M81/M82/NGC3077
... (CBR value: 48 km/sec) M82 — 202 km/sec (3.9 ± 0.3 Mpc) (CBR value: 296 km/sec) M81 is closer and approaching, while M82 is farther away and receding; ...
... (CBR value: 48 km/sec) M82 — 202 km/sec (3.9 ± 0.3 Mpc) (CBR value: 296 km/sec) M81 is closer and approaching, while M82 is farther away and receding; ...
ATLAS lifts the Cup: discovery of a new Milky Way satellite in Crater⋆†
... Draco, Fornax and Leo II have a property in common: a substantial RHB, pushing the peak of the RC/RHB region faintwards. This is to be compared with LGS 3 which exhibits a noticeable stump of BL stars extending from RC/RHB to brighter magnitudes at bluer V − I. As a result, in LGS 3 the RC/RHB LF pe ...
... Draco, Fornax and Leo II have a property in common: a substantial RHB, pushing the peak of the RC/RHB region faintwards. This is to be compared with LGS 3 which exhibits a noticeable stump of BL stars extending from RC/RHB to brighter magnitudes at bluer V − I. As a result, in LGS 3 the RC/RHB LF pe ...
Article PDF - IOPscience
... magnitudes of the objects detected in each image. The photometric measurements were performed using PSFs employing the “weighted PSF fitting mode,” which places more weight on the central part of the star profile and less on the outer pixels. The photometric procedure automatically applies aperture ...
... magnitudes of the objects detected in each image. The photometric measurements were performed using PSFs employing the “weighted PSF fitting mode,” which places more weight on the central part of the star profile and less on the outer pixels. The photometric procedure automatically applies aperture ...
AST1100 Lecture Notes
... the higher the luminosity and the higher the surface temperature. So the more massive stars settles on the left side of the main sequence whereas the less massive stars settles on the right side of the main sequence. Stars spend the largest part of their lives on the main sequence. During the time o ...
... the higher the luminosity and the higher the surface temperature. So the more massive stars settles on the left side of the main sequence whereas the less massive stars settles on the right side of the main sequence. Stars spend the largest part of their lives on the main sequence. During the time o ...
Summary: Star Formation Near and Far
... than is any evidence for continuing gas infall, and for some years they seemed to contradict the theoretical models in this respect. Now it is clear that infall, outflow, and rotation are all present simultaneously in many cases, and that continuing infall effects can indeed be seen when one looks h ...
... than is any evidence for continuing gas infall, and for some years they seemed to contradict the theoretical models in this respect. Now it is clear that infall, outflow, and rotation are all present simultaneously in many cases, and that continuing infall effects can indeed be seen when one looks h ...
Preparing astronomical observations and observing with OHP facilities
... the spot would be given by the diffraction image of the telescope’s aperture (in visible light, roughly 14 arcseconds divided by the aperture in cm, wich means an image of 0.15 arcsecond for 1 m-class telescopes). Because of air movements, the image never reaches this accuracy. The seeing at OHP is l ...
... the spot would be given by the diffraction image of the telescope’s aperture (in visible light, roughly 14 arcseconds divided by the aperture in cm, wich means an image of 0.15 arcsecond for 1 m-class telescopes). Because of air movements, the image never reaches this accuracy. The seeing at OHP is l ...
The Milky Way
... 5. What fundamental principle did Shapley use to calibrate the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variable stars? a. Light intensity falls off with the inverse square of distance. b. Stars that appear brighter are on average closer to Earth. c. Large pulsating objects have longer periods tha ...
... 5. What fundamental principle did Shapley use to calibrate the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variable stars? a. Light intensity falls off with the inverse square of distance. b. Stars that appear brighter are on average closer to Earth. c. Large pulsating objects have longer periods tha ...
Far Ultraviolet Spectroscopic Explorer
... Collectively, SNRs can affect star formation and galactic evolution processes. Some massive star SNe appear to be related to Gamma Ray Bursts. Hubble Space Telescope has played a key role in understanding these objects. ...
... Collectively, SNRs can affect star formation and galactic evolution processes. Some massive star SNe appear to be related to Gamma Ray Bursts. Hubble Space Telescope has played a key role in understanding these objects. ...
s-process
... -2.1, when low-mass AGB stars begin to contribute from double shell burning. The s-process then dominates Ba production. The origin of heavy metals at the lowest Galactic metallicity ([Fe/H] = -4) is still not understood, but may be dominated by the weak s-process, or by a separate r-process in mass ...
