How you can produce an electric current
... How you can produce an electric current – Electromagnetic Induction Most of our electricity comes from huge generators in power stations. There are smaller generators in cars (=______________________, picture on the right) and on some bicycles (= _____________, picture on the left). But how is this ...
... How you can produce an electric current – Electromagnetic Induction Most of our electricity comes from huge generators in power stations. There are smaller generators in cars (=______________________, picture on the right) and on some bicycles (= _____________, picture on the left). But how is this ...
Slide 1 - Cobb Learning
... What is an Electromagnet? When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire wrapped around a metal core, a very strong magnetic field is produced. This is called an electromagnet. The more coils wrapped around the core, the stronger the magnetic field that is produced. This stronger mag ...
... What is an Electromagnet? When an electric current is passed through a coil of wire wrapped around a metal core, a very strong magnetic field is produced. This is called an electromagnet. The more coils wrapped around the core, the stronger the magnetic field that is produced. This stronger mag ...
LECTURE 4 Announcements
... not touch, but are very close to each other, as shown. Indicate all the points where the net magnetic field is zero ...
... not touch, but are very close to each other, as shown. Indicate all the points where the net magnetic field is zero ...
Combustion Equation
... • A magnetic field is a region where magnetic materials and also wires carrying currents experience a force acting on them • They can be represented using field diagrams (arrows from North to South) • Strengths of a magnetic field can be increased using a magnetically “soft” iron core – these materi ...
... • A magnetic field is a region where magnetic materials and also wires carrying currents experience a force acting on them • They can be represented using field diagrams (arrows from North to South) • Strengths of a magnetic field can be increased using a magnetically “soft” iron core – these materi ...
Discussion 11
... Magnets & transformers A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. A method to detect a magnetic field is to scatter iron filings and observe their pattern. An electromagnet is a wire coil in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of an electric current. ...
... Magnets & transformers A magnet is a material or object that produces a magnetic field. A method to detect a magnetic field is to scatter iron filings and observe their pattern. An electromagnet is a wire coil in which the magnetic field is produced by the flow of an electric current. ...
Magnetism and Electromagnetism
... 6. Explain that magnets create magnetic fields. These cannot be seen. They fill the space around a magnet where the magnetic forces work, where they can attract or repel magnetic materials. ...
... 6. Explain that magnets create magnetic fields. These cannot be seen. They fill the space around a magnet where the magnetic forces work, where they can attract or repel magnetic materials. ...
electricity and magnet vocab
... open circuit - a circuit that has a break or opening; electric current cannot flow (the light will not turn on) series circuit – all the electrical charges flow in the same direction along the same path parallel circuit - electrical current flows through more than one path pigment - colored substanc ...
... open circuit - a circuit that has a break or opening; electric current cannot flow (the light will not turn on) series circuit – all the electrical charges flow in the same direction along the same path parallel circuit - electrical current flows through more than one path pigment - colored substanc ...
electric current
... Book 2, Chapter 3 Using Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide 1. A galvanometer uses the magnetic force from a current through a loop of wire in a circuit to measure? 2. A commutator is a device that reverses the current through a(n) 3. What is a coil of wire with a current called? 4. A turbine 5. W ...
... Book 2, Chapter 3 Using Electricity and Magnetism Study Guide 1. A galvanometer uses the magnetic force from a current through a loop of wire in a circuit to measure? 2. A commutator is a device that reverses the current through a(n) 3. What is a coil of wire with a current called? 4. A turbine 5. W ...
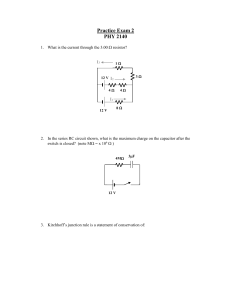
PHY 2140
... 10. An 8 turn coil encloses a triangular area with a height of 30 cm and base of 40 cm as shown. The coil lies in the plane of the page and carries a current of 6.00 A flowing clockwise around it. If the coil is in a uniform magnetic field of 2.00 x 10-4 T, directed towards the left of the page, wha ...
... 10. An 8 turn coil encloses a triangular area with a height of 30 cm and base of 40 cm as shown. The coil lies in the plane of the page and carries a current of 6.00 A flowing clockwise around it. If the coil is in a uniform magnetic field of 2.00 x 10-4 T, directed towards the left of the page, wha ...
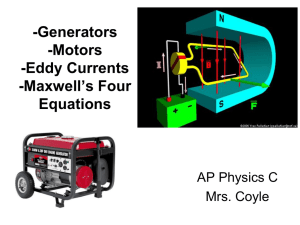
3 Generators, Motors, Eddy Currents, Maxwell`s Four Equations
... emax occurs when wt = 90o or 270o – This occurs when the magnetic field is in the plane of the coil and the time rate of change of flux is a maximum ...
... emax occurs when wt = 90o or 270o – This occurs when the magnetic field is in the plane of the coil and the time rate of change of flux is a maximum ...
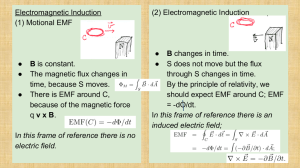
The Rules of Electromagnetism
... magnet (small motors) or by a current-carrying coil as above. The rotating assembly (known as the Armature) is supplied with current via the Commutator and the Brushes which make a sliding contact with the commutator. The purpose of the commutator is to reverse the armature current every half-revolu ...
... magnet (small motors) or by a current-carrying coil as above. The rotating assembly (known as the Armature) is supplied with current via the Commutator and the Brushes which make a sliding contact with the commutator. The purpose of the commutator is to reverse the armature current every half-revolu ...
Document
... In which is the dielectric constant of the material between the plates. For vacuum, the dielectric constant is 0 8.85x10-12 F/m ...
... In which is the dielectric constant of the material between the plates. For vacuum, the dielectric constant is 0 8.85x10-12 F/m ...
Magnetism - Howard Elementary School
... south on the outside of a magnet and south to north on the inside. Closer field lines mean stronger forces, further mean weaker. The strongest areas are near the poles. If a compass is brought near a magnet, it will align parallel with the magnetic field lines. Magnetic fields are produced by the mo ...
... south on the outside of a magnet and south to north on the inside. Closer field lines mean stronger forces, further mean weaker. The strongest areas are near the poles. If a compass is brought near a magnet, it will align parallel with the magnetic field lines. Magnetic fields are produced by the mo ...
Electromagnets
... itself. An electromagnet is a magnet made by placing a piece of iron or steel inside a coil of wire. As long as the coil carries a current, the metal acts as a magnet and iron coil increases the magnetic field of core the coil. But when the current is turned off, the magnetic domains in the metal be ...
... itself. An electromagnet is a magnet made by placing a piece of iron or steel inside a coil of wire. As long as the coil carries a current, the metal acts as a magnet and iron coil increases the magnetic field of core the coil. But when the current is turned off, the magnetic domains in the metal be ...