PowerPoint Presentation - Super Massive Black Holes
... supernova, sometimes referred to as a hypernova or quark-nova discovered on September 18, 2006. Brightest ever recorded supernova. Preliminary indications are that it was an unusually high-energy supernova of a very large star, around 150 solar masses. ...
... supernova, sometimes referred to as a hypernova or quark-nova discovered on September 18, 2006. Brightest ever recorded supernova. Preliminary indications are that it was an unusually high-energy supernova of a very large star, around 150 solar masses. ...
Learning Objectives Weeks 9-11 . 1. Know that star birth can begin
... 11. High-mass stars create heavy elements in their cores. A star of 8 or more solar masses evolves into a supergiant 100 times (or more) larger than the Sun. 12. High-mass stars violently blow apart in supernova explosions. By forming a dense core of iron, a massive star sows the seeds of its own de ...
... 11. High-mass stars create heavy elements in their cores. A star of 8 or more solar masses evolves into a supergiant 100 times (or more) larger than the Sun. 12. High-mass stars violently blow apart in supernova explosions. By forming a dense core of iron, a massive star sows the seeds of its own de ...
Peer Instruction/Active Learning
... b) Earth would be pulled into the black hole. c) X-‐rays would destroy Earth. d) Earth would be torn apart from the
... b) Earth would be pulled into the black hole. c) X-‐rays would destroy Earth. d) Earth would be torn apart from the
Powerpoint
... How big are stars? How far away are they? How bright are they? How hot? How old, and how long do they live? What is their chemical composition? How are they moving? Are they isolated or in clusters? By answering these questions, we not only learn about stars, but about the structure and evolution of ...
... How big are stars? How far away are they? How bright are they? How hot? How old, and how long do they live? What is their chemical composition? How are they moving? Are they isolated or in clusters? By answering these questions, we not only learn about stars, but about the structure and evolution of ...
Phobos
... and any associated planets. However, without identification and characterization of the foreground star, little can be said about the accompanying planet. The newly discovered host star, catalogued as OGLE-2003-BLG-235L/ MOA-2003-BLG53L, has a planetary companion that was discovered in 2003 through ...
... and any associated planets. However, without identification and characterization of the foreground star, little can be said about the accompanying planet. The newly discovered host star, catalogued as OGLE-2003-BLG-235L/ MOA-2003-BLG53L, has a planetary companion that was discovered in 2003 through ...
Astronomy Campus Assessment
... the same energy B. λ represents the distance between two wave peaks, therefore wave 3 has the most energy C. λ represents the distance between the top of a wave and the middle of a wave, therefore they all have the same energy D. λ represents the distance between two wave peaks, therefore wave 2 has ...
... the same energy B. λ represents the distance between two wave peaks, therefore wave 3 has the most energy C. λ represents the distance between the top of a wave and the middle of a wave, therefore they all have the same energy D. λ represents the distance between two wave peaks, therefore wave 2 has ...
Earth
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
... standard distance from Earth) from 20 pc. • Since the star will be “closer”, it will be brighter. • A brighter star has a smaller magnitude • Thus, we expect an absolute magnitude less than ...
Stellar Spire in the Eagle Nebula
... gas that reside in chaotic neighborhoods, where energy from newborn stars sculpts fantasy-like landscapes in the gas. The tower is a giant incubator for these newborn stars. A torrent of ultraviolet light from a band of massive, hot, young stars [off the top of the image] is eroding the pillar. The ...
... gas that reside in chaotic neighborhoods, where energy from newborn stars sculpts fantasy-like landscapes in the gas. The tower is a giant incubator for these newborn stars. A torrent of ultraviolet light from a band of massive, hot, young stars [off the top of the image] is eroding the pillar. The ...
Right Ascension
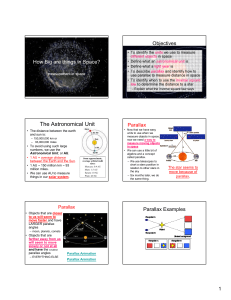
... A star at a distance of 1 parsec would have a parallax of one arcsecond – this is the definition of parsec, which is short for parallax arcsecond. A star at a distance of 2 parsecs would have a parallax of 0.5 arcsecond. So, measure the parallax, and you know the distance. The closest star, Proxima ...
... A star at a distance of 1 parsec would have a parallax of one arcsecond – this is the definition of parsec, which is short for parallax arcsecond. A star at a distance of 2 parsecs would have a parallax of 0.5 arcsecond. So, measure the parallax, and you know the distance. The closest star, Proxima ...
Stellar Death
... electrons cannot be forced any closer together due to the Pauli exclusion principle ...
... electrons cannot be forced any closer together due to the Pauli exclusion principle ...
Properties of Stars
... Sometimes the orbital plane is lined up so that the stars pass in front of each other as seen from the Earth. Each eclipse will cause the total light from the system to decrease. The amount of the decrease will depend on how much of each star is covered up (they can have different sizes) and on the ...
... Sometimes the orbital plane is lined up so that the stars pass in front of each other as seen from the Earth. Each eclipse will cause the total light from the system to decrease. The amount of the decrease will depend on how much of each star is covered up (they can have different sizes) and on the ...
Lecture17
... Stars don’t just occur in binaries and multiples, but large clusters as well. held together by their gravitational attraction to each other. born out of the same gas cloud (almost the same location) and at the same time. contains stars of different masses permits study of stellar evolution ...
... Stars don’t just occur in binaries and multiples, but large clusters as well. held together by their gravitational attraction to each other. born out of the same gas cloud (almost the same location) and at the same time. contains stars of different masses permits study of stellar evolution ...
Distance to the SMC
... Record all of your measurements for this part on your own paper and submit that data page with the rest of your work. For each of the four light curves for Cepheid variables, estimate the apparent magnitudes at maximum and the apparent magnitudes at minimum to the nearest 0.1 magnitude. Take the ave ...
... Record all of your measurements for this part on your own paper and submit that data page with the rest of your work. For each of the four light curves for Cepheid variables, estimate the apparent magnitudes at maximum and the apparent magnitudes at minimum to the nearest 0.1 magnitude. Take the ave ...
life
... L = Mean lifetime of intelligent life = 100 – 109 years •We have the ability to destroy civilization •We are also damaging our environment •We are using up non-renewable resources •Civilizations may “mature” – some evidence •Sustainable civilizations is technically possible ...
... L = Mean lifetime of intelligent life = 100 – 109 years •We have the ability to destroy civilization •We are also damaging our environment •We are using up non-renewable resources •Civilizations may “mature” – some evidence •Sustainable civilizations is technically possible ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.























