UNIVERSITY OF BRISTOL
... (25 marks total) (a) (6 marks) What is meant by a de Vaucouleurs (or r1/4) profile and for which galaxy type is it appropriate? How does the Sersic profile differ from this? (b) (12 marks) The bulge and disc components of a certain galaxy are observed to have half light (effective) radii of 3 arcsec ...
... (25 marks total) (a) (6 marks) What is meant by a de Vaucouleurs (or r1/4) profile and for which galaxy type is it appropriate? How does the Sersic profile differ from this? (b) (12 marks) The bulge and disc components of a certain galaxy are observed to have half light (effective) radii of 3 arcsec ...
Lesson 1 - The DK Foundation
... coins you can count degrees! Do not be afraid of getting completely confused. It is the first step to getting it straight if you persevere, after taking a short break to let the mind unscramble itself. If you use a computer to get at these answers then the person that you are cheating is yourself. I ...
... coins you can count degrees! Do not be afraid of getting completely confused. It is the first step to getting it straight if you persevere, after taking a short break to let the mind unscramble itself. If you use a computer to get at these answers then the person that you are cheating is yourself. I ...
Sun, Moon, Earth,
... • High mass stars (O and B) – Black Holes: “Objects” in space that have such high gravity that nothing (not even light) can escape them. • We can find them because…. – Stars that are close to them are “pulled” by the gravity of the black hole. – Gases in the area are pulled in so fast (like a drain ...
... • High mass stars (O and B) – Black Holes: “Objects” in space that have such high gravity that nothing (not even light) can escape them. • We can find them because…. – Stars that are close to them are “pulled” by the gravity of the black hole. – Gases in the area are pulled in so fast (like a drain ...
What is the “Meridian”?
... (Celestial sphere). If both were fixed and unchanging, we would always look to the same point in the sky to see the same object. BUT… We can be located anywhere on the Earth The Earth is rotating The Earth is orbiting the Sun The Moon is orbiting the Earth The planets are also orbiting the ...
... (Celestial sphere). If both were fixed and unchanging, we would always look to the same point in the sky to see the same object. BUT… We can be located anywhere on the Earth The Earth is rotating The Earth is orbiting the Sun The Moon is orbiting the Earth The planets are also orbiting the ...
Neither Star nor Trigram - 5 Yellow Focus of Attention
... comes in as factor behind pole reversal, changing Yin Qi into Yang. As we are practitioners of 9 Stars and Luoshu, then almost as an automation would we presume that such 3 Wood Luoshu had come to account of Star 3 to appear at the central Luoshu Palace. While rather, we’d have such 3 Wood Luoshu in ...
... comes in as factor behind pole reversal, changing Yin Qi into Yang. As we are practitioners of 9 Stars and Luoshu, then almost as an automation would we presume that such 3 Wood Luoshu had come to account of Star 3 to appear at the central Luoshu Palace. While rather, we’d have such 3 Wood Luoshu in ...
Exploring and Observing the Sun and Stars
... learners. The duration for this lesson is only a recommendation, and districts may modify the time frame to meet students’ needs. To better understand how your district may be implementing CSCOPE lessons, please contact your child’s teacher. (For your convenience, please find linked the TEA Commissi ...
... learners. The duration for this lesson is only a recommendation, and districts may modify the time frame to meet students’ needs. To better understand how your district may be implementing CSCOPE lessons, please contact your child’s teacher. (For your convenience, please find linked the TEA Commissi ...
The first photometric analysis of the overcontact binary MQ UMa with
... cool short-period binary merging. In this paper, we focus on the high fill-out, low mass ratio overcontact binaries which are at the late evolutionary stages of the contact configuration. Photometric analysis and orbital period studies of them will provide important information for the evolution and ...
... cool short-period binary merging. In this paper, we focus on the high fill-out, low mass ratio overcontact binaries which are at the late evolutionary stages of the contact configuration. Photometric analysis and orbital period studies of them will provide important information for the evolution and ...
The Age of the Milky Way - Astronomy Program
... illness, and therefore interpretation of symptoms. • In geology, the ages of rock formations can tell us about ice ages, magnetic pole reversals, volcanic activity, and climate. • In paleontology, ages of fossils are needed to understand evolution. • In archaeology, ages of finds are crucial for dat ...
... illness, and therefore interpretation of symptoms. • In geology, the ages of rock formations can tell us about ice ages, magnetic pole reversals, volcanic activity, and climate. • In paleontology, ages of fossils are needed to understand evolution. • In archaeology, ages of finds are crucial for dat ...
