Russell Diagram
... A binary star system consists of one star that is twice as massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
... A binary star system consists of one star that is twice as massive as the other. They are 2.0 AU apart and have an orbit period of 0.50 y. What is the mass of the smaller star in terms of solar masses? ...
- Stevenson High School
... The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the stars to rise and set each evening. In addition, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun places different regions of the sky in our nighttime view. A chart of the night sky will map the locations of the stars; a star wheel will let us know which stars w ...
... The rotation of the Earth on its axis causes the stars to rise and set each evening. In addition, the orbit of the Earth around the Sun places different regions of the sky in our nighttime view. A chart of the night sky will map the locations of the stars; a star wheel will let us know which stars w ...
1. Luminosity is another word for the vocabulary word ______. 2. If
... 1. Luminosity is another word for the vocabulary word _________. 2. If two stars are different colors, we can infer that they have different a. chemical compositions c. shapes b. masses d. temperature 3. Which magnitude is brightest? a. -2 c. 4 b. -4 4. The dimmest class of star is the a. O ...
... 1. Luminosity is another word for the vocabulary word _________. 2. If two stars are different colors, we can infer that they have different a. chemical compositions c. shapes b. masses d. temperature 3. Which magnitude is brightest? a. -2 c. 4 b. -4 4. The dimmest class of star is the a. O ...
Lucas - WordPress.com
... lived storm 23 times the size of the Earth. The 4 large Galilean satellites and at least 63 smaller moons orbit Jupiter. ...
... lived storm 23 times the size of the Earth. The 4 large Galilean satellites and at least 63 smaller moons orbit Jupiter. ...
Stars - TeacherWeb
... together by gravity and is composed of gas and emits light. • A star is born when the gases inside a nebula contract together. Inside the nebula you will find new starts. ...
... together by gravity and is composed of gas and emits light. • A star is born when the gases inside a nebula contract together. Inside the nebula you will find new starts. ...
galaxies and stars - Valhalla High School
... faster it is moving. • It takes 2 million years for light from the Andromeda galaxy to reach earth. • Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. ...
... faster it is moving. • It takes 2 million years for light from the Andromeda galaxy to reach earth. • Astronomers have classified most galaxies into three main categories: spiral, elliptical and irregular. ...
Powerpoint Presentation (large file)
... 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a “first-magnitude” or “second magnitude” star? 4. Why are some stars red and others blue? 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. W ...
... 1. How far away are the stars? 2. What evidence do astronomers have that the Sun is a typical star? 3. What is meant by a “first-magnitude” or “second magnitude” star? 4. Why are some stars red and others blue? 5. What are the stars made of? 6. As stars go, is our Sun especially large or small? 7. W ...
Kinds of Stars
... size. Include blue-white RIGEL, Whiteyellow CANOPUS, red SuperGiants ANTARES & BETELGUESE. REDSUPERGIANTS- Largest of all stars ...
... size. Include blue-white RIGEL, Whiteyellow CANOPUS, red SuperGiants ANTARES & BETELGUESE. REDSUPERGIANTS- Largest of all stars ...
Loving The Universe
... We see evidence from every direction that the universe is all of a piece and that it began as a single seed smaller than an atom. And in a very real sense, you and I were there. Every scrap of matter and energy in our blood and bones, and in the synapses of our thoughts can trace its lineage back t ...
... We see evidence from every direction that the universe is all of a piece and that it began as a single seed smaller than an atom. And in a very real sense, you and I were there. Every scrap of matter and energy in our blood and bones, and in the synapses of our thoughts can trace its lineage back t ...
Notes on Precession in Astronomy
... Celestial Pole, appears to be stationary while other stars appear to rotate around it as the Earth turns daily on its axis [see Star Trail photograph.] However, the specific star that is the North Star varies over time because of the Earth's Precession. Precession was first discovered by the Greek a ...
... Celestial Pole, appears to be stationary while other stars appear to rotate around it as the Earth turns daily on its axis [see Star Trail photograph.] However, the specific star that is the North Star varies over time because of the Earth's Precession. Precession was first discovered by the Greek a ...
What is a Scientist? - Cockeysville Middle School
... 2. Title a new page “Characteristics of Stars”. 3. Create a list of at least 6 characteristics. ESS-5B ...
... 2. Title a new page “Characteristics of Stars”. 3. Create a list of at least 6 characteristics. ESS-5B ...
Microsoft Power Point version
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
... But the Universe is 1.37 x 1010 yr old! Every M dwarf that was ever created is still on the main sequence!! ...
Monday, April 15
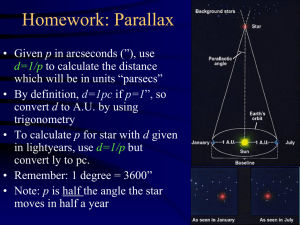
... which will be in units “parsecs” • By definition, d=1pc if p=1”, so convert d to A.U. by using trigonometry • To calculate p for star with d given in lightyears, use d=1/p but convert ly to pc. • Remember: 1 degree = 3600” • Note: p is half the angle the star moves in half a year ...
... which will be in units “parsecs” • By definition, d=1pc if p=1”, so convert d to A.U. by using trigonometry • To calculate p for star with d given in lightyears, use d=1/p but convert ly to pc. • Remember: 1 degree = 3600” • Note: p is half the angle the star moves in half a year ...
and Concept Self-test (1,2,3,5,6,7,8,9)
... one arc second as the Earth moves 2 AU’s from one side of the Sun to the other. A parsec is 3.26 light years long. 3. Two ways in which a star’s real motion translates into motion observable from Earth are Transverse (sideways motion) and Radial (toward or away) which allow us to determine actual ...
