1.Using the table above, decide if the element mercury (Hg) should
... As O/Si decreases, the fraction of O atoms bridging between Si atoms increases. As that happens, the structures become more interlinked and complex. Structures progress from momomeric SiO4- anions to dimers, rings, chains, double chains, sheets, and, finally, three-dimensional cages. b. Describe the ...
... As O/Si decreases, the fraction of O atoms bridging between Si atoms increases. As that happens, the structures become more interlinked and complex. Structures progress from momomeric SiO4- anions to dimers, rings, chains, double chains, sheets, and, finally, three-dimensional cages. b. Describe the ...
Synthesis of new nitric oxide donor derivatives
... Neutral atoms arenot found in coordination agents. There are one factor that all ligands have in common that one non – bonded pairs of es , which is used to form a coordination covalent bond with metal. ...
... Neutral atoms arenot found in coordination agents. There are one factor that all ligands have in common that one non – bonded pairs of es , which is used to form a coordination covalent bond with metal. ...
Instructor`s Notes Atomic Tiles: Play Your Way from Atoms to
... 3a. Students know the structure of the atom and know it is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3b. Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 5a. Students know re ...
... 3a. Students know the structure of the atom and know it is composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3b. Students know that compounds are formed by combining two or more different elements and that compounds have properties that are different from their constituent elements. 5a. Students know re ...
Chemistry 332 Basic Inorganic Chemistry II
... is the high energy NB which is primarily derived from a carbon 2p orbital. This means a lone pair of electrons is residing on the C atom. The LUMO on CO is the p*2p which are antibonding orbitals with significant 2p character. CO acts as a Lewis Base and a Lewis Acid. The back bond appearing in thi ...
... is the high energy NB which is primarily derived from a carbon 2p orbital. This means a lone pair of electrons is residing on the C atom. The LUMO on CO is the p*2p which are antibonding orbitals with significant 2p character. CO acts as a Lewis Base and a Lewis Acid. The back bond appearing in thi ...
Valence Bond description of the CO ligand
... Each model is often invoked without any warning in the literature therefore it is important to be able to identify their use. ...
... Each model is often invoked without any warning in the literature therefore it is important to be able to identify their use. ...
Chapter 12: Introduction to Organic Chemistry
... 1. If less than 2n+2 H’s, then unsaturated or cyclic B. Nomenclature 1. prefix cyclo- in front of parent chain 2. substituents numbered around ring a. such as to give lowest numbers b. 1,3 not 1,4 3. when two different groups present a. first alphabetically gets lowest number b. ignore di, tri, etc. ...
... 1. If less than 2n+2 H’s, then unsaturated or cyclic B. Nomenclature 1. prefix cyclo- in front of parent chain 2. substituents numbered around ring a. such as to give lowest numbers b. 1,3 not 1,4 3. when two different groups present a. first alphabetically gets lowest number b. ignore di, tri, etc. ...
Chapter3 Solutions
... electronegativity. This means that the shared electrons are shared essentially equally between the atoms involved in the bond. In a polar covalent bond, one atom attracts the electrons of the bond more strongly than the other. This results in a charge separation and one side of the bond is more nega ...
... electronegativity. This means that the shared electrons are shared essentially equally between the atoms involved in the bond. In a polar covalent bond, one atom attracts the electrons of the bond more strongly than the other. This results in a charge separation and one side of the bond is more nega ...
File
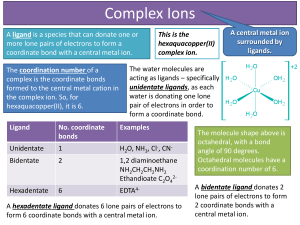
... Complex Ions A ligand is a species that can donate one or more lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. The coordination number of a complex is the coordinate bonds formed to the central metal cation in the complex ion. So, for hexaquacopper(II), it is 6. ...
... Complex Ions A ligand is a species that can donate one or more lone pairs of electrons to form a coordinate bond with a central metal ion. The coordination number of a complex is the coordinate bonds formed to the central metal cation in the complex ion. So, for hexaquacopper(II), it is 6. ...
1 " A Mixed-Metal Nitrido Carbonyl Cluster Compound. Synthesis
... bridged structure can be represented satisfactorily by a single Lewis structure. Such molecules are termed "electron deficient". The nature of the multicenter bonding in B2H6 was first described by Longuet-Higgins. Basically, four electrons hold the two boron atoms and the two bridging hydrogens tog ...
... bridged structure can be represented satisfactorily by a single Lewis structure. Such molecules are termed "electron deficient". The nature of the multicenter bonding in B2H6 was first described by Longuet-Higgins. Basically, four electrons hold the two boron atoms and the two bridging hydrogens tog ...
apbio ch 2 study guide
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
... Hydrogen bonds form when a hydrogen atom that is already covalently bonded to one electronegative atom is attracted to another electronegative atom. o In cells, the electronegative partners are typically nitrogen or oxygen. o Hydrogen bonds form because a polar covalent bond leaves the hydrogen atom ...