... -2.1, when low-mass AGB stars begin to contribute from double shell burning. The s-process then dominates Ba production. The origin of heavy metals at the lowest Galactic metallicity ([Fe/H] = -4) is still not understood, but may be dominated by the weak s-process, or by a separate r-process in mass ...
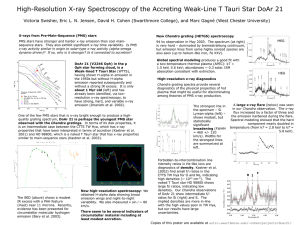
DoAr21_AAS2005 - Astronomy at Swarthmore College
... One of the few PMS stars that is x-ray bright enough to produce a highquality grating spectrum, DoAr 21 is perhaps the youngest PMS star observed with the Chandra gratings. In terms of its disk properties, it is an intermediate case between the CTTS TW Hya, which has x-ray properties that have been ...
... One of the few PMS stars that is x-ray bright enough to produce a highquality grating spectrum, DoAr 21 is perhaps the youngest PMS star observed with the Chandra gratings. In terms of its disk properties, it is an intermediate case between the CTTS TW Hya, which has x-ray properties that have been ...
ASTRONOMY AND ASTROPHYSICS Barium abundances in cool
... down to -2.60 plus two G-type metal-poor subgiants. Procyon is added as a reference star with its fundamental parameters well known from direct methods. Ba and Fe abundances are determined differentially with respect to the Sun which means that oscillator strengths f ij and van der Waals damping con ...
... down to -2.60 plus two G-type metal-poor subgiants. Procyon is added as a reference star with its fundamental parameters well known from direct methods. Ba and Fe abundances are determined differentially with respect to the Sun which means that oscillator strengths f ij and van der Waals damping con ...
First firm spectral classification of an early-B PMS star
... Evidence of accretion must come from the detection of circumstellar disks and bipolar jets, as observed around forming low-mass stars (e.g., Appenzeller & Mundt 1989). Disks and outflows around massive YSO candidates are being reported (Chini et al. 2004; Kraus et al. 2010; Chapter 3) but the physic ...
... Evidence of accretion must come from the detection of circumstellar disks and bipolar jets, as observed around forming low-mass stars (e.g., Appenzeller & Mundt 1989). Disks and outflows around massive YSO candidates are being reported (Chini et al. 2004; Kraus et al. 2010; Chapter 3) but the physic ...
The Sun
... – A binary star is two stars that are gravitationally bound together and that orbit a common center of mass. – More than half of the stars in the sky are either binary stars or members of multiple-star systems. – Astronomers are able to identify binary stars through several methods. • Accurate measu ...
... – A binary star is two stars that are gravitationally bound together and that orbit a common center of mass. – More than half of the stars in the sky are either binary stars or members of multiple-star systems. – Astronomers are able to identify binary stars through several methods. • Accurate measu ...
The Pleiades in the Salle des Taureaux", Grotte de Lascaux
... circles the position at the epoch -15300. The proper motions of the stars are shown by connecting lines between the black and white circles. The shifting by reason of the precession of equinoxes is taken into account. Software Hipparcos 2000.0 for the Atari ST 1040 from ANDREAS KAMMERER, Karlsruhe, ...
... circles the position at the epoch -15300. The proper motions of the stars are shown by connecting lines between the black and white circles. The shifting by reason of the precession of equinoxes is taken into account. Software Hipparcos 2000.0 for the Atari ST 1040 from ANDREAS KAMMERER, Karlsruhe, ...
Chapter 15
... 5. What fundamental principle did Shapley use to calibrate the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variable stars? a. Light intensity falls off with the inverse square of distance. b. Stars that appear brighter are on average closer to Earth. c. Large pulsating objects have longer periods tha ...
... 5. What fundamental principle did Shapley use to calibrate the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variable stars? a. Light intensity falls off with the inverse square of distance. b. Stars that appear brighter are on average closer to Earth. c. Large pulsating objects have longer periods tha ...
