The Chemical Basis of Life
... – Different forms of an element with the same atomic number but with different mass numbers – The atoms of some isotopes are stable – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
... – Different forms of an element with the same atomic number but with different mass numbers – The atoms of some isotopes are stable – Other isotopes are radioactive, having unstable atoms that spontaneously break apart (decay) to form other atoms – When radioactive atoms decay, energy is released ...
pblock - Chemistry Courses
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
... 2nd period: Only s and p orbitals are possible with n = 2 Therefore, the maximum number of bonds is 4 (single and/or double bonds) Examples: CH4, NF4+, BH43rd (and higher periods): can use d-orbitals to make bonds E.g. ...
non-metal chemistry notes
... than S-F bonds Î ↓ in bond strength as more bonds form make S-H bonds too weak to exist. ...
... than S-F bonds Î ↓ in bond strength as more bonds form make S-H bonds too weak to exist. ...
IPC – First Semester Exam Review Be able to classify an example
... Potassium (K) is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron. K gives up that 1 electron because it is easier to give up 1 electron than to gain 7 electrons to get a full outer shell. When K gives up the electron, it has one more positive proton than negative electron. Potassium starts with 19 positive pr ...
... Potassium (K) is in group 1 and has 1 valence electron. K gives up that 1 electron because it is easier to give up 1 electron than to gain 7 electrons to get a full outer shell. When K gives up the electron, it has one more positive proton than negative electron. Potassium starts with 19 positive pr ...
Chapter 24 Organometallic d
... orbital) and σ*-MO (acceptor) •can weaken or cleave the H-H bond ...
... orbital) and σ*-MO (acceptor) •can weaken or cleave the H-H bond ...
Biol 1406 notes Ch 2 8thed - Chemistry
... o There are 92 naturally occurring elements. o Each element has a unique symbol, usually the first one or two letters of its name. Some symbols are derived from Latin or German names. A compound is a substance that consists of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. o Table salt (sodium chloride or ...
... o There are 92 naturally occurring elements. o Each element has a unique symbol, usually the first one or two letters of its name. Some symbols are derived from Latin or German names. A compound is a substance that consists of two or more elements in a fixed ratio. o Table salt (sodium chloride or ...
Worksheet 9 Notes - Oregon State chemistry
... [FeF6]4- is high spin. Explain. How many unpaired electrons are present in [FeF6]4-? [F is F- ion]. High spin due to the F- ion being weak field: CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClThe iron ion in [FeF6]4- is 2+. This is because each of the six F- ions carries a charge of – 1 and the charge ...
... [FeF6]4- is high spin. Explain. How many unpaired electrons are present in [FeF6]4-? [F is F- ion]. High spin due to the F- ion being weak field: CN- > NO2- > en > NH3 > NCS- > H2O > F- > ClThe iron ion in [FeF6]4- is 2+. This is because each of the six F- ions carries a charge of – 1 and the charge ...
Chapter 22-Newest-CD
... Color and Magnetism • Color of a complex depends on: (i) the metal and (ii) its oxidation state. • Pale blue [Cu(H2O)6]2+ can be converted into dark blue [Cu(NH3)6]2+ by adding NH3(aq). • A partially filled d orbital is usually required for a complex to be colored. • So, d 0 metal ions are usually ...
... Color and Magnetism • Color of a complex depends on: (i) the metal and (ii) its oxidation state. • Pale blue [Cu(H2O)6]2+ can be converted into dark blue [Cu(NH3)6]2+ by adding NH3(aq). • A partially filled d orbital is usually required for a complex to be colored. • So, d 0 metal ions are usually ...
answers
... What types of isomers can be formed by a compound with this empirical formula? Geometric (cis and trans) isomerism is possible (as above). What is the d electron configuration of the Pt in this complex? Platinum is in group 10 so Pt(IV) has (10 – 4) = 6 d-electrons: 5d6. ...
