Document
... • “bed check” for electrons • description on how are electrons organized around the nucleus of protons and neutrons • Bohr model: Nils Bohr proposed electrons “orbit” around the atom’s nucleus in specific energy levels or orbits (electron shells) – these shells have a specific energy level – closer ...
... • “bed check” for electrons • description on how are electrons organized around the nucleus of protons and neutrons • Bohr model: Nils Bohr proposed electrons “orbit” around the atom’s nucleus in specific energy levels or orbits (electron shells) – these shells have a specific energy level – closer ...
Unit 1 Review, pages 138–145
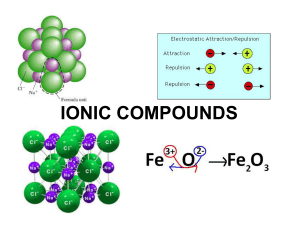
... repeating pattern by strong electrostatic forces. (b) Ionic compounds are hard because their strong bonds resist being stretched. (c) An ionic compound breaks when struck with a hammer because its lattice structure is offset, and like charges repel each other. (d) Ionic compounds conduct electricity ...
... repeating pattern by strong electrostatic forces. (b) Ionic compounds are hard because their strong bonds resist being stretched. (c) An ionic compound breaks when struck with a hammer because its lattice structure is offset, and like charges repel each other. (d) Ionic compounds conduct electricity ...
Solon City Schools
... • The tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element. • How fair it shares. • Big electronegativity means it pulls the electron toward it. • Atoms with large negative electron affinity have larger ...
... • The tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element. • How fair it shares. • Big electronegativity means it pulls the electron toward it. • Atoms with large negative electron affinity have larger ...
Chapter 2
... • The tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element. • How fair it shares. • Big electronegativity means it pulls the electron toward it. • Atoms with large negative electron affinity have larger ...
... • The tendency for an atom to attract electrons to itself when it is chemically combined with another element. • How fair it shares. • Big electronegativity means it pulls the electron toward it. • Atoms with large negative electron affinity have larger ...
Section 8.3 Names and Formulas of Ionic Compounds Formula Unit
... two different elements (one metallic cation and one nonmetallic anion). ...
... two different elements (one metallic cation and one nonmetallic anion). ...
Chap. 9 - Chemical Bonds
... If the electrons are equally distributed (shared) along the bond axis then this type of bond is called NONPOLAR covalent bonds. A dipole moment can be used to visualize the polarity of the bond and is represented by an arrow pointing towards the more electronegative atom and a “+” on the tail. ...
... If the electrons are equally distributed (shared) along the bond axis then this type of bond is called NONPOLAR covalent bonds. A dipole moment can be used to visualize the polarity of the bond and is represented by an arrow pointing towards the more electronegative atom and a “+” on the tail. ...
Chemistry Midterm Review 2006
... 15. What is electronegativity? What is the period and group trend? Which one has a higher electronegativity; C, N, or K? 16. Define ionization energy. What is the period and group trend? Which has a higher ionization energy; Na, K, Mg, or P? 17. Define atomic radius. What is the period and group tre ...
... 15. What is electronegativity? What is the period and group trend? Which one has a higher electronegativity; C, N, or K? 16. Define ionization energy. What is the period and group trend? Which has a higher ionization energy; Na, K, Mg, or P? 17. Define atomic radius. What is the period and group tre ...
Nature of Molecules and Water
... – Na atom loses an electron to become Na+ – Cl atom gains an electron to become Cl– – Opposite charges attract so that Na+ and Cl– remain associated as an ionic compound • Electrical attraction of water molecules can disrupt forces holding ions together ...
... – Na atom loses an electron to become Na+ – Cl atom gains an electron to become Cl– – Opposite charges attract so that Na+ and Cl– remain associated as an ionic compound • Electrical attraction of water molecules can disrupt forces holding ions together ...
The Periodic Table of Elements and Atoms…
... • Element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down any further. It is in its simplest form! Each element is represented by an atom. • Molecules are particles made up of two or more atoms bonded together that make up substances. ...
... • Element is a pure substance that cannot be broken down any further. It is in its simplest form! Each element is represented by an atom. • Molecules are particles made up of two or more atoms bonded together that make up substances. ...
non-polar bond
... it consists of connected hexangonal rings. It is also a network solid Unlike diamond however, these rings form layers that are not connected and can slide across one another. ...
... it consists of connected hexangonal rings. It is also a network solid Unlike diamond however, these rings form layers that are not connected and can slide across one another. ...
Ch6 Chemistry in Biology PowerPoint
... 14. Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron 15. The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 16. An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; ...
... 14. Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron 15. The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 16. An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; ...
Document
... 14. Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron 15. The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 16. An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; ...
... 14. Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron 15. The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 16. An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; ...
Document
... Are attractive forces in which hydrogen that is covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom is also weakly bonded to an unshared electron pair of another ...
... Are attractive forces in which hydrogen that is covalently bonded to a very electronegative atom is also weakly bonded to an unshared electron pair of another ...
