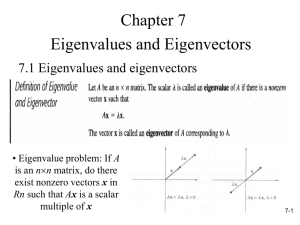
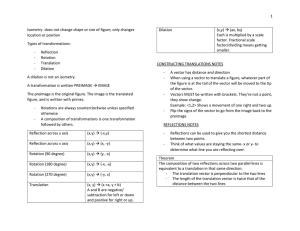
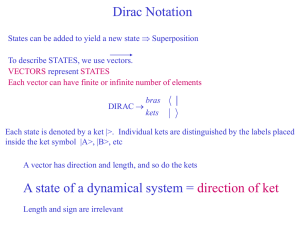
Course Code: Title of the Course
... the rotational Inertia Torque. Newton’s second law for Rotation. Work and Rotational Kinetic Energy. ...
... the rotational Inertia Torque. Newton’s second law for Rotation. Work and Rotational Kinetic Energy. ...
2.1-2.4
... components using the x and y axes system. • Each component of the vector is shown as a magnitude and a direction. • The directions are based on the x and y axes. We use the “unit vectors” i and j to designate the x and y axes. ...
... components using the x and y axes system. • Each component of the vector is shown as a magnitude and a direction. • The directions are based on the x and y axes. We use the “unit vectors” i and j to designate the x and y axes. ...
Chapter 11
... point O, greatest first (b) which particles have negative angular momentum about point O. ...
... point O, greatest first (b) which particles have negative angular momentum about point O. ...
Lecture 7.3 1. Angular Momentum
... they have zero torques. If the person pulls his/her arms in, he/she will reduce the moment of inertia. Indeed the same mass is now distributed closer to the rotational axis. Since the angular momentum of the system should stay the same this will result in the increase of the angular speed of rotatio ...
... they have zero torques. If the person pulls his/her arms in, he/she will reduce the moment of inertia. Indeed the same mass is now distributed closer to the rotational axis. Since the angular momentum of the system should stay the same this will result in the increase of the angular speed of rotatio ...
(2*(3+4))
... Engineers often have to convert from one unit of measurement to another; this can be tricky sometimes. You need to think through the process carefully. For example, convert 5 acres to hectares, given that an acre is 4840 square yards, a yard is 36 inches, an inch is 2.54 cm, and a hectare is 10000 m ...
... Engineers often have to convert from one unit of measurement to another; this can be tricky sometimes. You need to think through the process carefully. For example, convert 5 acres to hectares, given that an acre is 4840 square yards, a yard is 36 inches, an inch is 2.54 cm, and a hectare is 10000 m ...
Leap Frog Solar System
... components of displacement, and summing the squares. The gravitational potential energy for the interaction between planet bodies a 6= b is then calculated using this value. The kinetic energy of each planet body can be calculated independently, and finally these six values are added together to giv ...
... components of displacement, and summing the squares. The gravitational potential energy for the interaction between planet bodies a 6= b is then calculated using this value. The kinetic energy of each planet body can be calculated independently, and finally these six values are added together to giv ...
Slide 1
... Depends on the net force applied and the distance of the net force from the axis of rotation. τ = Fnet r ...
... Depends on the net force applied and the distance of the net force from the axis of rotation. τ = Fnet r ...