astronomy timeline
... actually redshifted lines of hydrogen. This showed that quasars are moving rapidly away from us and are extremely distant. p. 500, Box F 16.2 ...
... actually redshifted lines of hydrogen. This showed that quasars are moving rapidly away from us and are extremely distant. p. 500, Box F 16.2 ...
No Slide Title
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
... • We learn about stars by studying energy. – Stars produce a full range of electromagnetic radiation, from high-energy X-rays to low-energy radio waves. – Scientists use optical telescopes to study visible light and radio telescopes to study radio waves emitted from astronomical objects. – Earth’s a ...
light
... the aid of new observations of Blanco 1, an high-Galactic latitude, Pleiades-age cluster, I will show how deriving stellar age must be based upon very high quality observational data and a diverse range of stellar models. ...
... the aid of new observations of Blanco 1, an high-Galactic latitude, Pleiades-age cluster, I will show how deriving stellar age must be based upon very high quality observational data and a diverse range of stellar models. ...
A Star is Born!
... • The Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) represents the onset or start of nuclear burning (fusion) • The properties of a star on the ZAMS are primarily determined by its mass, somewhat dependent on composition (He and heavier elements) ...
... • The Zero Age Main Sequence (ZAMS) represents the onset or start of nuclear burning (fusion) • The properties of a star on the ZAMS are primarily determined by its mass, somewhat dependent on composition (He and heavier elements) ...
The Milky Way – A Classic Galaxy
... • Calibration has been hard; Cepheids too far away for ground-based parallaxes in order to measure distances. Space-based more successful, but still squishy. • Calibrated using some complex methods and also using Main Sequence Fitting for those in star clusters. First and best example: bright open c ...
... • Calibration has been hard; Cepheids too far away for ground-based parallaxes in order to measure distances. Space-based more successful, but still squishy. • Calibrated using some complex methods and also using Main Sequence Fitting for those in star clusters. First and best example: bright open c ...
Star Basics
... the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. One example is the luminous H II region surrounding star cluster M ...
... the hydrogen lines are weak. Both HeI and HeII (singly ionized helium) are seen in the higher temperature examples. The radiation from O5 stars is so intense that it can ionize hydrogen over a volume of space 1000 light years across. One example is the luminous H II region surrounding star cluster M ...
Take Home #2 Complete the following on your own paper. Do not
... D. Models will probably change because new technology will provide better information about the life cycle of stars. 20) Studying star clusters is essential to understand stars because individual stars change at such a slow rate. Studying these clusters allows scientists to observe stars that are si ...
... D. Models will probably change because new technology will provide better information about the life cycle of stars. 20) Studying star clusters is essential to understand stars because individual stars change at such a slow rate. Studying these clusters allows scientists to observe stars that are si ...
Oct 2017 - What`s Out Tonight?
... all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focuse ...
... all night and always outshines any star. Everyone enjoys its 4 tens of thousands stars held together by their mutual gravity. All Galilean moons and cloud bands, easily visible at 50x. It is posof the globulars that can be seen in the sky are part of our Milky sible to see the moons with well-focuse ...
2017 MIT Invitational
... plotted (34534 objects). The main cluster sequences are clearly visible; however there is some field star contamination present in key regions, particularly along the RGB and main sequence. Even ...
... plotted (34534 objects). The main cluster sequences are clearly visible; however there is some field star contamination present in key regions, particularly along the RGB and main sequence. Even ...
Stars
... • The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. • In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
... • The North Star is called Polaris and located directly above the North Pole. This star appears in the same place every night all year long. • In the Northern Hemisphere, if you find Polaris you will be able to tell which direction is north. ...
`Eye` stars at planetarium
... on Mt. Palomar. Photographs taken through the telescope are on view plastic forms to c r a w l through, in the new show at the Hudson River Museum's planetarium. plastic two-by-fours to build with and a collapsible see-saw. What looks like a white marble or catastrophic stellar explosion sundial is ...
... on Mt. Palomar. Photographs taken through the telescope are on view plastic forms to c r a w l through, in the new show at the Hudson River Museum's planetarium. plastic two-by-fours to build with and a collapsible see-saw. What looks like a white marble or catastrophic stellar explosion sundial is ...
The Life Cycle of Stars
... against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell used spectral class against absolute magnitude. Their resultant plots showed that the relationship between temperature and luminosity of a star was not random but instead appeared t ...
