Lesson 5 Magnetism and Electricity Notes
... Has the same parts as a motor (power source, magnet, and wire loop attached to a shaft). ...
... Has the same parts as a motor (power source, magnet, and wire loop attached to a shaft). ...
Electromagnetic Induction
... Where F force on conductor (N), B = magnetic field strength (T), I = current in conductor (A) and L = length of conductor in magnetic field (m) A current flowing parallel to a magnetic field experiences no force. The formula has been generalised, noting that the force is zero when the angle is zero ...
... Where F force on conductor (N), B = magnetic field strength (T), I = current in conductor (A) and L = length of conductor in magnetic field (m) A current flowing parallel to a magnetic field experiences no force. The formula has been generalised, noting that the force is zero when the angle is zero ...
P3 Revision 2016 File
... accelerates towards the centre of the circle. This centripetal acceleration is because the objects velocity is changing because its direction is changing. P = pressure in Nm-2 or Ncm-2 or Pa Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. F is force in Newtons A is X sectional area in cm-2 or m-2 ...
... accelerates towards the centre of the circle. This centripetal acceleration is because the objects velocity is changing because its direction is changing. P = pressure in Nm-2 or Ncm-2 or Pa Acceleration is the rate of change of velocity. F is force in Newtons A is X sectional area in cm-2 or m-2 ...
HW8
... 3. A transformer is supplying power to a neon sign. These are special transformers called ballasts. The neon tube is basically an open circuit when we turn on the power. If we can apply a high voltage (~10 kV) the tube breaks down and we have approximately a short circuit and the gas glows. We have ...
... 3. A transformer is supplying power to a neon sign. These are special transformers called ballasts. The neon tube is basically an open circuit when we turn on the power. If we can apply a high voltage (~10 kV) the tube breaks down and we have approximately a short circuit and the gas glows. We have ...
Name_________________________________
... 12. If the gases of a space ship press down and the space ship flies up, which of Newton’s Laws best describes this scenario? _________________________________________________________________ 13. When electrons flow through a wire it is known as a(n) a. electric current b. magnetic field c. electric ...
... 12. If the gases of a space ship press down and the space ship flies up, which of Newton’s Laws best describes this scenario? _________________________________________________________________ 13. When electrons flow through a wire it is known as a(n) a. electric current b. magnetic field c. electric ...
4th grade Physical Science Part 2
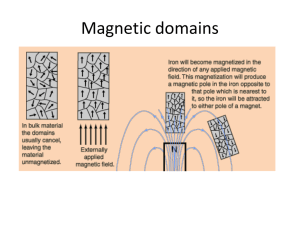
... magnets by using like poles to repel and the opposite poles to attract, making the ...
... magnets by using like poles to repel and the opposite poles to attract, making the ...
ELECTROMAGNETIC INDUCTION AND ALTERNATING CURRENT
... A wheel with 10 metallic spokes each 0.5 m long is rotated with a speed of 120 rev/min in a plane normal to the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field at a place. If BH = 0.4 G at the place .What is the induced emf between the axle and the rim of the wheel? 25. Two circular coils, one of ra ...
... A wheel with 10 metallic spokes each 0.5 m long is rotated with a speed of 120 rev/min in a plane normal to the horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field at a place. If BH = 0.4 G at the place .What is the induced emf between the axle and the rim of the wheel? 25. Two circular coils, one of ra ...
Advanced Analog Circuits
... • Time Constant (T): way to characterize time to charge/discharge a capacitor or inductor • 1*T: 63% of the maximum charge • 5*T: fully charged ...
... • Time Constant (T): way to characterize time to charge/discharge a capacitor or inductor • 1*T: 63% of the maximum charge • 5*T: fully charged ...
Solutions Manual
... Michael Faraday discovered that a voltage is induced in a length of electric wire moving in a magnetic field. The induced voltage may be increased by using a stronger magnetic field, increasing the velocity of the conductor, or increasing the effective length of the conductor. 15. Critical Thinking ...
... Michael Faraday discovered that a voltage is induced in a length of electric wire moving in a magnetic field. The induced voltage may be increased by using a stronger magnetic field, increasing the velocity of the conductor, or increasing the effective length of the conductor. 15. Critical Thinking ...
Practice Sheet #24
... _____ 5. In the region around a magnet in which magnetic forces act exists the a. magnetic field. c. pole. b. domain. d. solenoid. _____ 6. An electric fan has an electric motor inside to change a. mechanical energy into electrical energy. b. thermal energy into electrical energy. c. electrical ener ...
... _____ 5. In the region around a magnet in which magnetic forces act exists the a. magnetic field. c. pole. b. domain. d. solenoid. _____ 6. An electric fan has an electric motor inside to change a. mechanical energy into electrical energy. b. thermal energy into electrical energy. c. electrical ener ...
Energy_Impact on Global - Saint Leo University Faculty
... • 1820: Link discovered between electricity and magnetism establishing field of study called “electromagnetism” • An electric current creates a magnetic field ...
... • 1820: Link discovered between electricity and magnetism establishing field of study called “electromagnetism” • An electric current creates a magnetic field ...