Chemistry Midterm Review Study Guide 2012
... 4. a. Which has the larger radius, Al or In? In b. Which has the larger radius, Se or Ca? Ca c. Which has a larger radius, Ca or Ca+2 Ca (would get smaller if lost 2 e-) d. Which has greater ionization energies as a class, metals or nonmetals? nonmetals e. Which has the greater ionization energy, As ...
... 4. a. Which has the larger radius, Al or In? In b. Which has the larger radius, Se or Ca? Ca c. Which has a larger radius, Ca or Ca+2 Ca (would get smaller if lost 2 e-) d. Which has greater ionization energies as a class, metals or nonmetals? nonmetals e. Which has the greater ionization energy, As ...
Atoms in Combination: The Chemical Bond
... electron to chlorine, which is one electron shy of the “magic” number 18. The result is the ionic compound sodium chloride—ordinary table salt. In these diagrams, electrons are represented as dots in shells around a nucleus. ...
... electron to chlorine, which is one electron shy of the “magic” number 18. The result is the ionic compound sodium chloride—ordinary table salt. In these diagrams, electrons are represented as dots in shells around a nucleus. ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
Study Guide 1st Semester
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
... 31. What is a valence electron? 32. Where are the alkali metal elements found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkali metals? 33. Where are the alkaline earth metals found? How do their electron configurations end? What are some typical behaviors of alkal ...
Semester Exam Review - Teach-n-Learn-Chem
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
Atomic Structure: SOL Review #1 Name: Historical Developments 1
... all things made of tiny particles solid sphere model; Atomic Theory: all elements made of atoms, atoms of an element are identical cathode ray tube; discovered electron; plum pudding model oil drop; discovered mass and charge of electron gold foil; discovered nucleus; the atom is mostly empty space ...
... all things made of tiny particles solid sphere model; Atomic Theory: all elements made of atoms, atoms of an element are identical cathode ray tube; discovered electron; plum pudding model oil drop; discovered mass and charge of electron gold foil; discovered nucleus; the atom is mostly empty space ...
Chemistry I Honors – Semester Exam Review – Fall 2000
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
... STRATEGY: Start by reading through your notes to refresh your memory on these topics. Then, use this review sheet as a starting point to identify the areas on which you need to spend more study time. For those areas, go back to homework assignments, quizzes, and reviews to practice more problems. I ...
Chapter One Powerpoint - Geneva Area City Schools
... • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. • Fundamental building block of matter • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, more stable substances and is made of one type of atom. • A compound is a substance that ...
... • An atom is the smallest unit of an element that maintains the chemical identity of that element. • Fundamental building block of matter • An element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down into simpler, more stable substances and is made of one type of atom. • A compound is a substance that ...
The Atomic Theory
... of electricity which passes through a solution. The weights of the substances deposited by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their chemical equivalents. Stoney (1874) made the hypothesis that there was a fundamental unit of electricity and he suggested the name electron. To accoun ...
... of electricity which passes through a solution. The weights of the substances deposited by the same quantity of electricity are proportional to their chemical equivalents. Stoney (1874) made the hypothesis that there was a fundamental unit of electricity and he suggested the name electron. To accoun ...
Chemistry Midterm Review Sheet
... Stoichiometry Review Problems 1) The combustion of a sample of butane, C4H10, produces 3.46 g of water, as well as CO2 a) Write the balanced equation for the reaction b) How many moles of water were formed? How many molecules? c) How many moles of butane burned? d) How many grams of butane burned? e ...
... Stoichiometry Review Problems 1) The combustion of a sample of butane, C4H10, produces 3.46 g of water, as well as CO2 a) Write the balanced equation for the reaction b) How many moles of water were formed? How many molecules? c) How many moles of butane burned? d) How many grams of butane burned? e ...
PROPERTIES_OF_MATTER
... but elements cannot. • Compounds and the elements from which they are formed have different properties ...
... but elements cannot. • Compounds and the elements from which they are formed have different properties ...
PPT format - Columbia University
... Element: An element is a substance which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical processes. Examples: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen. Atomic interpretation: An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. Hydrogen (H) atoms, carbon atoms (C), oxygen atoms (O). Compound: A c ...