... What types of isomers can be formed by a compound with this empirical formula? Geometric (cis and trans) isomerism is possible (as above). What is the d electron configuration of the Pt in this complex? Platinum is in group 10 so Pt(IV) has (10 – 4) = 6 d-electrons: 5d6. ...
8th Grade: First Semester Final Review
... 2. Sample answer: An electron cloud is the space around an atom’s nucleus in which the electrons move. 3. Sample answer: One way I could separate a mixture is by using a strainer to separate components of different sizes. Another method I could use is evaporation, which could be used to separate a l ...
... 2. Sample answer: An electron cloud is the space around an atom’s nucleus in which the electrons move. 3. Sample answer: One way I could separate a mixture is by using a strainer to separate components of different sizes. Another method I could use is evaporation, which could be used to separate a l ...
Synthesis and Crystal Structure of Nicotinamide Cobalt (II) Complexes
... the body, known as pellagra disease. Victims of pellagra show unusually high serum and urinary copper levels (1). The nicotinic acid derivative N,N-diethylnicotinamide (DENA) is an important respiratory stimulant (2). Transition metal complexes with biochemical molecules show interesting physical an ...
... the body, known as pellagra disease. Victims of pellagra show unusually high serum and urinary copper levels (1). The nicotinic acid derivative N,N-diethylnicotinamide (DENA) is an important respiratory stimulant (2). Transition metal complexes with biochemical molecules show interesting physical an ...
CHAPTER TEN MOLECULAR GEOMETRY MOLECULAR
... VALENCE BOND THEORY Hybridization – mixing of two or more atomic orbitals to form a new set of hybrid orbitals. 1. Mix at least 2 nonequivalent atomic orbitals (e.g. s and p). Hybrid orbitals have very different shape from original atomic orbitals. 2. Number of hybrid orbitals is equal to number of ...
... VALENCE BOND THEORY Hybridization – mixing of two or more atomic orbitals to form a new set of hybrid orbitals. 1. Mix at least 2 nonequivalent atomic orbitals (e.g. s and p). Hybrid orbitals have very different shape from original atomic orbitals. 2. Number of hybrid orbitals is equal to number of ...
Chemistry 199 - Oregon State chemistry
... How many d-electrons does V+ have? Sketch the energy level diagram for low-spin V+. octahedral complexes. Sketch the energy level diagram for high-spin V+. V is in Group 5 (it has five valence electrons). V+ has four valence electrons (5-1=4). The valence electrons in the transition metal ions are d ...
... How many d-electrons does V+ have? Sketch the energy level diagram for low-spin V+. octahedral complexes. Sketch the energy level diagram for high-spin V+. V is in Group 5 (it has five valence electrons). V+ has four valence electrons (5-1=4). The valence electrons in the transition metal ions are d ...
Chemistry 199 - Oregon State chemistry
... How many d-electrons does V+ have? Sketch the energy level diagram for low-spin V+. octahedral complexes. Sketch the energy level diagram for high-spin V+. V is in Group 5 (it has five valence electrons). V+ has four valence electrons (5-1=4). The valence electrons in the transition metal ions are d ...
... How many d-electrons does V+ have? Sketch the energy level diagram for low-spin V+. octahedral complexes. Sketch the energy level diagram for high-spin V+. V is in Group 5 (it has five valence electrons). V+ has four valence electrons (5-1=4). The valence electrons in the transition metal ions are d ...
Sections 6.4 - 6.5
... • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in wate ...
... • Aluminum: use in the automotive and aerospace industry as DURALUMINIUM alloyed with Mg and Cu; in ship building as HYDRONALIUM, alloyed with 3-12 % Mg – with disastrous consequences in the BC SeaCat Ferry building program and the Falkland War: Al/Mg + n O2(g) → Al2O3 + MgO + lots of heat ! in wate ...
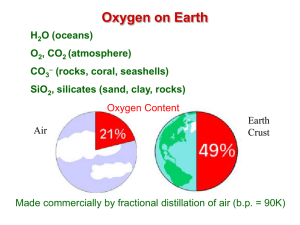
Chapter 4: Introduction to Earth Chemistry Section 1 Notes
... In a chemical formula, the ___________ that appears after the symbol for an element shows the number of __________________________ that are in a molecule. For example: H2O = 2 H (hydrogen atoms) + 1 O (oxygen atom) Chemical Equations Elements and compounds often combine through _____________________ ...
