The correct answers are written in bold, italic and underlined. The
... • Ultraviolet and X radiation The peak emission for dense, warm objects will be at infrared wavelengths, and this radiation can penetrate the dust and gas clouds. 11. What will be the influence of rotational motion on a dense molecular cloud of dust and gas as it condenses into stars? • Condensation ...
... • Ultraviolet and X radiation The peak emission for dense, warm objects will be at infrared wavelengths, and this radiation can penetrate the dust and gas clouds. 11. What will be the influence of rotational motion on a dense molecular cloud of dust and gas as it condenses into stars? • Condensation ...
8.1 Touring the Night Sky Pg. 308 #1
... that planets like Jupiter and Saturn are often called gas giants because they are mostly made of gas, like stars. The only thing keeping them from actually being stars is their mass. If Jupiter was 80x bigger, then it could be classified as a star. Another similarity between the two is that stars ac ...
... that planets like Jupiter and Saturn are often called gas giants because they are mostly made of gas, like stars. The only thing keeping them from actually being stars is their mass. If Jupiter was 80x bigger, then it could be classified as a star. Another similarity between the two is that stars ac ...
Star Formation/Llfe Cycle Notes
... a. Free fall contraction b. Kelvin-Helmoltz contraction-slows contraction (molecules begin to be forced into bouncing off each other, increasing pressure, and temp and slowing contraction) c. Known as Protostar of YSO, before it reaches main sequence d. Center of protostar gets dense enough and ther ...
... a. Free fall contraction b. Kelvin-Helmoltz contraction-slows contraction (molecules begin to be forced into bouncing off each other, increasing pressure, and temp and slowing contraction) c. Known as Protostar of YSO, before it reaches main sequence d. Center of protostar gets dense enough and ther ...
Galactic astronomy - Sierra College Astronomy Home Page
... Pure H & He stars, the first stars born after the Big Bang when very little metals existed. Stellar models tell us that Pop III stars would have been massive, shortlived, and none would have survived to current times. ...
... Pure H & He stars, the first stars born after the Big Bang when very little metals existed. Stellar models tell us that Pop III stars would have been massive, shortlived, and none would have survived to current times. ...
Chapter 10 Hertzsprung-Russel Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
Solar System Astrometry
... Mission facts 9 Darwin will use a flotilla of six space telescopes, each of which will be at least 1.5 metres in diameter. They will work together to scan the nearby Universe, looking for signs of life on Earth-like planets. 9 At optical wavelengths, a star outshines an Earth-like planet by a bill ...
... Mission facts 9 Darwin will use a flotilla of six space telescopes, each of which will be at least 1.5 metres in diameter. They will work together to scan the nearby Universe, looking for signs of life on Earth-like planets. 9 At optical wavelengths, a star outshines an Earth-like planet by a bill ...
Student Worksheet - Indiana University Astronomy
... nm (24 m or 0.024 mm), in the mid-infrared range of the spectrum. The flux density (brightness) of a star in each waveband is measured in units of milli-Jansky. A Jansky is 10-26 watts per square meter per frequency interval (and a milli-Jansky is 10-29 watts per square meter per frequency interval ...
... nm (24 m or 0.024 mm), in the mid-infrared range of the spectrum. The flux density (brightness) of a star in each waveband is measured in units of milli-Jansky. A Jansky is 10-26 watts per square meter per frequency interval (and a milli-Jansky is 10-29 watts per square meter per frequency interval ...
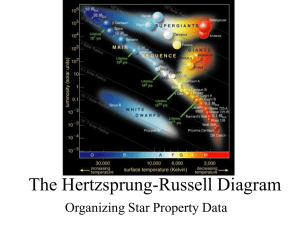
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... The H-R Diagram The “H-R” Diagram was invented around 1910 to organize stars based on their properties. The diagram is a graph. Vertically the scale is increasing Luminosity Horizontally the scale is Spectral Class/Temperature From Hot (O class) to Cool (M class). ...
... The H-R Diagram The “H-R” Diagram was invented around 1910 to organize stars based on their properties. The diagram is a graph. Vertically the scale is increasing Luminosity Horizontally the scale is Spectral Class/Temperature From Hot (O class) to Cool (M class). ...
