January
... distance, astronomers can compare the cluster CM diagram against the standard CM diagram and determine distance. Distances within our galaxy and into some of the nearby galaxies can be measured using this technique. Astronomers then use Cepheid Variables (named after delta Cephei) to measure distanc ...
... distance, astronomers can compare the cluster CM diagram against the standard CM diagram and determine distance. Distances within our galaxy and into some of the nearby galaxies can be measured using this technique. Astronomers then use Cepheid Variables (named after delta Cephei) to measure distanc ...
Lifecycle of Dust in Galaxies - The National Academies of Sciences
... The measurement of the dust being consumed in the formation of new stars can be measured by studying young stellar objects (YSOs) and HII regions. The Spitzer SAGE surveys are sensitive to YSOs more massive than a few solar masses and, effectively, all of the HII regions. For the LMC, the view of st ...
... The measurement of the dust being consumed in the formation of new stars can be measured by studying young stellar objects (YSOs) and HII regions. The Spitzer SAGE surveys are sensitive to YSOs more massive than a few solar masses and, effectively, all of the HII regions. For the LMC, the view of st ...
ASTR 1101-001 Spring 2008 - Louisiana State University
... – A white dwarf, if the MS star is moderately low-mass; – A neutron star, if the MS star is high-mass ...
... – A white dwarf, if the MS star is moderately low-mass; – A neutron star, if the MS star is high-mass ...
Can TMT Image Habitable Planets ?
... BUT: conventional instrument development process is slow compared to the pace of science in technology progress in our field → Schedule for (near-)first light instrument on ELT is very challenging… still lots of work to be done → We are exploring, and advocating for a fast path from 8-m telescope to ...
... BUT: conventional instrument development process is slow compared to the pace of science in technology progress in our field → Schedule for (near-)first light instrument on ELT is very challenging… still lots of work to be done → We are exploring, and advocating for a fast path from 8-m telescope to ...
The Star Finder Book - Starpath School of Navigation
... combinations. Navigators soon learn the value of the moon, Venus, or Jupiter for combination with star sights, since these three bodies can be seen during the brighter part of twilight when stars are faint but the horizon is still sharp. We also demonstrate how the Star Finder can be used to answer ...
... combinations. Navigators soon learn the value of the moon, Venus, or Jupiter for combination with star sights, since these three bodies can be seen during the brighter part of twilight when stars are faint but the horizon is still sharp. We also demonstrate how the Star Finder can be used to answer ...
QUINN_2004 - Armagh Observatory
... become egg shaped. This means that the star is brightest when the viewed side on, I.e. when more of the star is is view. ...
... become egg shaped. This means that the star is brightest when the viewed side on, I.e. when more of the star is is view. ...
Ay 112 Midterm review
... solutions. When 2 stars orbit each other they follow Kepler’s laws. The orbits are ellipses with the center of mass located at a common focal point for the two ellipses. The product of mass times ...
... solutions. When 2 stars orbit each other they follow Kepler’s laws. The orbits are ellipses with the center of mass located at a common focal point for the two ellipses. The product of mass times ...
Visual Photometry - El Camino College
... The magnitude system Purpose: This lab is designed to familiarize you with the magnitude system of star brightness and to help you learn how to make simple measurements by direct comparison/calibration. When performing this lab for the 2nd time, using a telescope, we will also learn about a current ...
... The magnitude system Purpose: This lab is designed to familiarize you with the magnitude system of star brightness and to help you learn how to make simple measurements by direct comparison/calibration. When performing this lab for the 2nd time, using a telescope, we will also learn about a current ...
1.3 Lifecycle of stars
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a su ...
... A star of more than 8 solar masses can fuse elements far beyond carbon in its core, leading to a very different fate. Its path across the H-R diagram is essentially a straight line—it stays at just about the same luminosity as it cools off. Eventually the star dies in a violent explosion called a su ...
