Periodic Table Review Key
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
... 9. Which elements have one valence electron? F,E 10. Which elements have a full outer cloud (octet)? B, H 11. Which element has 2 valence electrons? C 12. Which elements have 8 valence electrons? H 13. Which element is more reactive F or B? F 14. Which elements are considered noble gases? B, H 15. W ...
Inorganic Chemistry Lesson 3
... (i.e. a chemical formula of water) means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in each water molecule. Is the composition of molecules arbitrary, or there is some law that defines it? If such a law does exists, then is it possible to predict composition of molecules? Yes, it is possible ...
... (i.e. a chemical formula of water) means there are two hydrogen atoms and one oxygen atom in each water molecule. Is the composition of molecules arbitrary, or there is some law that defines it? If such a law does exists, then is it possible to predict composition of molecules? Yes, it is possible ...
Interactive PDF File - Western Oregon University
... solids, they are most often electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized. ...
... solids, they are most often electrically insulating, but when melted or dissolved they become highly conductive, because the ions are mobilized. ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
Condition - Future Website of mrbentley2
... 6. Draw the Lewis dot structures of the following ionic compounds. Then, using a different colored pen, show how one element “steals” the other’s electrons, resulting in two ions. (Hint: Some of the compounds may require multiple numbers of one type of element - be sure to draw in the extra element ...
... 6. Draw the Lewis dot structures of the following ionic compounds. Then, using a different colored pen, show how one element “steals” the other’s electrons, resulting in two ions. (Hint: Some of the compounds may require multiple numbers of one type of element - be sure to draw in the extra element ...
3. Chapter 2: Basic Chemistry for Biology
... 14. Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron 15. The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 16. An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; ...
... 14. Which of these is not a subatomic particle? a) proton; b) ion; c) neutron; d) electron 15. The outermost electron shell of every Noble Gas element (except Helium) has ___ electrons. a) 1; b) 2; c) 4; d) 6; e) 8 16. An organic molecule is likely to contain all of these elements except ___. a) C; ...
IONIC AND COVALENT COMPOUNDS A. Why do Atoms Form
... B. How Do You Name Salts? [naming chemical substances =______________] 1. Naming Ions (based on the chemical symbols within the periodic table) a) monatomic ions = cation or anion formed from a single atom ** cations = use the element’s name (followed by ion) ex. Na+ = sodium ion Mg2+ = magnesium io ...
... B. How Do You Name Salts? [naming chemical substances =______________] 1. Naming Ions (based on the chemical symbols within the periodic table) a) monatomic ions = cation or anion formed from a single atom ** cations = use the element’s name (followed by ion) ex. Na+ = sodium ion Mg2+ = magnesium io ...
Grade 10 NSC Chemistry Curriculum
... • Understand the meaning of prefixes di-, tri- etc • Metallic bonding: - Sharing a delocalized electron cloud among positive nuclei in the metal - Revise the cation and the anion list done in grade 9 - Revise the names of compounds - Revise relative molecular mass for covalent molecules - Revise rel ...
... • Understand the meaning of prefixes di-, tri- etc • Metallic bonding: - Sharing a delocalized electron cloud among positive nuclei in the metal - Revise the cation and the anion list done in grade 9 - Revise the names of compounds - Revise relative molecular mass for covalent molecules - Revise rel ...
Year 10 Science Chemistry Examination November 2011 Part A
... Copper nitrate and potassium carbonate Zinc nitrate and sodium chloride Aluminium Chloride and copper nitrate ...
... Copper nitrate and potassium carbonate Zinc nitrate and sodium chloride Aluminium Chloride and copper nitrate ...
File - Ms. Buicke maths and science
... If an atom loses an electron then it becomes a positive ion. If an atom gains an electron then it becomes a negative ion. In ionic bonding positive ions are attracted to negative ions. An ionic bond is a bond formed by the force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions An example of an ioni ...
... If an atom loses an electron then it becomes a positive ion. If an atom gains an electron then it becomes a negative ion. In ionic bonding positive ions are attracted to negative ions. An ionic bond is a bond formed by the force of attraction between two oppositely charged ions An example of an ioni ...
Quantum Chemistry Predicts Multiply Bonded Diuranium
... occupying 12 orbitals. These orbitals are linear combinations of U 7s, 7p, 6d, and 5f orbitals with Cl 3p orbitals. The U-U and U-Cl bond distances and the U-U-Cl angle have been optimized at the CASPT2 level of theory. The ground state of U2Cl6 is a singlet state with the electronic configuration ( ...
... occupying 12 orbitals. These orbitals are linear combinations of U 7s, 7p, 6d, and 5f orbitals with Cl 3p orbitals. The U-U and U-Cl bond distances and the U-U-Cl angle have been optimized at the CASPT2 level of theory. The ground state of U2Cl6 is a singlet state with the electronic configuration ( ...
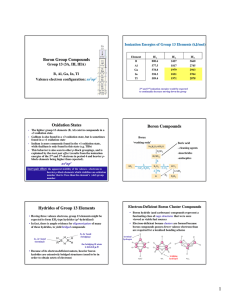
Boron Group Compounds Oxidation States Boron
... • Having three valence electrons, group 13 elements might be expected to form EH3-type hydrides (sp2-hybridized) • In fact, there is ample evidence for oligomerization of many of these hydrides, to yield bridged compounds ...