... Element: An element is a substance which cannot be decomposed into simpler substances by chemical processes. Examples: hydrogen, carbon, oxygen. Atomic interpretation: An element is a substance that contains only one kind of atom. Hydrogen (H) atoms, carbon atoms (C), oxygen atoms (O). Compound: A c ...
Atoms, molecules and ions
... different than those of all other elements. • Compounds are formed of more than one element. In all compounds, the ratio between the number of atoms of two elements is either an integer or a simple fraction . ...
... different than those of all other elements. • Compounds are formed of more than one element. In all compounds, the ratio between the number of atoms of two elements is either an integer or a simple fraction . ...
The only sure evidence that a chemical reaction has occured is
... What is shown by A in Graph 1? What is shown by B in Graph 1? What type of reaction is shown in Graph 1? Which graph illustrates the type of reaction that occurs when wood burns? ...
... What is shown by A in Graph 1? What is shown by B in Graph 1? What type of reaction is shown in Graph 1? Which graph illustrates the type of reaction that occurs when wood burns? ...
ionization energies
... • In ch. 4, we begin to answer many questions about chemical reactivity • Why is it that some atoms join together and form molecules, while others don’t? ...
... • In ch. 4, we begin to answer many questions about chemical reactivity • Why is it that some atoms join together and form molecules, while others don’t? ...
Pre-Knowledge: Chemistry and Physics Vocabulary Atomic Number
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
... The sum of the number of neutrons and protons in the nucleus of an atom. Nucleus The small “core” of the atom, where most of its mass and all of its positive charge is concentrated. Except for ordinary hydrogen (which has only a proton), atomic nuclei consist of protons and neutrons. For this reason ...
Matter_and_Change2
... Matter with a uniform and definite composition (also called a pure substance). All samples of a substance have identical physical properties. ...
... Matter with a uniform and definite composition (also called a pure substance). All samples of a substance have identical physical properties. ...
matter and - cloudfront.net
... Chemistry The study of the composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. ...
... Chemistry The study of the composition of matter and the changes that matter undergoes. ...
Atoms and Elements: Are they Related?
... identical in mass and properties 3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms. 4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms. ...
... identical in mass and properties 3) Compounds are formed by a combination of two or more different kinds of atoms. 4) A chemical reaction is a rearrangement of atoms. ...
Name__________________________________ Block______
... 9. Mixtures can only be separated by chemical means. 10. Chemical changes produce new substances with new chemical properties. 11. A substance in the solid phase can be changed into the liquid phase. 12. Elements are composed of a single type of atom. 13. Solutions, elements and compounds are all un ...
... 9. Mixtures can only be separated by chemical means. 10. Chemical changes produce new substances with new chemical properties. 11. A substance in the solid phase can be changed into the liquid phase. 12. Elements are composed of a single type of atom. 13. Solutions, elements and compounds are all un ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
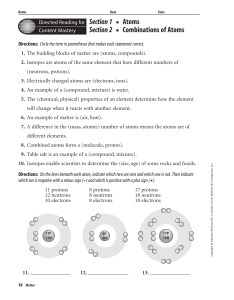
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
... 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a (compound, mixture) is water. 5. The (chemical, physical) properties of an el ...
History of chemistry

The history of chemistry represents a time span from ancient history to the present. By 1000 BC, civilizations used technologies that would eventually form the basis to the various branches of chemistry. Examples include extracting metals from ores, making pottery and glazes, fermenting beer and wine, extracting chemicals from plants for medicine and perfume, rendering fat into soap, making glass, and making alloys like bronze.The protoscience of chemistry, alchemy, was unsuccessful in explaining the nature of matter and its transformations. However, by performing experiments and recording the results, alchemists set the stage for modern chemistry. The distinction began to emerge when a clear differentiation was made between chemistry and alchemy by Robert Boyle in his work The Sceptical Chymist (1661). While both alchemy and chemistry are concerned with matter and its transformations, chemists are seen as applying scientific method to their work.Chemistry is considered to have become an established science with the work of Antoine Lavoisier, who developed a law of conservation of mass that demanded careful measurement and quantitative observations of chemical phenomena. The history of chemistry is intertwined with the history of thermodynamics, especially through the work of Willard Gibbs.