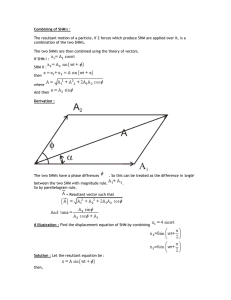
PHYS101 Sec 001 Hour Exam No. 3 Page: 1
... 13 A rogue star is observed to be headed directly for our sun. The expected collision will cause a supernova explosion with an initial are of electromagnetic radiation capable of destroying everything in its path. Before the collision occurs, you get into a spaceship and speed away at 185,000 miles ...
... 13 A rogue star is observed to be headed directly for our sun. The expected collision will cause a supernova explosion with an initial are of electromagnetic radiation capable of destroying everything in its path. Before the collision occurs, you get into a spaceship and speed away at 185,000 miles ...
document
... force needs to exist for Newton’s laws to hold true. Example: Being in a car going around a circular race track. You feel pushed towards one side of the car. You can say that this “push” is some imaginary force rather than the inertia of your body. This imaginary force is called the centrifuga ...
... force needs to exist for Newton’s laws to hold true. Example: Being in a car going around a circular race track. You feel pushed towards one side of the car. You can say that this “push” is some imaginary force rather than the inertia of your body. This imaginary force is called the centrifuga ...
Rigid Body - Kinematics
... Commutative (unlike finite rotation) Behaves as an axial vector (like angular momentum) ...
... Commutative (unlike finite rotation) Behaves as an axial vector (like angular momentum) ...
Higher ODU Printed Notes
... Momentum In any collision or explosion free of external forces, the total momentum remains the same. This can be applied to the interaction of two objects moving in one dimension, in the absence of net external forces. For any collision: Total momentum of all objects before ...
... Momentum In any collision or explosion free of external forces, the total momentum remains the same. This can be applied to the interaction of two objects moving in one dimension, in the absence of net external forces. For any collision: Total momentum of all objects before ...
Physics 1. Mechanics Problems
... Problem 10.2. A particle, initially resting in the coordinate origin, suddenly breaks up into three particles with the masses m1 , m2 , and m3 . The particle m1 has the charge q > 0. It starts moving into negative x-direction in the homogeneous magnetic field B = (0, 0, B). After having completed ha ...
... Problem 10.2. A particle, initially resting in the coordinate origin, suddenly breaks up into three particles with the masses m1 , m2 , and m3 . The particle m1 has the charge q > 0. It starts moving into negative x-direction in the homogeneous magnetic field B = (0, 0, B). After having completed ha ...
Physics Exam – Circular Motion – Place all answers on the test
... an open-air glass. If the glass is held level and at rest (such that there is no acceleration), then the candle flame extends in an upward direction. However, if you hold the glass-candle system with an outstretched arm and spin in a circle at a constant rate (such that the flame experiences an acce ...
... an open-air glass. If the glass is held level and at rest (such that there is no acceleration), then the candle flame extends in an upward direction. However, if you hold the glass-candle system with an outstretched arm and spin in a circle at a constant rate (such that the flame experiences an acce ...
Parachute Jumping, Falling, and Landing
... a velocity of 0.555 m/s straight out (direction of the xaxis) from the side of an airplane which is moving at a velocity of 115 m/s (direction of the y-axis). The airplane is flying at an altitude (height on the z-axis) of 4000 meters. When the jumper leaves the aircraft, he is high enough in altitu ...
... a velocity of 0.555 m/s straight out (direction of the xaxis) from the side of an airplane which is moving at a velocity of 115 m/s (direction of the y-axis). The airplane is flying at an altitude (height on the z-axis) of 4000 meters. When the jumper leaves the aircraft, he is high enough in altitu ...
12.3 Velocity and Acceleration
... Velocity and Acceleration As an object moves along a curve in the plane, the coordinates x and y of its center of mass are each functions of time t. Rather than using the letters f and g to represent these two functions, it is convenient to write x = x(t) and y = y(t). So, the position vector r(t) ...
... Velocity and Acceleration As an object moves along a curve in the plane, the coordinates x and y of its center of mass are each functions of time t. Rather than using the letters f and g to represent these two functions, it is convenient to write x = x(t) and y = y(t). So, the position vector r(t) ...
Introductory module: a video introduction to Modellus
... force between objects, knowing their mass and the distance between them. If one of the objects (a planet...) has a large mass m1 and is placed on the origin of a reference frame xOy, one can assume that only an object with a small mass (a spaceship, a satellite, anything you want…), m2, will be acce ...
... force between objects, knowing their mass and the distance between them. If one of the objects (a planet...) has a large mass m1 and is placed on the origin of a reference frame xOy, one can assume that only an object with a small mass (a spaceship, a satellite, anything you want…), m2, will be acce ...
here.
... For a single particle dynamical variables may be regarded as functions f (r, p). The potential V(r) is a function on configuration space and a function on phase space. xi are called coordinate functions on configuration space. xi , p j are called coordinate functions on phase space. In general, dyna ...
... For a single particle dynamical variables may be regarded as functions f (r, p). The potential V(r) is a function on configuration space and a function on phase space. xi are called coordinate functions on configuration space. xi , p j are called coordinate functions on phase space. In general, dyna ...