Lesson 3 Power Notes Outline
... Neutron stars rotate very rapidly. Some emit a rotating beam of electromagnetic radiation. These stars are called pulsars. ...
... Neutron stars rotate very rapidly. Some emit a rotating beam of electromagnetic radiation. These stars are called pulsars. ...
Bill Nye – Outer Space Worksheet
... c. 540 million kilometers 14. It will take light at least forty years to reach the nearest star. b. False ...
... c. 540 million kilometers 14. It will take light at least forty years to reach the nearest star. b. False ...
The Fate of Massive Stars
... increased opacity due to presence of various Ions (including Fe) in stellar atmosphere Diagonal upper-luminosity cutoff that is temperature dependent Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM ...
... increased opacity due to presence of various Ions (including Fe) in stellar atmosphere Diagonal upper-luminosity cutoff that is temperature dependent Hotter --> Higher Luminosity cutoff Greater mass-loss/stellar winds for cooler stars at lower luminosities Stellar winds important contribution to ISM ...
Finding Black Holes Left Behind by Single Stars
... behviour of about 12 million stars over the span of a decade or so. About a dozen certain microlensing events were detected (plus lots of previously unknown variable stars, a rich byproduct). This allowed the astronomers involved to set some interesting limits on the numbers of black holes in the ha ...
... behviour of about 12 million stars over the span of a decade or so. About a dozen certain microlensing events were detected (plus lots of previously unknown variable stars, a rich byproduct). This allowed the astronomers involved to set some interesting limits on the numbers of black holes in the ha ...
An Introduction To Parallax
... is more than 200,000 times further away than the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. This means that the shift in angle we observe in Alpha Centauri is less than 1 second of arc, or less than the thickness of a hair seen across a large rooma . It was not until the mid–19th century that astronomers were a ...
... is more than 200,000 times further away than the diameter of the Earth’s orbit. This means that the shift in angle we observe in Alpha Centauri is less than 1 second of arc, or less than the thickness of a hair seen across a large rooma . It was not until the mid–19th century that astronomers were a ...
How big are stars? How do we know?
... – If we can see from pictures taken over time that the stars are orbiting each other, the system is a visual binary – If the stars are so close together (or distant from Earth) that their spectra blur together, the system is called a spectroscopic binary – If the stars are oriented edge-on to the Su ...
... – If we can see from pictures taken over time that the stars are orbiting each other, the system is a visual binary – If the stars are so close together (or distant from Earth) that their spectra blur together, the system is called a spectroscopic binary – If the stars are oriented edge-on to the Su ...
Intro Lecture: Stars - University of Redlands
... with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI produced the first image of Mizar A. That image was the highest angul ...
... with a telescope. Spectroscopic observations show periodic Doppler shifts in the spectra of Mizar A and B, indicating that they are each binary stars. But they were too close to be directly imaged - until 2 May 1996, when the NPOI produced the first image of Mizar A. That image was the highest angul ...
GEARS Workshop Monday - Georgia Southern University
... evolved version of our Sun about 1,000 light years from Earth. Chandra X-ray Observatory data are colored in purple, and optical data from the 3-meter Shane telescope at Lick Observatory are shown in orange, green and blue. BP Psc is surrounded by a dusty and gaseous disk and has a pair of jets seve ...
... evolved version of our Sun about 1,000 light years from Earth. Chandra X-ray Observatory data are colored in purple, and optical data from the 3-meter Shane telescope at Lick Observatory are shown in orange, green and blue. BP Psc is surrounded by a dusty and gaseous disk and has a pair of jets seve ...
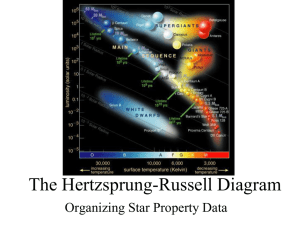
The Hertzsprung-Russell Diagram
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
... expect stars of the same size but different temperatures to form a diagonal line called an equal radius line. Equal Radius lines can be added to an H-R diagram ...
Scientists classify stars by
... 1. Stars are also classified by their brightness. 2. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is called apparent magnitude. 3. The actual brightness of a star is called absolute magnitude. Example: The SUN has an absolute magnitude of 4.8 when compared to the other stars. The SUN has an apparent ...
... 1. Stars are also classified by their brightness. 2. The brightness of a star as seen from Earth is called apparent magnitude. 3. The actual brightness of a star is called absolute magnitude. Example: The SUN has an absolute magnitude of 4.8 when compared to the other stars. The SUN has an apparent ...
