(a) From , 2013 General Chemistry I
... Suppose that 1.00 mol of ideal gas molecules maintained at 292 K and 3.00 atm expands from 8.00 L to 20.00 L and a final pressure of 1.20 atm by two different paths. (a) Path A is an isothermal, reversible expansion. (b) Path B has two parts. In step 1, the gas is cooled at constant volume until its ...
... Suppose that 1.00 mol of ideal gas molecules maintained at 292 K and 3.00 atm expands from 8.00 L to 20.00 L and a final pressure of 1.20 atm by two different paths. (a) Path A is an isothermal, reversible expansion. (b) Path B has two parts. In step 1, the gas is cooled at constant volume until its ...
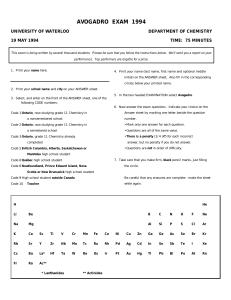
avogadro exam 1994 - University of Waterloo
... volume is heated until the average energy of the gas molecules is doubled. Which other aspect of this system is also doubled? ...
... volume is heated until the average energy of the gas molecules is doubled. Which other aspect of this system is also doubled? ...
Chemical Dynamics at Surfaces
... the third of four sons of Charles Langmuir and Sadie, neé Comings. His early education was obtained in various schools and institutes in the USA, and in Paris (1892-1895). He graduated as a metallurgical engineer from the School of Mines at Columbia University in 1903. Postgraduate work in Physical ...
... the third of four sons of Charles Langmuir and Sadie, neé Comings. His early education was obtained in various schools and institutes in the USA, and in Paris (1892-1895). He graduated as a metallurgical engineer from the School of Mines at Columbia University in 1903. Postgraduate work in Physical ...
Chem G 9
... neutrons will have different mass numbers and are called isotopes. Students should appreciate that a natural sample of an element is likely to contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. In determining the atomic mass of the element we must take into account that it is a mixture of isotopes with diff ...
... neutrons will have different mass numbers and are called isotopes. Students should appreciate that a natural sample of an element is likely to contain a mixture of two or more isotopes. In determining the atomic mass of the element we must take into account that it is a mixture of isotopes with diff ...
AP Chemistry - Freehold Regional High School District
... Carbon forms a large number of compounds since it can form four bonds. ...
... Carbon forms a large number of compounds since it can form four bonds. ...
Chapter 3 Secondary Organic Aerosol Formation by Heterogeneous
... involved to some extent in formation of SOA, uncertainty remains as to the likely aerosol-phase chemical reactions involving absorbed gas-phase organic compounds. The reactive uptake mechanism for relatively small, volatile organic compounds (short-chain aldehydes and ketones) is not well understood ...
... involved to some extent in formation of SOA, uncertainty remains as to the likely aerosol-phase chemical reactions involving absorbed gas-phase organic compounds. The reactive uptake mechanism for relatively small, volatile organic compounds (short-chain aldehydes and ketones) is not well understood ...
Chemistry - RESONANCE PCCP IDEAL for NTSE, IJSO, Olympiads
... minimum value of atomic ratio as to get the simplest ratio of the atoms of elements present in the compound. (iii) If the simplest ratio is fractional, then values of simplest ratio of each element is multiplied by smallest integer to get the simplest whole number for each of the element. PAGE # 4 ...
... minimum value of atomic ratio as to get the simplest ratio of the atoms of elements present in the compound. (iii) If the simplest ratio is fractional, then values of simplest ratio of each element is multiplied by smallest integer to get the simplest whole number for each of the element. PAGE # 4 ...
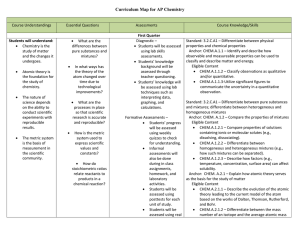
Subject Area Standard Area Organizing Category Grade Level
... CHEM.A.2.3.2: Compare and/or predict the properties (e.g., electron affinity, ionization energy, chemical reactivity, electronegativity, atomic radius) of selected elements by using their locations on the periodic table and known trends. ...
... CHEM.A.2.3.2: Compare and/or predict the properties (e.g., electron affinity, ionization energy, chemical reactivity, electronegativity, atomic radius) of selected elements by using their locations on the periodic table and known trends. ...
Fundamentals
... 2. Precipitation reactions (when a solid is produced by reaction of two or more components in solution). 3. Oxidation/reduction reactions (will also be studied later in detail). 4. Combustion reactions in which a compound reacts with oxygen to produce the most stable oxidation products. (the excepti ...
... 2. Precipitation reactions (when a solid is produced by reaction of two or more components in solution). 3. Oxidation/reduction reactions (will also be studied later in detail). 4. Combustion reactions in which a compound reacts with oxygen to produce the most stable oxidation products. (the excepti ...
Glossary - Chemistry (Intro)
... Notation of E.: Elements of the periodic table are assigned with a mass- and atomic number to quantify its number of protons (Z) and number of protons and neutrons (A); see chemistry atom. Representative E.: Elements in groups 1A through 7A, all of which have incompletely filled s or p subshell of h ...
... Notation of E.: Elements of the periodic table are assigned with a mass- and atomic number to quantify its number of protons (Z) and number of protons and neutrons (A); see chemistry atom. Representative E.: Elements in groups 1A through 7A, all of which have incompletely filled s or p subshell of h ...