Practice Questions for chapters 10 and 11
... electron-pair geometry) identical to its molecular geometry? (a) H2S (b) SF4 (c) XeF4 (d) SiCl4 (e) NH3 Hint: p.p. 409-420. 2. Which of the following molecules have same molecular geometry? (a) CO2 and CF4 (b) NH3 and BF3 (c) H2O and CS2 (d) NO3- and CO32(e) SF4 and CF4 Hint: Tables 10.1 and 10.2. 3 ...
... electron-pair geometry) identical to its molecular geometry? (a) H2S (b) SF4 (c) XeF4 (d) SiCl4 (e) NH3 Hint: p.p. 409-420. 2. Which of the following molecules have same molecular geometry? (a) CO2 and CF4 (b) NH3 and BF3 (c) H2O and CS2 (d) NO3- and CO32(e) SF4 and CF4 Hint: Tables 10.1 and 10.2. 3 ...
Radioactive Reactions
... forces between protons. B Neutrons effectively block the protons and keep them far apart to prevent repulsion. C Electrostatic forces between neutrons and protons hold the nucleus together. ...
... forces between protons. B Neutrons effectively block the protons and keep them far apart to prevent repulsion. C Electrostatic forces between neutrons and protons hold the nucleus together. ...
Bonding and Nomenclature
... Chemical compounds that are formed by chemical bonds help make the body function as it does Ex: stomach would not be able to digest ...
... Chemical compounds that are formed by chemical bonds help make the body function as it does Ex: stomach would not be able to digest ...
Inf_flat_Periodicity_notes
... Going down G16, catenation, strength of single bonds, reactivity decrease. Stability of highest oxidation state decreases down the columb. Dioxides of G16 become increasingly basic and co-od # steadily goes down. 22.5 The Elements of Group 17 Because the halogens are highly reactive, none is found ...
... Going down G16, catenation, strength of single bonds, reactivity decrease. Stability of highest oxidation state decreases down the columb. Dioxides of G16 become increasingly basic and co-od # steadily goes down. 22.5 The Elements of Group 17 Because the halogens are highly reactive, none is found ...
Final Review Answers
... a) resonance structures b) dipole c) electronegativity d) London dispersion forces 8) Classify each of the following substances as having ionic bonds, covalent bonds, or metallic bonds. a) brass metallic b) sodium bromide ionic c) methane cov. d) water cov. e) calcium chloride ionic 9) List all atom ...
... a) resonance structures b) dipole c) electronegativity d) London dispersion forces 8) Classify each of the following substances as having ionic bonds, covalent bonds, or metallic bonds. a) brass metallic b) sodium bromide ionic c) methane cov. d) water cov. e) calcium chloride ionic 9) List all atom ...
Matter - Humble ISD
... • Are also exchange reactions because electrons are exchanged between reactants – Electron donors lose electrons and are oxidized ...
... • Are also exchange reactions because electrons are exchanged between reactants – Electron donors lose electrons and are oxidized ...
Slide 1
... 1. draw the Lewis dot structure 2. draw circles around each atom and the electrons associated with it. Remember that formal charges are associated with covalent bonds and that all electrons are shared equally. 3. compare to the group number for that atom. If the number is larger the formal charge is ...
... 1. draw the Lewis dot structure 2. draw circles around each atom and the electrons associated with it. Remember that formal charges are associated with covalent bonds and that all electrons are shared equally. 3. compare to the group number for that atom. If the number is larger the formal charge is ...
Physical and Chemical Properties
... Elements: If there are 110+ elements, how is it possible to have millions of different substances? • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. ...
... Elements: If there are 110+ elements, how is it possible to have millions of different substances? • Compounds are substances that form when two or more elements combine from a chemical change. ...
Chapter 2
... (b) After electron transfer, the oppositely charged ions formed attract each other. ...
... (b) After electron transfer, the oppositely charged ions formed attract each other. ...
Oxidation Numbers and Ionic Compounds
... Polyatomic ions are groups of covalently bonded atoms that carry an overall charge. Drawing the structure formulas for the MOLECULES below: Remember… Constructing Dot Diagrams for the polyatomic ions is the same as constructing Dot Diagrams for molecules, except the difference in charge (+ or -) mus ...
... Polyatomic ions are groups of covalently bonded atoms that carry an overall charge. Drawing the structure formulas for the MOLECULES below: Remember… Constructing Dot Diagrams for the polyatomic ions is the same as constructing Dot Diagrams for molecules, except the difference in charge (+ or -) mus ...
Naming Covalently Bonded Molecules
... Lattice energy – energy required to separate the ions in an ionic compound Smaller ions have greater lattice energies. Larger charges also have greater lattice energies. ...
... Lattice energy – energy required to separate the ions in an ionic compound Smaller ions have greater lattice energies. Larger charges also have greater lattice energies. ...
RULES OF CHEMICAL NOMENCLATURE I. Elements (periodic
... B. Naming salts (other than binary) 1. name of metal plus name of ...
... B. Naming salts (other than binary) 1. name of metal plus name of ...
Glossary
... Duality − the notion that matter and light have both wave and particle characteristics. ...
... Duality − the notion that matter and light have both wave and particle characteristics. ...