High-Speed Ballistic Stellar Interlopers
... stars produced much larger bow shocks than the stars in the Hubble study, suggesting that they are more massive stars with more powerful stellar winds. The stars in this Hubble study are likely the lower-mass and/or lower-speed counterparts to the massive stars with bow shocks detected by IRAS. The ...
... stars produced much larger bow shocks than the stars in the Hubble study, suggesting that they are more massive stars with more powerful stellar winds. The stars in this Hubble study are likely the lower-mass and/or lower-speed counterparts to the massive stars with bow shocks detected by IRAS. The ...
giant molecular clouds
... In stars slightly more massive than the sun, a more powerful energy generation mechanism than the PP chain takes over: ...
... In stars slightly more massive than the sun, a more powerful energy generation mechanism than the PP chain takes over: ...
The Stars and the Solar System
... patterns, and planets. a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as number, size, color, and patterns. ...
... patterns, and planets. a. Recognize the physical attributes of stars in the night sky such as number, size, color, and patterns. ...
EM review
... Measuring the brightness of stars (and NEAS) The observed brightness of a star is given by its apparent magnitude. (First devised by Hipparchus who made a catalogue of about 850) The brightest stars: m=1. Dimmest stars (visible to the naked eye) m=6. The magnitude scale has been shown to be loga ...
... Measuring the brightness of stars (and NEAS) The observed brightness of a star is given by its apparent magnitude. (First devised by Hipparchus who made a catalogue of about 850) The brightest stars: m=1. Dimmest stars (visible to the naked eye) m=6. The magnitude scale has been shown to be loga ...
Hertzsprung-Russell Diagrams and Distance to Stars
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
... to the stars were unknown, one could not determine the intrinsic brightness of a star, but only its apparent brightness. As we’ve already said, a bright star that’s very far away would appear much fainter than a dim star that’s much closer. To overcome this problem, scientists began to look at stars ...
The_Birth_of_a_Star
... increases – like a skater who pulls her arms in while spinning 2. If nothing slow the rotation down, the speed will increase until the star is torn apart 3. One way that rotational energy is diminished is by the star splitting into a double star system 4. Another rout is for the star to spin off mat ...
... increases – like a skater who pulls her arms in while spinning 2. If nothing slow the rotation down, the speed will increase until the star is torn apart 3. One way that rotational energy is diminished is by the star splitting into a double star system 4. Another rout is for the star to spin off mat ...
Test 2 Review Topics
... 7. Be able to determine which band of the electromagnetic spectrum (gamma-rays radio) has the highest or lowest λ, ν, and energy. 8. Determine which star is hotter from the color. 9. What is an atmospheric window? 10. Recall whether a lens or mirror is used as the primary objective for refracting ...
... 7. Be able to determine which band of the electromagnetic spectrum (gamma-rays radio) has the highest or lowest λ, ν, and energy. 8. Determine which star is hotter from the color. 9. What is an atmospheric window? 10. Recall whether a lens or mirror is used as the primary objective for refracting ...
Chapter 21 notes - Clinton Public Schools
... *galaxies: huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 3 types: spiral galaxies: bulge in middle and arms that spiral outward, like pinwheel. Most new stars form in these spiral arms elliptical galaxy: like round flattened balls, contains billion ...
... *galaxies: huge group of single stars, star systems, star clusters, dust, and gas bound together by gravity. 3 types: spiral galaxies: bulge in middle and arms that spiral outward, like pinwheel. Most new stars form in these spiral arms elliptical galaxy: like round flattened balls, contains billion ...
How to Find the North Star ppt
... traditionally named after its apparent form or identified with a mythological figure. Modern astronomers divide the sky into eighty-eight constellations with defined boundaries Erroneously ...
... traditionally named after its apparent form or identified with a mythological figure. Modern astronomers divide the sky into eighty-eight constellations with defined boundaries Erroneously ...
Stars with mass less than 0.5 solar masses
... remember them: they are the initials of this sentence: Oh Be A Fine Girl, Kiss Me. In the y-axis, the absolute magnitude of the stars (not to be confused with the apparent magnitude) is reported, with, on the other side of the diagram, the luminosity compared to the Sun. So, the hottest, brightest s ...
... remember them: they are the initials of this sentence: Oh Be A Fine Girl, Kiss Me. In the y-axis, the absolute magnitude of the stars (not to be confused with the apparent magnitude) is reported, with, on the other side of the diagram, the luminosity compared to the Sun. So, the hottest, brightest s ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.