UNIT 7 Lab
... a. Tie a small object to one end of a string, put the other end of the string through a straw and then tie about 200g of mass to the other end. Holding the straw, twirl the object around in a circle (Try to make the circle as horizontal as possible.) b. Draw a force diagram for the object and for th ...
... a. Tie a small object to one end of a string, put the other end of the string through a straw and then tie about 200g of mass to the other end. Holding the straw, twirl the object around in a circle (Try to make the circle as horizontal as possible.) b. Draw a force diagram for the object and for th ...
Physics – Mechanics
... can be inferred from the problem (gravity occurs in most problems, but goes unsaid, so list ag = −9.8 m ...
... can be inferred from the problem (gravity occurs in most problems, but goes unsaid, so list ag = −9.8 m ...
Third Midterm Exam Solutions
... Problem 4 (20 points): A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs straight down, giving her a moment of inertia about her rotation axis of Ii = 18 kg·m2 . She then tucks into a small ball, decreasing this moment of inertia to If = 3.6 kg·m2 . While tucked, she makes two complete revol ...
... Problem 4 (20 points): A diver comes off a board with arms straight up and legs straight down, giving her a moment of inertia about her rotation axis of Ii = 18 kg·m2 . She then tucks into a small ball, decreasing this moment of inertia to If = 3.6 kg·m2 . While tucked, she makes two complete revol ...
Anisotropy of Inertia from the CMB Anisotropy
... overhead. What then is the cause of this force? Similarly to the Aristotelian case, the immediate cause of this force is the rotation relative to an inertial frame. Therefore it appears that Newtonian space-time can exert forces on matter. However, this contradicts Newton’s third law since the matte ...
... overhead. What then is the cause of this force? Similarly to the Aristotelian case, the immediate cause of this force is the rotation relative to an inertial frame. Therefore it appears that Newtonian space-time can exert forces on matter. However, this contradicts Newton’s third law since the matte ...
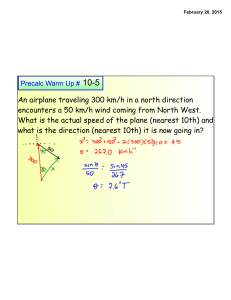
An airplane traveling 300 km/h in a north direction
... direction, are applied at a point A. What is the resulting FORCE at A? (You need a direction AND a magnitude) ...
... direction, are applied at a point A. What is the resulting FORCE at A? (You need a direction AND a magnitude) ...
Find it HERE
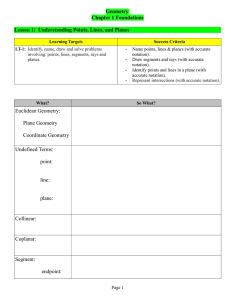
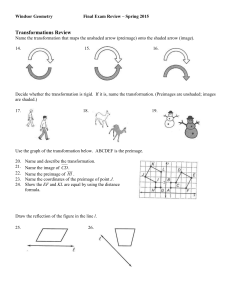
... 65. If 2 polygons are similar, then the corresponding angles are_____ and the corresponding sides are ______. 66. If approximately 6 out of every 7 dentists in Parker recommend chewing sugar-free gum, and there are 43 dentists in Parker, about how many of them recommend chewing sugar-free gum? 67. A ...
... 65. If 2 polygons are similar, then the corresponding angles are_____ and the corresponding sides are ______. 66. If approximately 6 out of every 7 dentists in Parker recommend chewing sugar-free gum, and there are 43 dentists in Parker, about how many of them recommend chewing sugar-free gum? 67. A ...