Astro-MilkyWay
... 5. What fundamental principle did Shapley use to calibrate the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variable stars? a. Light intensity falls off with the inverse square of distance. b. Stars that appear brighter are on average closer to Earth. c. Large pulsating objects have longer periods tha ...
... 5. What fundamental principle did Shapley use to calibrate the period-luminosity relationship for Cepheid variable stars? a. Light intensity falls off with the inverse square of distance. b. Stars that appear brighter are on average closer to Earth. c. Large pulsating objects have longer periods tha ...
Astronomy Unit 4 Galaxies
... 3. Flattened, circular region our solar system is within. _______________________ 4. Central region of the Milky Way that contains older stars. ___________________ 5. Spherical region of faint stars that surrounds our galaxy. ____________________ 6. First person to estimate the size of our galaxy by ...
... 3. Flattened, circular region our solar system is within. _______________________ 4. Central region of the Milky Way that contains older stars. ___________________ 5. Spherical region of faint stars that surrounds our galaxy. ____________________ 6. First person to estimate the size of our galaxy by ...
Geo-centric astronomy from Pythagoras to Ptolemy File
... in which he advanced the heliocentric model as an alternative hypothesis. Archimedes wrote: You (King Gelon) are aware the 'universe' is the name given by most astronomers to the sphere the center of which is the center of the Earth, while its radius is equal to the straight line between the center ...
... in which he advanced the heliocentric model as an alternative hypothesis. Archimedes wrote: You (King Gelon) are aware the 'universe' is the name given by most astronomers to the sphere the center of which is the center of the Earth, while its radius is equal to the straight line between the center ...
Variable Star Spectroscopy 2008
... Be Stars are main sequence hot (B type) stars which show emission lines, particularly at H alpha from discs of circumstellar material. These discs are generally unstable and build and decay with time. The mechanisms of disc formation and decay are only approximately understood. This is a typical lin ...
... Be Stars are main sequence hot (B type) stars which show emission lines, particularly at H alpha from discs of circumstellar material. These discs are generally unstable and build and decay with time. The mechanisms of disc formation and decay are only approximately understood. This is a typical lin ...
Physics: Principle and Applications, 7e (Giancoli) Chapter 33
... position of a particular star varies by 0.00014° due to parallax. How many kilometers is this star from Earth? A) 1.2 × 1011 km B) 1.2 × 1014 km C) 1.2 × 1017 km D) 1.2 × 1020 km Answer: B Var: 1 7) The earth's orbit has a mean radius of 1.5 × 108 km. Over a six-month period, the apparent position o ...
... position of a particular star varies by 0.00014° due to parallax. How many kilometers is this star from Earth? A) 1.2 × 1011 km B) 1.2 × 1014 km C) 1.2 × 1017 km D) 1.2 × 1020 km Answer: B Var: 1 7) The earth's orbit has a mean radius of 1.5 × 108 km. Over a six-month period, the apparent position o ...
1. This question is about some of the properties of Barnard`s star
... The table gives information on the peak absolute magnitude and the peak apparent brightness of two Cepheid stars. star ...
... The table gives information on the peak absolute magnitude and the peak apparent brightness of two Cepheid stars. star ...
Rotation Periods of Wide Binaries in the Kepler Field
... same distance, then the magnitude difference between the two stars and their color index difference should be strongly correlated. The correlation may not be a simple one: the main sequence is not linear; some of the more massive stars may be evolved; some of the youngest, low-mass stars may not hav ...
... same distance, then the magnitude difference between the two stars and their color index difference should be strongly correlated. The correlation may not be a simple one: the main sequence is not linear; some of the more massive stars may be evolved; some of the youngest, low-mass stars may not hav ...
Navigating the Night Sky – Teacher Guide Argos Online Subject
... • Identify features of the star map: o How are constellations labeled? - All capital letters o How are stars labeled? -Lowercase (except first letter) o What do the symbols mean? -Open clusters, globular clusters, galaxies, etc…(see legend) o Why are the stars different sizes on the map? -Different ...
... • Identify features of the star map: o How are constellations labeled? - All capital letters o How are stars labeled? -Lowercase (except first letter) o What do the symbols mean? -Open clusters, globular clusters, galaxies, etc…(see legend) o Why are the stars different sizes on the map? -Different ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.