... one arc second as the Earth moves 2 AU’s from one side of the Sun to the other. A parsec is 3.26 light years long. 3. Two ways in which a star’s real motion translates into motion observable from Earth are Transverse (sideways motion) and Radial (toward or away) which allow us to determine actual ...
PowerPoint - Chandra X
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
... The young Sun-like stars in Orion produce violent X-ray outbursts, or flares, that are much more frequent and energetic than anything seen today from our Sun. The range of flare energies is large, with some of the stars producing flares that are a hundred times larger than others. The different flar ...
Answers to Science Semester 1Review Possible hazards in the lab
... mains sequence, red giant, white dwarf. 38. Our sun is in the adulthood stage of its life. The sun still has at least five billion more years left in this stage, 39. Stars are classified into classes based on their temperature. 40. Classes from coolest to hottest are: M K G F A B O. 41. Absolute mag ...
... mains sequence, red giant, white dwarf. 38. Our sun is in the adulthood stage of its life. The sun still has at least five billion more years left in this stage, 39. Stars are classified into classes based on their temperature. 40. Classes from coolest to hottest are: M K G F A B O. 41. Absolute mag ...
solar system formation and gal
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
... What happens to the Nebula? • Over time it flattens into a disc-like shape while spinning in one direction • Astronomers theorize that any planets forming during this phase would form in the same flat plane and would rotate and revolve around the star in the same way • Using technology, astronomers ...
Astronomy 162 Lab 4: Stars
... Magnitude on the y-axis. From this diagram, astronomers can study the relationship between temperature and brightness. This relationship leads to some important observations. Firstly, the diagram is divided into three groups: Giants and Super Giants at the top, a long line of Main Sequence stars in ...
... Magnitude on the y-axis. From this diagram, astronomers can study the relationship between temperature and brightness. This relationship leads to some important observations. Firstly, the diagram is divided into three groups: Giants and Super Giants at the top, a long line of Main Sequence stars in ...
The Danger of Deadly Cosmic Explosions
... radiation • Penetrates underground and underseas. • Equivalent to 1 kiloton TNT / km2 over earth surface • Kills everything exposed. • Destroys atmosphere, brings on nuclear winter. ...
... radiation • Penetrates underground and underseas. • Equivalent to 1 kiloton TNT / km2 over earth surface • Kills everything exposed. • Destroys atmosphere, brings on nuclear winter. ...
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best
... A) The rotation dissipates and any residual is left in small overall rotation of the star. B) The rotation rate remains the same and results in stellar rotation. C) The rotation rate increases and results in fast rotation of the star. D) The rotation rate increases and results in a disk of material ...
... A) The rotation dissipates and any residual is left in small overall rotation of the star. B) The rotation rate remains the same and results in stellar rotation. C) The rotation rate increases and results in fast rotation of the star. D) The rotation rate increases and results in a disk of material ...
c - Fsusd
... 25) According to Hubble’s law, the farther away a galaxy is, ______. a) the slower it is moving away from Earth b) the sooner it will stop moving c) the faster it is moving away from Earth ...
... 25) According to Hubble’s law, the farther away a galaxy is, ______. a) the slower it is moving away from Earth b) the sooner it will stop moving c) the faster it is moving away from Earth ...
Lecture 13 - Main Sequence Stars
... stars on the main sequence, but the chemical composition of stars change with time as the star burns hydrogen into helium. • This causes the other properties to change with time and we can track these changes via motion of the star in the HR diagram. ...
... stars on the main sequence, but the chemical composition of stars change with time as the star burns hydrogen into helium. • This causes the other properties to change with time and we can track these changes via motion of the star in the HR diagram. ...
Astronomical Ideas Fall 2012 Homework 4 Solutions 1. Two stars
... massive stars that still burn H on the main sequence is a clock, because we know that the cluster needs to be old enough so that all of the more massive stars have already burned up all of their Hydrogen and left the main sequence. ...
... massive stars that still burn H on the main sequence is a clock, because we know that the cluster needs to be old enough so that all of the more massive stars have already burned up all of their Hydrogen and left the main sequence. ...
Lyra

Lyra (/ˈlaɪərə/; Latin for lyre, from Greek λύρα) is a small constellation. It is one of 48 listed by the 2nd century astronomer Ptolemy, and is one of the 88 constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union. Lyra was often represented on star maps as a vulture or an eagle carrying a lyre, and hence sometimes referred to as Aquila Cadens or Vultur Cadens. Beginning at the north, Lyra is bordered by Draco, Hercules, Vulpecula, and Cygnus. Lyra is visible from the northern hemisphere from spring through autumn, and nearly overhead, in temperate latitudes, during the summer months. From the southern hemisphere, it is visible low in the northern sky during the winter months.The lucida or brightest star—and one of the brightest stars in the sky—is the white main sequence star Vega, a corner of the Summer Triangle. Beta Lyrae is the prototype of a class of stars known as Beta Lyrae variables, binary stars so close to each other that they become egg-shaped and material flows from one to the other. Epsilon Lyrae, known informally as the Double Double, is a complex multiple star system. Lyra also hosts the Ring Nebula, the second-discovered and best-known planetary nebula.