Earth in the Universe
... much different paths of evolution. • Exist as a main sequence for a much shorter time, about 100 million years. • These stars still turn into super giants. • They then undergo a supernova and quickly collapse forming a center that is so dense only neutrons can exist (neutron star) • Even larger star ...
... much different paths of evolution. • Exist as a main sequence for a much shorter time, about 100 million years. • These stars still turn into super giants. • They then undergo a supernova and quickly collapse forming a center that is so dense only neutrons can exist (neutron star) • Even larger star ...
A Search for New Solar-Type Post-T Tauri Stars in
... The Taurus-Auriga and Sco-Cen regions of recent star formation were active approximately 1-3 and 10-30 Myr ago, respectively. Over the past several decades several hundred young stars have been identified in each of these regions based on various techniques including objective prism surveys for chro ...
... The Taurus-Auriga and Sco-Cen regions of recent star formation were active approximately 1-3 and 10-30 Myr ago, respectively. Over the past several decades several hundred young stars have been identified in each of these regions based on various techniques including objective prism surveys for chro ...
ppt
... Therefore stars have an extremely large gravitational attraction that keeps their plasma held together. As gravity acts equally in all directions the plasma that forms the star is moulded into a sphere. But there must be some force keeping the star from collapsing in on itself. Because stars are so ...
... Therefore stars have an extremely large gravitational attraction that keeps their plasma held together. As gravity acts equally in all directions the plasma that forms the star is moulded into a sphere. But there must be some force keeping the star from collapsing in on itself. Because stars are so ...
CHANDRA AUTOMATED POINT SOURCE PROCESSING FOR CALIBRATION MONITORING Chandra X-ray Center (CXC)
... nominal aimpoint for sources combined from throughout the Chandra mission. Highly piled-up (bright) sources are apparent with EE radii less than 2.3 arcsec. The curve fits a polynomial of the form, EE = 8e-5θ2-0.01θ+3.0. By filtering on time or energy we can detect shifts in this fit which indicate ...
... nominal aimpoint for sources combined from throughout the Chandra mission. Highly piled-up (bright) sources are apparent with EE radii less than 2.3 arcsec. The curve fits a polynomial of the form, EE = 8e-5θ2-0.01θ+3.0. By filtering on time or energy we can detect shifts in this fit which indicate ...
Measuring large distances
... The easiest way to measure the distance to a planet or star is through a method called parallax. • The parallax method (or triangulation, as it’s sometimes known) depends on having a baseline of known length. • A distant object is sighted accurately from both ends of the baseline. The angles to the ...
... The easiest way to measure the distance to a planet or star is through a method called parallax. • The parallax method (or triangulation, as it’s sometimes known) depends on having a baseline of known length. • A distant object is sighted accurately from both ends of the baseline. The angles to the ...
Stars I - Astronomy Centre
... further than the Sun • This single measurement increased the known size of the Universe by 10,000-fold! • Today, only 54 stars in 37 systems (singles, binaries or triples) are known within 15 light-years - stars are few and far between ...
... further than the Sun • This single measurement increased the known size of the Universe by 10,000-fold! • Today, only 54 stars in 37 systems (singles, binaries or triples) are known within 15 light-years - stars are few and far between ...
lecture12
... A classification of the stellar black body For historical reasons, astronomers classify the temperatures of stars on a scale defined by spectral types, called O B A F G K M, ranging from the hottest (type O) to the coolest (type M) stars. ...
... A classification of the stellar black body For historical reasons, astronomers classify the temperatures of stars on a scale defined by spectral types, called O B A F G K M, ranging from the hottest (type O) to the coolest (type M) stars. ...
PHY299B Poster-Justin Hudson-v2
... help clean up our images that could be altered by dust or other things interrupting the light coming into the telescope. • Once it is night, calibration of the telescope, then focusing on a star that is easily identifiable. This lets the computer running the telescope where in the sky it is looking ...
... help clean up our images that could be altered by dust or other things interrupting the light coming into the telescope. • Once it is night, calibration of the telescope, then focusing on a star that is easily identifiable. This lets the computer running the telescope where in the sky it is looking ...
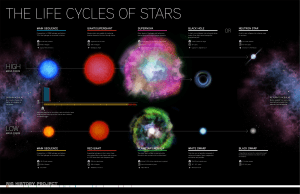
Life Cycles of Stars
... Expending hydrogen in their cores, these stars extend their outer layers and can grow to > 100 times their main sequence size. ...
... Expending hydrogen in their cores, these stars extend their outer layers and can grow to > 100 times their main sequence size. ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.