Exam 1 Review Sheet Honors Biology This is to be used for
... you think we completely ignore gravity on the atomic level? (Hint: why do we ignore electrons when calculating mass?) 13. The nucleus of elements larger than hydrogen obviously has more than one proton in close proximity. How can this be if the electromagnetic force is pushing these like charges ap ...
... you think we completely ignore gravity on the atomic level? (Hint: why do we ignore electrons when calculating mass?) 13. The nucleus of elements larger than hydrogen obviously has more than one proton in close proximity. How can this be if the electromagnetic force is pushing these like charges ap ...
Review Material
... The ionization energy of an atom or ion is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the ground state of the isolated gaseous atom or ion. The first ionization energy, I1, is the energy needed to remove the first electron from a neutral atom. For example, the first ionization energy for ...
... The ionization energy of an atom or ion is the minimum energy required to remove an electron from the ground state of the isolated gaseous atom or ion. The first ionization energy, I1, is the energy needed to remove the first electron from a neutral atom. For example, the first ionization energy for ...
Electron Rule.
... stable structures. Bonding in TM Complexes: Many TM complexes will form with 18 electrons around the central metal atom. It was first observed by Sedgwick in 1927. ...
... stable structures. Bonding in TM Complexes: Many TM complexes will form with 18 electrons around the central metal atom. It was first observed by Sedgwick in 1927. ...
Chemistry and “Magic Numbers” 18
... stable structures. Bonding in TM Complexes: Many TM complexes will form with 18 electrons around the central metal atom. It was first observed by Sedgwick in 1927. ...
... stable structures. Bonding in TM Complexes: Many TM complexes will form with 18 electrons around the central metal atom. It was first observed by Sedgwick in 1927. ...
File
... 2. Solve for the Unknown Determine how many electrons need to be removed from boron and how many electrons need to be added to selenium to form noble gas configurations. __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ____________________________ ...
... 2. Solve for the Unknown Determine how many electrons need to be removed from boron and how many electrons need to be added to selenium to form noble gas configurations. __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________ ____________________________ ...
Ionic Bonding - KMChemistryMatters
... Drawing Lewis Structures 1. Add the valence electrons. 2. Write symbols for the atoms and show which atoms are connected to which. 3. Complete the octet for the central atom then complete the octets of the other atoms. 4. Place leftover electrons on the central atom. 5. If there are not enough elec ...
... Drawing Lewis Structures 1. Add the valence electrons. 2. Write symbols for the atoms and show which atoms are connected to which. 3. Complete the octet for the central atom then complete the octets of the other atoms. 4. Place leftover electrons on the central atom. 5. If there are not enough elec ...
Instructor`s Guide - Ventura Educational Systems
... More often than not, atoms bond with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. Covalent Molecules, like water (H2O) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH), form when valence electron from one atom are shared with valence electrons from a second atom to form a Covalent Bond. Forming covalent bonds lowers the pote ...
... More often than not, atoms bond with other atoms to form molecules and compounds. Covalent Molecules, like water (H2O) and ethanol (CH3CH2OH), form when valence electron from one atom are shared with valence electrons from a second atom to form a Covalent Bond. Forming covalent bonds lowers the pote ...
The crystal chemistry of the ionic bond
... Cation coordination and the radius rule. A polyhedron of spherical anions is grouped around each cation, such that the number of anions that may surround the cation is a function of the radius ratio, R = rcat/ran. ...
... Cation coordination and the radius rule. A polyhedron of spherical anions is grouped around each cation, such that the number of anions that may surround the cation is a function of the radius ratio, R = rcat/ran. ...
THE CHEMICAL BASIS OF LIFE
... After studying the key terms of this chapter, match the phrases below with the alphabetized list of terms. acid ...
... After studying the key terms of this chapter, match the phrases below with the alphabetized list of terms. acid ...
Chapter 1 Structure and Bonding
... c) Coordination weakens C=C bond (137.5 pm, 1516 cm-1) compared to free ethylene (133.7 pm, 1623 cm-1) ...
... c) Coordination weakens C=C bond (137.5 pm, 1516 cm-1) compared to free ethylene (133.7 pm, 1623 cm-1) ...
CHEMISTRY 103 – Practice Problems #3 Chapters 8 – 10 http
... 17. A central atom with 2 lone pairs and 3 bonding pairs of e- will have a molecular shape of: a. linear b. trigonal pyramid c. trigonal planar d. T-shape e. trigonal bipyramid 18. In Lewis dot structures, which electron interactions repel the most? a. bonding pair–bonding pair b. bonding pair–lone ...
... 17. A central atom with 2 lone pairs and 3 bonding pairs of e- will have a molecular shape of: a. linear b. trigonal pyramid c. trigonal planar d. T-shape e. trigonal bipyramid 18. In Lewis dot structures, which electron interactions repel the most? a. bonding pair–bonding pair b. bonding pair–lone ...