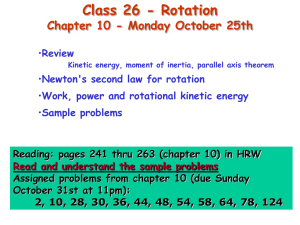
Monday, Nov. 11, 2002
... What is the unit and dimension of angular momentum? kg m2 / s 2 p Note that L depends on origin O. Why? Because r changes x What else do you learn? The direction of L is +z Since p is mv, the magnitude of L becomes L mvr sin What do you learn from this? The point O has to be inertial. Monday, ...
... What is the unit and dimension of angular momentum? kg m2 / s 2 p Note that L depends on origin O. Why? Because r changes x What else do you learn? The direction of L is +z Since p is mv, the magnitude of L becomes L mvr sin What do you learn from this? The point O has to be inertial. Monday, ...
Section 2.2
... In its most basic form a matrix A has an inverse if there is a matrix B such that AB BA I and if this matrix B exists at all then we label it B A −1 Theorem 4 hints at a future method to determine if a matrix has an inverse or not. There is a function called the determinant that you apply it t ...
... In its most basic form a matrix A has an inverse if there is a matrix B such that AB BA I and if this matrix B exists at all then we label it B A −1 Theorem 4 hints at a future method to determine if a matrix has an inverse or not. There is a function called the determinant that you apply it t ...
IMPULSE AND MOMENTUM Impulse is the concept we use to
... its recoil is negligible. The cannon fires an 85 kg shell horizontally with an initial velocity of +551 m/s. The cannon is then unbolted and friction eliminated. Find the velocity of an identical shell fired by this loose cannon if the energy from the burning gunpowder does not change. During a coll ...
... its recoil is negligible. The cannon fires an 85 kg shell horizontally with an initial velocity of +551 m/s. The cannon is then unbolted and friction eliminated. Find the velocity of an identical shell fired by this loose cannon if the energy from the burning gunpowder does not change. During a coll ...
Lecture20.pdf
... the sum (or the resultant) of the vectors u and v . We call u − v the difference of the vectors u and v . Consider a rectangular coordinate system in the plane. Since every point in the plane is ⎛a⎞ determined by an ordered pair, we can identify a geometric point ( a, b ) with a vector ⎜ ⎟ . ⎝b ⎠ He ...
... the sum (or the resultant) of the vectors u and v . We call u − v the difference of the vectors u and v . Consider a rectangular coordinate system in the plane. Since every point in the plane is ⎛a⎞ determined by an ordered pair, we can identify a geometric point ( a, b ) with a vector ⎜ ⎟ . ⎝b ⎠ He ...
1 Topic : Rotating Co-ordinate Systems - (SRL)
... Earth is not an inertial frame. If we were observers on the Sun we would see it racing along at 66,700 mph in an elliptical orbit. An observer at Earth's center would see you rotating at 1,038 mph. Yet, as far as we are concerned it seems nearly inertial, with deviations diÆcult to detect. In this s ...
... Earth is not an inertial frame. If we were observers on the Sun we would see it racing along at 66,700 mph in an elliptical orbit. An observer at Earth's center would see you rotating at 1,038 mph. Yet, as far as we are concerned it seems nearly inertial, with deviations diÆcult to detect. In this s ...