... against their colour (hence effective temperature). Independently in 1913 the American astronomer Henry Norris Russell used spectral class against absolute magnitude. Their resultant plots showed that the relationship between temperature and luminosity of a star was not random but instead appeared t ...
Slide 1
... Many of these super planets are closer to their star than Mercury is to the Sun. How does one form such a “hot Jupiter”? As of February 2012, Kepler has revealed 2321 planets – 281 are Jupiter-sized or larger (6 REarth < R < 22 REarth); – 1118 are Neptune-sized (2 REarth < R < 6 REarth); – 676 are s ...
... Many of these super planets are closer to their star than Mercury is to the Sun. How does one form such a “hot Jupiter”? As of February 2012, Kepler has revealed 2321 planets – 281 are Jupiter-sized or larger (6 REarth < R < 22 REarth); – 1118 are Neptune-sized (2 REarth < R < 6 REarth); – 676 are s ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... The discovery of stars brighter then first-magnitude extended the apparent magnitude scale upwards to 0 and then -1 and so on. The invention and development of telescopes allowed for the discovery of stars dimmer then +6, so the scale was extended downwards, +7 and so on. In the 19th century astr ...
... The discovery of stars brighter then first-magnitude extended the apparent magnitude scale upwards to 0 and then -1 and so on. The invention and development of telescopes allowed for the discovery of stars dimmer then +6, so the scale was extended downwards, +7 and so on. In the 19th century astr ...
Name: Astronomy Lab: The Hertzsprung-Russell (H
... the horizontal axis. The magnitude-color diagram is used for stars too faint to record their spectra and the luminosity-effective temperature diagram is used by theoretical astronomers calculating the properties of stellar models. The important property in common among all three is that they compare ...
... the horizontal axis. The magnitude-color diagram is used for stars too faint to record their spectra and the luminosity-effective temperature diagram is used by theoretical astronomers calculating the properties of stellar models. The important property in common among all three is that they compare ...
O star
... spectral type and the luminosity class of a star from its spectrum. This is extraordinarily valuable, as it means that, just from the spectrum of a star, one can plot it in on the H-R diagram. BUT: if you can plot a star on the H-R diagram, you know its absolute magnitude! And if you know its absolu ...
... spectral type and the luminosity class of a star from its spectrum. This is extraordinarily valuable, as it means that, just from the spectrum of a star, one can plot it in on the H-R diagram. BUT: if you can plot a star on the H-R diagram, you know its absolute magnitude! And if you know its absolu ...
The Stars - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... chemical testing of actual samples of stellar matter electromagnetic radiation spacecraft in orbit around distant stars both B and C above no data is used ...
... chemical testing of actual samples of stellar matter electromagnetic radiation spacecraft in orbit around distant stars both B and C above no data is used ...
Double Stars in Scorpio`s Claws
... stars that are a rewarding challenge to any astronomer. Some of these are actual double stars (pairs of stars that orbit about each other), others are ‘apparent doubles’ – stars that simply lie along the same line of sight, but are very distant from each other in space. The map below indicates the l ...
... stars that are a rewarding challenge to any astronomer. Some of these are actual double stars (pairs of stars that orbit about each other), others are ‘apparent doubles’ – stars that simply lie along the same line of sight, but are very distant from each other in space. The map below indicates the l ...
File - YEAR 11 EBSS PHYSICS DETAILED STUDIES
... The reason for the changes between the classes was to do with some atoms becoming ionised at various temperature and at cooler temperature the light may not have sufficient energy to excite the atoms to create spectral lines. This meant the temperature of a star could be determined without worryin ...
... The reason for the changes between the classes was to do with some atoms becoming ionised at various temperature and at cooler temperature the light may not have sufficient energy to excite the atoms to create spectral lines. This meant the temperature of a star could be determined without worryin ...
Absolute magnitude
... http://media.wwnorton.com/college/astronomy/animations/interactive/hrexplorer.html ...
... http://media.wwnorton.com/college/astronomy/animations/interactive/hrexplorer.html ...
Hipparcos

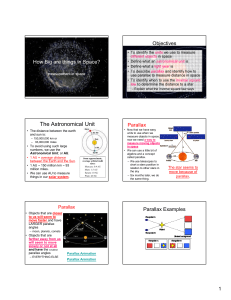
Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.