are usually formed by losing all electrons in the Lewis diagram or gaining enough to create a full Lewis diagram. Ions are shown in brackets with the charge on the outs ...
... Periodic Table. If the element does not form an ion simply state “no ion”. The first two are done for you as an example. Hint: Ions are usually formed by losing all electrons in the Lewis diagram or gaining enough to create a full Lewis diagram. Ions are shown in brackets with the charge on the outs ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.