... • Having three valence electrons, group 13 elements might be expected to form EH3-type hydrides (sp2-hybridized) • In fact, there is ample evidence for oligomerization of many of these hydrides, to yield bridged compounds ...
File
... The diagram shows sodium ions (+) and chloride ions (-) in part of a crystal of table salt, sodium chloride. (i) How are sodium ions and chloride ions formed from their atoms? (ii) What force holds the ions together in sodium chloride? (iii)Name one other compound that is composed of ions. ...
... The diagram shows sodium ions (+) and chloride ions (-) in part of a crystal of table salt, sodium chloride. (i) How are sodium ions and chloride ions formed from their atoms? (ii) What force holds the ions together in sodium chloride? (iii)Name one other compound that is composed of ions. ...
Review Questions– Form B
... Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 19.0 is 55 % abundant; the isotope with a mass number 21 of is 45% abundant. What is the average atomic mass for element Z? ...
... Consider an element Z that has two naturally occurring isotopes with the following percent abundances: the isotope with a mass number of 19.0 is 55 % abundant; the isotope with a mass number 21 of is 45% abundant. What is the average atomic mass for element Z? ...
Chemistry Final Review 2017 1. List a set of elements
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
... 19. How can you distinguish between formulas represent one ionic compound and one molecular compound? 20. Which element forms an ionic compound when it reacts with lithium? 21. The bonds in BaO are best described as __. 22. Which type of bond results when one or more valence electrons are transferre ...
File - Mr Weng`s IB Chemistry
... • Some atoms, like Be and B, might form stable compounds with incomplete octets of electrons. • Resonance structures occur when there is more than one possible position for a double bond in a molecule. • Shapes of species are determined by the repulsion of electron pairs according to VSEPR theory. • ...
... • Some atoms, like Be and B, might form stable compounds with incomplete octets of electrons. • Resonance structures occur when there is more than one possible position for a double bond in a molecule. • Shapes of species are determined by the repulsion of electron pairs according to VSEPR theory. • ...
Matter—anything that has mass and occupies space Weight—pull of
... Formed by sharing of two or more valence shell electrons Allows each atom to fill its valence shell at least part of the time ...
... Formed by sharing of two or more valence shell electrons Allows each atom to fill its valence shell at least part of the time ...
Calculating & Naming Compounds
... …to fill the outer level of electrons of elements you can predict bonding by observing trends on ...
... …to fill the outer level of electrons of elements you can predict bonding by observing trends on ...
Atomic Theory (2
... 1.) What is an ion? 2.) How are ions formed? 3.) Why do ions form readily? (Be specific- in terms of stability) 4.) What is an anion? 5.) What is a cation? 6.) What type of elements form anions? 7.) What type of elements form cations? 8.) What is the relationship between valence electrons and ionic ...
... 1.) What is an ion? 2.) How are ions formed? 3.) Why do ions form readily? (Be specific- in terms of stability) 4.) What is an anion? 5.) What is a cation? 6.) What type of elements form anions? 7.) What type of elements form cations? 8.) What is the relationship between valence electrons and ionic ...
Bonding Considerations
... of electrons between them in what is known as a SIGMA (s)bond. It is also possible for atoms to share more than one pair of electrons. These multiple bonds are known as PI (p)bonds. The atoms involved in bonding have attained a Noble Gas configuration. ...
... of electrons between them in what is known as a SIGMA (s)bond. It is also possible for atoms to share more than one pair of electrons. These multiple bonds are known as PI (p)bonds. The atoms involved in bonding have attained a Noble Gas configuration. ...
Phy. Sci Mid-term review
... Continue to break more and more intermolecular bonds till there are none in a gas. b) How much heat energy is needed to boil a 10.0 g piece of ice that has a temperature of – 30.0°C ...
... Continue to break more and more intermolecular bonds till there are none in a gas. b) How much heat energy is needed to boil a 10.0 g piece of ice that has a temperature of – 30.0°C ...
Intermolecular Attractions
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
... Draw the electron dot formula. Then state how many bonding and unbonding pairs are present. A) NBr3 B) Water C) Chlorite ion (ClO2- ) D) CF2Cl2 ...
Improving our understanding of molecular geometry and the VSEPR
... see in Table 1 and Fig. 2. Three ligands can pack more closely than four which in turn can pack more closely than six, so for a given ligand the bond length increases with coordination number. Two ligands are not restricted by packing and so have an even shorter bond length (Fig. 2). ...
... see in Table 1 and Fig. 2. Three ligands can pack more closely than four which in turn can pack more closely than six, so for a given ligand the bond length increases with coordination number. Two ligands are not restricted by packing and so have an even shorter bond length (Fig. 2). ...
Lecture two
... • “bed check” for electrons • description on how are electrons organized around the nucleus of protons and neutrons • Bohr model: Nils Bohr proposed electrons “orbit” around the atom’s nucleus in specific energy levels or orbits (electron shells) – these shells have a specific energy level – closer ...
... • “bed check” for electrons • description on how are electrons organized around the nucleus of protons and neutrons • Bohr model: Nils Bohr proposed electrons “orbit” around the atom’s nucleus in specific energy levels or orbits (electron shells) – these shells have a specific energy level – closer ...
Periodic Trends & the Periodic Table
... • Metalloids have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. • In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and ...
... • Metalloids have some chemical and physical properties of metals and other properties of nonmetals. • In the periodic table, the metalloids lie along the border between metals and ...