Learning Outcomes Leaving Certificate Chemistry
... Becquerel’s discovery of radiation from uranium salts Marie and Pierre Curie’s discovery of polonium and radium comment on the widespread occurrence of radioactivity distinguish between a chemical reaction and a nuclear reaction (simple equations required, confine to α and β emissions) state thr ...
... Becquerel’s discovery of radiation from uranium salts Marie and Pierre Curie’s discovery of polonium and radium comment on the widespread occurrence of radioactivity distinguish between a chemical reaction and a nuclear reaction (simple equations required, confine to α and β emissions) state thr ...
Balanced Equations And Equilibrium Constants
... Balanced Equations And Equilibrium Constants Introduction Rules to Keep in Mind Problems Solutions 1) SnO2(s) + 2 H2(g) <→ Sn(s) + 2 H2O(g) References Contributors ...
... Balanced Equations And Equilibrium Constants Introduction Rules to Keep in Mind Problems Solutions 1) SnO2(s) + 2 H2(g) <→ Sn(s) + 2 H2O(g) References Contributors ...
Biochemistry Part A PPT
... • Inorganic matter- mostly non living, but essential to living organism • *in general does not contain “C”- Carbon • Exceptions: CO, CO2 • Abundant, and represent raw materials needed to build life ...
... • Inorganic matter- mostly non living, but essential to living organism • *in general does not contain “C”- Carbon • Exceptions: CO, CO2 • Abundant, and represent raw materials needed to build life ...
CHAPTER 8 PERIODIC RELATIONSHIPS AMONG THE ELEMENTS
... Strategy: In comparing ionic radii, it is useful to classify the ions into three categories: (1) isoelectronic ions, (2) ions that carry the same charges and are generated from atoms of the same periodic group, and (3) ions that carry different charges but are generated from the same atom. In case ( ...
... Strategy: In comparing ionic radii, it is useful to classify the ions into three categories: (1) isoelectronic ions, (2) ions that carry the same charges and are generated from atoms of the same periodic group, and (3) ions that carry different charges but are generated from the same atom. In case ( ...
The d- and f- Block Element Block Elements The d- and f
... an atom more than the other orbitals (i.e., s and p), hence, they are more influenced by the surroundings as well as affecting the atoms or molecules n surrounding them. In some respects, ions of a given d configuration (n = 1 – 9) have similar magnetic and electronic properties. With partly filled ...
... an atom more than the other orbitals (i.e., s and p), hence, they are more influenced by the surroundings as well as affecting the atoms or molecules n surrounding them. In some respects, ions of a given d configuration (n = 1 – 9) have similar magnetic and electronic properties. With partly filled ...
1 - Cathedral High School
... 4.5.1 Compare and explain the following properties of substances resulting from different types of bonding: melting and boiling points, volatility, conductivity and solubility. Consider melting points, boiling points and volatility of similar substances, such as F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2, and substances w ...
... 4.5.1 Compare and explain the following properties of substances resulting from different types of bonding: melting and boiling points, volatility, conductivity and solubility. Consider melting points, boiling points and volatility of similar substances, such as F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2, and substances w ...
LESSON ASSIGNMENT LESSON 2 Elements of Chemical Change
... possible: Combination reactions, decomposition reactions, single replacement reactions, and double replacement reactions. (1) Combination reactions. A combination reaction can be represented by the chemical equation A + B --> AB (one atom of A plus one atom of B yield one molecule of AB). A specific ...
... possible: Combination reactions, decomposition reactions, single replacement reactions, and double replacement reactions. (1) Combination reactions. A combination reaction can be represented by the chemical equation A + B --> AB (one atom of A plus one atom of B yield one molecule of AB). A specific ...
physical setting chemistry
... Which statement correctly describes what occurs when this reaction takes place in a closed system? ...
... Which statement correctly describes what occurs when this reaction takes place in a closed system? ...
SUPPORT MATERIAL CLASS – X(science) FIRST TERM
... which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations – The chemical equation in which the no. of atoms of different eleme ...
... which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations – The chemical equation in which the no. of atoms of different eleme ...
Document
... which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations – The chemical equation in which the no. of atoms of different eleme ...
... which one or more new substances are formed. 2 )Chemical Equations – Representation of a chemical reaction in terms of symbols and formulae of the reactants and products is known as chemical equation. 3) Balanced Chemical equations – The chemical equation in which the no. of atoms of different eleme ...
physical setting chemistry
... 55 On the same grid, plot the data from the data table. Circle and connect the points. [1] 56 Based on the data in the table, state the relationship between the boiling point at 1 atmosphere and molar mass for these four substances. [1] 57 State, in terms of intermolecular forces, why the boiling po ...
... 55 On the same grid, plot the data from the data table. Circle and connect the points. [1] 56 Based on the data in the table, state the relationship between the boiling point at 1 atmosphere and molar mass for these four substances. [1] 57 State, in terms of intermolecular forces, why the boiling po ...
Section 2 Types of Chemical Reactions
... • List four kinds of single-displacement reactions and three kinds of double-displacement reactions. • Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants. ...
... • List four kinds of single-displacement reactions and three kinds of double-displacement reactions. • Predict the products of simple reactions given the reactants. ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.