... In a chemical formula, the ___________ that appears after the symbol for an element shows the number of __________________________ that are in a molecule. For example: H2O = 2 H (hydrogen atoms) + 1 O (oxygen atom) Chemical Equations Elements and compounds often combine through _____________________ ...
Chemistry Test Study Guide
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
... 21. A mixture is created when two pure substances are combined so that each of the pure substances retains its own properties. 22. Where is the majority of the mass of an atom located? In the nucleus.(Protons and Neutrons) 23. If an atom loses electron’s, will it have a positive or negative charge? ...
1 5.03, Inorganic Chemistry Prof. Daniel G. Nocera Lecture 9 May 11
... maximum stabilization afforded by metal-metal σ bond formation In each case, the clusters assume an octahedral coordination as a result of burying 6 d electrons in what is formally t2g orbitals. The system loses the number of CO’s that is equivalent to the number of e–s in M-Lσ*. This permits maximu ...
... maximum stabilization afforded by metal-metal σ bond formation In each case, the clusters assume an octahedral coordination as a result of burying 6 d electrons in what is formally t2g orbitals. The system loses the number of CO’s that is equivalent to the number of e–s in M-Lσ*. This permits maximu ...
C1403_Final Exam p. 1 Friday, January 23, 2004 Printed Last Name
... e. None of the above are correct 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a differe ...
... e. None of the above are correct 8. According to valence bond theory, methane (CH4), ammonia (NH3), and water (H2O) all involve sp3 hybridization. Why do these molecules have different bond angles? a. The central atom has a different number of valence electrons. b. These molecules can form a differe ...
18 Valence Electron Rule
... In class I complexes, the Δ o splitting is small and often applies to 3d metals and σ ligands at lower end of the spectrochemical series. In this case the t2g orbital is nonbonding in nature and may be occupied by 0−6 electrons (Figure 2). The e g * orbital is weakly antibonding and may be occupie ...
... In class I complexes, the Δ o splitting is small and often applies to 3d metals and σ ligands at lower end of the spectrochemical series. In this case the t2g orbital is nonbonding in nature and may be occupied by 0−6 electrons (Figure 2). The e g * orbital is weakly antibonding and may be occupie ...
Valence Bond Concepts Applied to MM Force Field Development
... • Covalent bonds are formed by the interaction of singly-occupied orbitals of the central atom and the ligands. • Hybridization of these orbitals provides a mechanism for maximizing bond strength by concentrating electron density in the bonding region. • Hybrid orbitals located on the same atom must ...
... • Covalent bonds are formed by the interaction of singly-occupied orbitals of the central atom and the ligands. • Hybridization of these orbitals provides a mechanism for maximizing bond strength by concentrating electron density in the bonding region. • Hybrid orbitals located on the same atom must ...
Chapter 08
... Lewis Structures and Formal Charge When there is more than one possible structure, the best arrangement is determined by the following guidelines: 1) A Lewis structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferred. 2) Small formal charges are preferred to large formal charges. ...
... Lewis Structures and Formal Charge When there is more than one possible structure, the best arrangement is determined by the following guidelines: 1) A Lewis structure in which all formal charges are zero is preferred. 2) Small formal charges are preferred to large formal charges. ...
Unique properties of p block elements Elias lectures 2 August
... more probability of finding an electron pair (bonding or lone pair). An electron pair domain is a region in space where there is an enhanced probability of finding an electron pair. An electron pair domain extends around the most probable position of finding an electron pair as determined by the Pau ...
... more probability of finding an electron pair (bonding or lone pair). An electron pair domain is a region in space where there is an enhanced probability of finding an electron pair. An electron pair domain extends around the most probable position of finding an electron pair as determined by the Pau ...