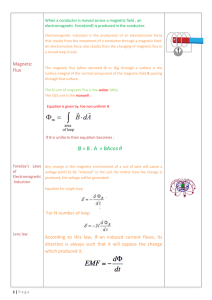
B . A = BA - RAJEEV Classes
... Emf induced in a straight conductor in uniform magnetic field When a straight conductor is moved through a magnetic field an e.m.f. is induced between its ends. This movement must be in such a direction that the conductor cuts through the lines of magnetic flux, and will be a maximum when it moves a ...
... Emf induced in a straight conductor in uniform magnetic field When a straight conductor is moved through a magnetic field an e.m.f. is induced between its ends. This movement must be in such a direction that the conductor cuts through the lines of magnetic flux, and will be a maximum when it moves a ...
8J Summary Sheet
... Pressure is the amount of force pushing on a certain area. For a certain area, the bigger the force, the bigger the pressure. For a certain force, the bigger the area, the smaller the pressure. In this picture, the thumb is putting a force onto the head of the pin. The force is transferred to the po ...
... Pressure is the amount of force pushing on a certain area. For a certain area, the bigger the force, the bigger the pressure. For a certain force, the bigger the area, the smaller the pressure. In this picture, the thumb is putting a force onto the head of the pin. The force is transferred to the po ...
R Ch 37 Electric Induction pg 1
... • Electromagnetic Waves have an magnetic half and an electric half that; • 1) move as a wave • 2) are at 90 degrees to each other • 3) they can move through a vacuum (space) ...
... • Electromagnetic Waves have an magnetic half and an electric half that; • 1) move as a wave • 2) are at 90 degrees to each other • 3) they can move through a vacuum (space) ...
Section Summary - Login for National High School Learn Center
... The magnetic field produced by a current has three distinct characteristics. The field can be turned on or off, have its direction reversed, or have its strength changed. To turn the magnetic field on or off, you simply turn the current on or off. To reverse the direction of the magnetic field, you ...
... The magnetic field produced by a current has three distinct characteristics. The field can be turned on or off, have its direction reversed, or have its strength changed. To turn the magnetic field on or off, you simply turn the current on or off. To reverse the direction of the magnetic field, you ...
☺ PLAN 1. Ampere’s law 2. Applications
... 2. Applications Require a high symmetry. ♣ Magnetic field due to i in a long straight wire — again. (Faster. No need to assume that the wire diameter is zero.) ♣ Magnetic field inside the wire. ♣ Solenoid. ♣ Toroid. ...
... 2. Applications Require a high symmetry. ♣ Magnetic field due to i in a long straight wire — again. (Faster. No need to assume that the wire diameter is zero.) ♣ Magnetic field inside the wire. ♣ Solenoid. ♣ Toroid. ...
Chapter 6 - Topic 11 - Electromagnetic induction – AHL.
... Essential idea: Generation and transmission of alternating current (ac) electricity has transformed the world. 11.2 – Power generation and transmission Nature of science 3.5 Bias: In the late 19th century Edison was a proponent of direct current electrical energy transmission while Westinghouse and ...
... Essential idea: Generation and transmission of alternating current (ac) electricity has transformed the world. 11.2 – Power generation and transmission Nature of science 3.5 Bias: In the late 19th century Edison was a proponent of direct current electrical energy transmission while Westinghouse and ...
Magnetism
... is, it changes directions—but in the outer circuit it travels in only one direction, and drops to zero twice with each rotation of the loop. By arranging more loops, a steadier direct current can be obtained. Source: "direct-current motor: electric current alternation." Online . Britannica Student E ...
... is, it changes directions—but in the outer circuit it travels in only one direction, and drops to zero twice with each rotation of the loop. By arranging more loops, a steadier direct current can be obtained. Source: "direct-current motor: electric current alternation." Online . Britannica Student E ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
III. Producing Electric Current
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
... D. Transformer Transformer increases or decreases AC voltage primary coil AC produces a magnetic field that ...
Year 8 Physics ‐ Magnets
... o increasing the number of turns of wire around the coil o winding the coil around a core made from iron ...
... o increasing the number of turns of wire around the coil o winding the coil around a core made from iron ...