A Collection of Curricula for the STARLAB Deep Sky Objects
... Nebulae absorb light from nearby stars and radiate it back into space. Most nebulae glow red, the color of hydrogen gas. The brightest nebula is the Orion Nebula (see slide #60) which can be seen with the unaided eye in a dark sky. Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to ...
... Nebulae absorb light from nearby stars and radiate it back into space. Most nebulae glow red, the color of hydrogen gas. The brightest nebula is the Orion Nebula (see slide #60) which can be seen with the unaided eye in a dark sky. Nebulae are very important in astronomy because they are the key to ...
RS Oph
... RS Oph is the second brightest member of a rare class of cataclysmic variable star known as recurrent novae (Nr). These stars are novae where more than one outburst has been observed and appear to be intermediate in class between the classical novae (single major outburst) and dwarf novae (frequent ...
... RS Oph is the second brightest member of a rare class of cataclysmic variable star known as recurrent novae (Nr). These stars are novae where more than one outburst has been observed and appear to be intermediate in class between the classical novae (single major outburst) and dwarf novae (frequent ...
http://hcs.harvard.edu/~jus/0302/bester.pdf
... to establish a scaling factor between them. Fortunately, as a general rule background stars move very little, usually less than one arc second per century. Over 52 years this corresponds to a motion of only 0.13 mm on the 1941 image, which is actually smaller than our measurement error of ±0.2 mm. T ...
... to establish a scaling factor between them. Fortunately, as a general rule background stars move very little, usually less than one arc second per century. Over 52 years this corresponds to a motion of only 0.13 mm on the 1941 image, which is actually smaller than our measurement error of ±0.2 mm. T ...
Binarity in carbon-enhanced metal-poor stars
... radial velocity standards is strengthened by a clear observed trend of the radial velocity standards’ offsets with their literature values versus the observation date. The total magnitude of this variation over the full observing period is 2.7 km s−1 with small scatter. We are uncertain about its or ...
... radial velocity standards is strengthened by a clear observed trend of the radial velocity standards’ offsets with their literature values versus the observation date. The total magnitude of this variation over the full observing period is 2.7 km s−1 with small scatter. We are uncertain about its or ...
Game - Mr McIvor
... Earth and Space for $500 This is a network of artificial satellites revolving around the Earth that send out continous location and time signals which are used as a ...
... Earth and Space for $500 This is a network of artificial satellites revolving around the Earth that send out continous location and time signals which are used as a ...
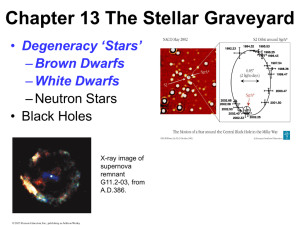
Chapter 13 The Stellar Graveyard
... We do not know exactly how, but if there are charged particles trapped by the strong magnetic field of the neutron stars near the magnetic poles, the strong magnetic field directs the radiation field along the magnetic axis of the neutron stars. • If the axis of the magnetic dipole is not aligned wi ...
... We do not know exactly how, but if there are charged particles trapped by the strong magnetic field of the neutron stars near the magnetic poles, the strong magnetic field directs the radiation field along the magnetic axis of the neutron stars. • If the axis of the magnetic dipole is not aligned wi ...
The Halo of the Milky Way
... We show that the star counts in the spheroid of the Milky Way are not symmetric about the l = 0◦ , l = 180◦ plane. The minimum counts are found towards l = 155◦ . The Galactic longitude of maximum star counts depends on the magnitude and color selection of the halo stars. We interpret this as eviden ...
... We show that the star counts in the spheroid of the Milky Way are not symmetric about the l = 0◦ , l = 180◦ plane. The minimum counts are found towards l = 155◦ . The Galactic longitude of maximum star counts depends on the magnitude and color selection of the halo stars. We interpret this as eviden ...
Star Formation in Our Galaxy - Wiley-VCH
... darker patches indicate giant molecular clouds. Also shown, according to their relative brightness, are the more prominent stars, along with principle constellations. ...
... darker patches indicate giant molecular clouds. Also shown, according to their relative brightness, are the more prominent stars, along with principle constellations. ...
GRADE 12A: Physics 7
... non-SI units for astronomical distances. Point out that parallax measurements can only be used for relatively nearby stars (closer than about 100 pc). For more distant stars, less direct methods must be used. Explain how the HR diagram can be used in the following ways to estimate distances of stars ...
... non-SI units for astronomical distances. Point out that parallax measurements can only be used for relatively nearby stars (closer than about 100 pc). For more distant stars, less direct methods must be used. Explain how the HR diagram can be used in the following ways to estimate distances of stars ...
3.7 Isotope Effect - Institute for Astronomy | ETH
... transparent only in the optical, in selected windows in the near infrared and in a broad radio wavelength region. Most of the infrared light reaching us from space is absorbed by molecular bands due to water vapor and carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Radiation with shorter wavelengths than ...
... transparent only in the optical, in selected windows in the near infrared and in a broad radio wavelength region. Most of the infrared light reaching us from space is absorbed by molecular bands due to water vapor and carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. Radiation with shorter wavelengths than ...
S T A R S
... What is the distance from the earth ? There are different ways of measuring interstellar distances. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. In light years, Alpha Centuri is 4.2 light years away. The speed of light is about 3 x 10 to the 8th power m/s or 186 000 miles per second. ...