4b Telescopes
... pollution and you may be able to see only stars of magnitude 4 or brighter – that means only about 250 stars. The dimmest magnitude you can see in real conditions is called the ‘limiting magnitude’. ...
... pollution and you may be able to see only stars of magnitude 4 or brighter – that means only about 250 stars. The dimmest magnitude you can see in real conditions is called the ‘limiting magnitude’. ...
Globular Clusters
... the so-called RR LYRAE STARS. These stars have light variation amplitudes less than a couple of magnitudes and periods ranging from 0.2 to 1.1 days. Since their mean absolute magnitude is constant and fairly independent of metallicity (to within 0.3 mag), the RR Lyrae variables and the GCs, in turn, ...
... the so-called RR LYRAE STARS. These stars have light variation amplitudes less than a couple of magnitudes and periods ranging from 0.2 to 1.1 days. Since their mean absolute magnitude is constant and fairly independent of metallicity (to within 0.3 mag), the RR Lyrae variables and the GCs, in turn, ...
Stellar radii from long-baseline interferometry
... The cool dwarfs 61 Cyg A and B are the nearest stars in the northern hemisphere. They are a visual binary pair with a very long orbital period (≈ 700 yrs). In 1838, 61 Cyg became the first star whose distance from Earth was estimated accurately (Bessel 1838), shortly before Procyon’s, and it is now k ...
... The cool dwarfs 61 Cyg A and B are the nearest stars in the northern hemisphere. They are a visual binary pair with a very long orbital period (≈ 700 yrs). In 1838, 61 Cyg became the first star whose distance from Earth was estimated accurately (Bessel 1838), shortly before Procyon’s, and it is now k ...
3D maps of the local interstellar medium: searching for the imprints
... distances to a billion stars and, second, to the massive photometric/spectroscopic stellar surveys in progress or preparation that benefit from new multiplex techniques and large detectors. An example of IS absorption data inversion is shown in Figure 1. A merged catalog of color excess measurement ...
... distances to a billion stars and, second, to the massive photometric/spectroscopic stellar surveys in progress or preparation that benefit from new multiplex techniques and large detectors. An example of IS absorption data inversion is shown in Figure 1. A merged catalog of color excess measurement ...
chapter 14 - Astronomy
... 3. Electron degeneracy is the state of a gas in which its electrons are packed as densely as nature permits. The temperature of such a high-density gas is not dependent on the pressure as it is in a “normal” gas. 4. In the case of the degenerate core of a red giant, the more massive the core is, the ...
... 3. Electron degeneracy is the state of a gas in which its electrons are packed as densely as nature permits. The temperature of such a high-density gas is not dependent on the pressure as it is in a “normal” gas. 4. In the case of the degenerate core of a red giant, the more massive the core is, the ...
STC-Scripting Guide for Celestia
... used the Hipparcos satellite to measure the distances to many stars. Imaginary stars have to be given fake Hipparcos numbers in Celestia. Usually people use numbers between 300000 and 600000, to avoid conflicts with existing real stars that are in the database of Celestia. If a HIP number for a new ...
... used the Hipparcos satellite to measure the distances to many stars. Imaginary stars have to be given fake Hipparcos numbers in Celestia. Usually people use numbers between 300000 and 600000, to avoid conflicts with existing real stars that are in the database of Celestia. If a HIP number for a new ...
Brown et al. 2008 Studying Resolved Stellar
... first well documented era of star formation in the Galaxy and indeed in the Universe. A lower limit to the age of the Universe from these clusters has been and still is an important cosmological constraint. The age of the Universe, 13.7 ± 0.2 Gyr, is derived from measurement of the angular power spe ...
... first well documented era of star formation in the Galaxy and indeed in the Universe. A lower limit to the age of the Universe from these clusters has been and still is an important cosmological constraint. The age of the Universe, 13.7 ± 0.2 Gyr, is derived from measurement of the angular power spe ...
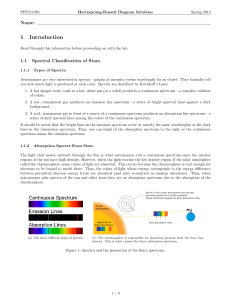
1 Introduction - High Point University
... 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R di ...
... 3. Check show luminosity classes and show isoradius lines (if they are not already checked). The green region (Dwarfs (V)) is known as the main sequence and contains all stars that are fusing hydrogen into helium as their primary energy source. Over 90% of all stars fall in this region on the H-R di ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.