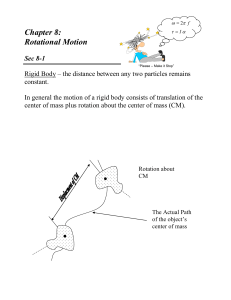
Rotational Motion 3
... the forces involves two component equations. Any torque about a point in that plane will have only a component perpendicular to the plane, so the condition on the torques gives only one equation. Only situations with three or fewer unknowns can be completely determined by these conditions. Stress an ...
... the forces involves two component equations. Any torque about a point in that plane will have only a component perpendicular to the plane, so the condition on the torques gives only one equation. Only situations with three or fewer unknowns can be completely determined by these conditions. Stress an ...
Synopsis of Geometric Algebra
... where | a | is a positive scalar (= real number) called the magnitude or length of a, and | a | = 0 if and only if a = 0. Both distributive rules (1.2) are needed, because multiplication is not commutative. Although the vector space Vn is closed under vector addition, it is not closed under multipli ...
... where | a | is a positive scalar (= real number) called the magnitude or length of a, and | a | = 0 if and only if a = 0. Both distributive rules (1.2) are needed, because multiplication is not commutative. Although the vector space Vn is closed under vector addition, it is not closed under multipli ...
Group-Symmetries and Quarks - USC Department of Physics
... Symmetries in Physics Isospin: Quantum number related to the Strong Interactions For a two-nucleon system, the spin singlet and triplet states are: ...
... Symmetries in Physics Isospin: Quantum number related to the Strong Interactions For a two-nucleon system, the spin singlet and triplet states are: ...
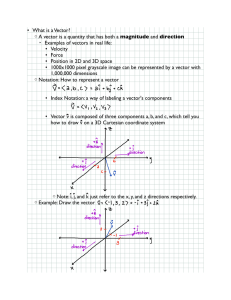
Chapter 3. Vector - People Server at UNCW
... • A scalar is a mathematical quantity whose value does not depend on the orientation of a coordinate system. The magnitude of a vector is a true scalar since it does not change when the coordinate axis is rotated. However, the components of vector (Ax, Ay) and (Ax′, Ay′), are not scalars. • It is po ...
... • A scalar is a mathematical quantity whose value does not depend on the orientation of a coordinate system. The magnitude of a vector is a true scalar since it does not change when the coordinate axis is rotated. However, the components of vector (Ax, Ay) and (Ax′, Ay′), are not scalars. • It is po ...