... What is the distance from the earth ? There are different ways of measuring interstellar distances. A light year is the distance that light travels in one year. In light years, Alpha Centuri is 4.2 light years away. The speed of light is about 3 x 10 to the 8th power m/s or 186 000 miles per second. ...
March 2016 BRAS Addendum Newsletter
... space experiment to test and work out the procedures to observe lower frequency gravitational waves (lower than the waves detected by LIGO) emitted by different astronomical sources, such as the merging of super-massive black holes at the center of large galaxies. LISA Pathfinder has started its sci ...
... space experiment to test and work out the procedures to observe lower frequency gravitational waves (lower than the waves detected by LIGO) emitted by different astronomical sources, such as the merging of super-massive black holes at the center of large galaxies. LISA Pathfinder has started its sci ...
ISP205L Spring 2006 Supplementary Instructions for SkyGazer Homework Assignments
... Part 1. It will help if you click "control/define horizon", then select "Translucent" and "Show Cardinal Points". Set the time step to 10 min and change time in single steps until Venus rises. Part 2. In addition to following the instructions in the book, go to the Planet Panel and select the Sun, s ...
... Part 1. It will help if you click "control/define horizon", then select "Translucent" and "Show Cardinal Points". Set the time step to 10 min and change time in single steps until Venus rises. Part 2. In addition to following the instructions in the book, go to the Planet Panel and select the Sun, s ...
Lab #10 (Apr 10-13)
... the sky over time, and so there was some hope we could use parallax to determine how far away the stars are. Sirius is the brightest star in the sky, and astronomers (correctly) deduced that one reason for its brightness is that it is closer to the Earth than most other stars.! ...
... the sky over time, and so there was some hope we could use parallax to determine how far away the stars are. Sirius is the brightest star in the sky, and astronomers (correctly) deduced that one reason for its brightness is that it is closer to the Earth than most other stars.! ...
Abstract - chara - Georgia State University
... The hunt for low mass companions is an extremely active area of observational astronomy today. The search includes low mass stars, brown dwarfs and planets, both jovian and terrestrial. Low mass stars and brown dwarfs are very cool and faint and are therefore very hard to detect. Large scale infrar ...
... The hunt for low mass companions is an extremely active area of observational astronomy today. The search includes low mass stars, brown dwarfs and planets, both jovian and terrestrial. Low mass stars and brown dwarfs are very cool and faint and are therefore very hard to detect. Large scale infrar ...
Slides from Dr. Frank`s Lecture17
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
... 1) The binary separation decreases because of gravitational radiation and other angular momentum losses. 2) The component stars will evolve and change size (for example becoming a red giant) Conclusion: Long period (wide) binaries may never become interacting while short period (close) binaries are ...
Wide Eye Debris telescope allows to catalogue objects in any orbital
... scopes are a key for the implementation of a dynamic fence concept. The dynamic concept is based on the fact that the quick motion telescope cyclically scrolls the strip of sky of main interest in order to intercept all the particles going through it with the orbital parameters compatible for the ty ...
... scopes are a key for the implementation of a dynamic fence concept. The dynamic concept is based on the fact that the quick motion telescope cyclically scrolls the strip of sky of main interest in order to intercept all the particles going through it with the orbital parameters compatible for the ty ...
Power Point Presentation
... Burning rate is higher for more massive stars - hence their lifetimes on the main sequence are much shorter and they are rather rare Red dwarf stars are the most common as they burn hydrogen slowly and live the longest Often called dwarfs (but not the same as White Dwarfs) because they are smaller t ...
... Burning rate is higher for more massive stars - hence their lifetimes on the main sequence are much shorter and they are rather rare Red dwarf stars are the most common as they burn hydrogen slowly and live the longest Often called dwarfs (but not the same as White Dwarfs) because they are smaller t ...
Lecture 9
... Evolution of 4M☉ Stars For stars less than 6M☉ these last slides describe the evolution pretty well. There are some differences in the details that depend on the initial main-sequence mass. For stars that start with 4M☉, it gets hot enough in the cores to (1) avoid the helium flash and (2) to st ...
... Evolution of 4M☉ Stars For stars less than 6M☉ these last slides describe the evolution pretty well. There are some differences in the details that depend on the initial main-sequence mass. For stars that start with 4M☉, it gets hot enough in the cores to (1) avoid the helium flash and (2) to st ...
Cepheids in M100 - Indiana University Astronomy
... Compare the size of M100 to its distance (M100 is similar in size to our own Milky Way, with a diameter of about 30,000 parsecs). Could the variation in distance result from the difference in location of the Cepheid variables within M100? ...
... Compare the size of M100 to its distance (M100 is similar in size to our own Milky Way, with a diameter of about 30,000 parsecs). Could the variation in distance result from the difference in location of the Cepheid variables within M100? ...
Article “What Astronomers Do” (appendix C) one per student
... these lines, he catalogued about 600 of them [Freedman, Kaufmann, 2002], introducing in the process an alphabetical classification system that is still sometimes used. Later, Fraunhofer made pioneering observations of some of the brighter stars, which became a puzzle to him because of the significan ...
... these lines, he catalogued about 600 of them [Freedman, Kaufmann, 2002], introducing in the process an alphabetical classification system that is still sometimes used. Later, Fraunhofer made pioneering observations of some of the brighter stars, which became a puzzle to him because of the significan ...
Collaborations with East Asian VLBI stations
... KVN participation provides shorter and denser UV > better image China participation expands east-west baseline > better astrometry ...
... KVN participation provides shorter and denser UV > better image China participation expands east-west baseline > better astrometry ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.