It`s cosmic! - NSW Department of Education
... You have just completed a life cycle that shows how an averagesized star dies. It slowly fades away and becomes a black dwarf. Large stars, that have much more mass than our Sun, die in a very spectacular way. They blow apart in a gigantic explosion. The explosion forms a supernova. A supernova can ...
... You have just completed a life cycle that shows how an averagesized star dies. It slowly fades away and becomes a black dwarf. Large stars, that have much more mass than our Sun, die in a very spectacular way. They blow apart in a gigantic explosion. The explosion forms a supernova. A supernova can ...
NuSeti-2015 - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... escapes. The expansion stops and star contracts due to gravity. And the process repeats. ...
... escapes. The expansion stops and star contracts due to gravity. And the process repeats. ...
aaswinter06
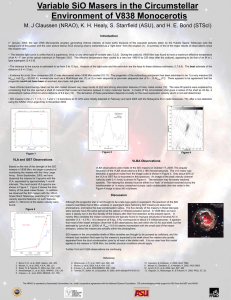
... In January 2002, the star V838 Monocerotis erupted, generating intense interest, at least partly because of the exquisite pictures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see the background of this poster and the color picture below) ACS showing what is interpreted as a “light echo” from the eruption ( ...
... In January 2002, the star V838 Monocerotis erupted, generating intense interest, at least partly because of the exquisite pictures taken by the Hubble Space Telescope (see the background of this poster and the color picture below) ACS showing what is interpreted as a “light echo” from the eruption ( ...
TWO DIFFERENT ALTITUDES
... 22. The wandering point on the Earth's surface that all magnetic compasses point towards is the ______________________. 23. Depending on the location of an observer on the earth's surface, the North Pole can be several degrees away from the ________________. 24. The __________________ is currently i ...
... 22. The wandering point on the Earth's surface that all magnetic compasses point towards is the ______________________. 23. Depending on the location of an observer on the earth's surface, the North Pole can be several degrees away from the ________________. 24. The __________________ is currently i ...
Killer Skies
... weight, a star must fuse oxygen much faster than it fused hydrogen. Hydrogen fusion can last 7 million years in a 25solar-mass star. The same star will fuse its oxygen in 6 months and its silicon in just one day. ...
... weight, a star must fuse oxygen much faster than it fused hydrogen. Hydrogen fusion can last 7 million years in a 25solar-mass star. The same star will fuse its oxygen in 6 months and its silicon in just one day. ...
Today in Astronomy 142
... Beyond the Chandrasekhar mass: neutron stars ! The maximum mass calculation involves general relativity and an equation of state that includes the strong interaction. The maximum mass is about 2.2 M⊙; it could not possibly be > 3 M⊙. ! Neutron stars generally have very large magnetic fields (conser ...
... Beyond the Chandrasekhar mass: neutron stars ! The maximum mass calculation involves general relativity and an equation of state that includes the strong interaction. The maximum mass is about 2.2 M⊙; it could not possibly be > 3 M⊙. ! Neutron stars generally have very large magnetic fields (conser ...
6 The mysterious universe
... ever before. Observations using telescopes showed that many different types of objects in the sky could be identified. These included single or double stars, groups of stars called galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. In 1718, English astronomer Edmond Halley, w ...
... ever before. Observations using telescopes showed that many different types of objects in the sky could be identified. These included single or double stars, groups of stars called galaxies, clusters of galaxies, and clouds of gas and dust called nebulae. In 1718, English astronomer Edmond Halley, w ...
18th Cambridge Workshop on Cool Stars, Stellar Systems, and the... Proceedings of Lowell Observatory (9-13 June 2014)
... correlate – at least to some extent – with stellar parameters such as rotation, mass and age. We are however not yet able to completely describe these relations quantitatively under the form of scaling laws. Addressing the topic of spaceweather therefore requires a twofold effort: on the one hand co ...
... correlate – at least to some extent – with stellar parameters such as rotation, mass and age. We are however not yet able to completely describe these relations quantitatively under the form of scaling laws. Addressing the topic of spaceweather therefore requires a twofold effort: on the one hand co ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.