Circular Motion and the Law of Gravity
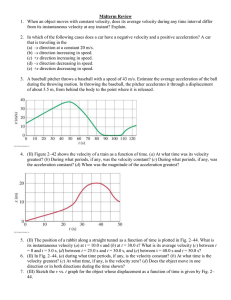
... The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a reference line. Use 0° on the right side of a horizontal line. The light bulb is locate at a distance r from the axel as it moves counter clockwise from 0°. It moves t ...
... The light bulb on the Ferris wheel is moving about an axis. The axis is a fixed point in the center of the Ferris wheel. Establish a reference line. Use 0° on the right side of a horizontal line. The light bulb is locate at a distance r from the axel as it moves counter clockwise from 0°. It moves t ...
Navier-Stokes Equation
... Mathematicians and physicists believe that an explanation for and the prediction of both the breeze and the turbulence can be found through an understanding of solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations. Although these equations were written down in the 19th century, our understanding of them remains ...
... Mathematicians and physicists believe that an explanation for and the prediction of both the breeze and the turbulence can be found through an understanding of solutions to the Navier-Stokes equations. Although these equations were written down in the 19th century, our understanding of them remains ...
Stress, Strain, Virtual Power and Conservation Principles
... Scalars, vectors and tensors are mathematical entities that are used in applications to represent meaningful physical quantities. Consider two systems of coordinates ui and ui∗ which are related by the coordinate transformation rules described above. Physical quantities of interest can be represente ...
... Scalars, vectors and tensors are mathematical entities that are used in applications to represent meaningful physical quantities. Consider two systems of coordinates ui and ui∗ which are related by the coordinate transformation rules described above. Physical quantities of interest can be represente ...
Revision 05/10/06 (PDF)
... the resulting image is smaller than its pre-image. If |k| > 1, the mapping results in a dilation centered at the origin, for which the resulting image is larger than its pre-image. If k = 1, the mapping results in the identity transformation, for which the resulting image is the same size as its pre ...
... the resulting image is smaller than its pre-image. If |k| > 1, the mapping results in a dilation centered at the origin, for which the resulting image is larger than its pre-image. If k = 1, the mapping results in the identity transformation, for which the resulting image is the same size as its pre ...
Concepts Students will Use and Understand
... Scale Factor: The ratio of any two corresponding lengths of the sides of two similar figures Similar Figures: Figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size ...
... Scale Factor: The ratio of any two corresponding lengths of the sides of two similar figures Similar Figures: Figures that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size ...
115PowerPointReview
... Momentum is conserved! The Law of Conservation of Momentum: “In the absence of an unbalanced external force, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.” po (truck) mvo (500)(5) 2500kg * m / s po ( car ) (400)( 2) 800kg * m / s po (total) ...
... Momentum is conserved! The Law of Conservation of Momentum: “In the absence of an unbalanced external force, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision.” po (truck) mvo (500)(5) 2500kg * m / s po ( car ) (400)( 2) 800kg * m / s po (total) ...
Here - Columbia Physics
... is not homogeneous because if −g on the right hand side is nonzero the equation contains a term involving the variable to a power different from 1 (in this case 0). To each linear inhomogenous differential equation we may associate a homogenous equation obtained by removing all of the terms proporti ...
... is not homogeneous because if −g on the right hand side is nonzero the equation contains a term involving the variable to a power different from 1 (in this case 0). To each linear inhomogenous differential equation we may associate a homogenous equation obtained by removing all of the terms proporti ...
Concept Summary
... 4. Choose a convenient coordinate system if one is not specified for you to use. Decide positive and negative direction. 5. Write down the values given to you and identify what they represent (e.g., the 2 m/s given is the final velocity). 6. Identify and write down what variables/quantities you are ...
... 4. Choose a convenient coordinate system if one is not specified for you to use. Decide positive and negative direction. 5. Write down the values given to you and identify what they represent (e.g., the 2 m/s given is the final velocity). 6. Identify and write down what variables/quantities you are ...