γ The potential for intensity interferometry with -ray telescope arrays
... Abstract. Intensity interferometry exploits a quantum optical effect in order to measure objects with extremely small angular scales. The first experiment to use this technique was the Narrabri intensity interferometer, which was successfully used in the 1970s to measure 32 stellar diameters at opti ...
... Abstract. Intensity interferometry exploits a quantum optical effect in order to measure objects with extremely small angular scales. The first experiment to use this technique was the Narrabri intensity interferometer, which was successfully used in the 1970s to measure 32 stellar diameters at opti ...
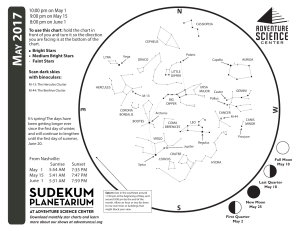
1705 chart front
... difference from night to night, but you will over the course of weeks or months. What we see in today’s pre-dawn sky is a preview of the early evening sky in later months. Go out before dawn this month for a look ahead at the summer night sky. Just before dawn, the Summer Triangle is high the sky an ...
... difference from night to night, but you will over the course of weeks or months. What we see in today’s pre-dawn sky is a preview of the early evening sky in later months. Go out before dawn this month for a look ahead at the summer night sky. Just before dawn, the Summer Triangle is high the sky an ...
The Milky Way - Houston Community College System
... Star appears slightly shifted from different positions of the Earth on its orbit The farther away the star is (larger d), the smaller the parallax angle p ...
... Star appears slightly shifted from different positions of the Earth on its orbit The farther away the star is (larger d), the smaller the parallax angle p ...
PHYS 2410 General Astronomy Homework 1
... 10. ___________ is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris. ...
... 10. ___________ is the brightest star in the constellation of Ursa Majoris. ...
Ch. 17 (RGs & WDs)
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
... This work is protected by United States copyright laws and is provided solely for the use of instructors in teaching their courses and assessing student learning. Dissemination or sale of any part of this work (including on the World Wide Web) will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permit ...
www.aavso.org
... Even today, many amateur astronomers still measure magnitudes using their eyes and submit data to an organization such as the AAVSO (American Association of Variable Star Observers) which can be used by professional astronomers for research. ...
... Even today, many amateur astronomers still measure magnitudes using their eyes and submit data to an organization such as the AAVSO (American Association of Variable Star Observers) which can be used by professional astronomers for research. ...
Sample exam 2
... lamp changes and you look through the spectroscope. The emission wavelengths are different! Alarmed, you turn the power back down and the gas emits the original wavelengths. Explain these observations, specifically with regard to the helium gas; in other words, what happened to the helium? You may a ...
... lamp changes and you look through the spectroscope. The emission wavelengths are different! Alarmed, you turn the power back down and the gas emits the original wavelengths. Explain these observations, specifically with regard to the helium gas; in other words, what happened to the helium? You may a ...
Universe and Star Formation - White Plains Public Schools
... Red-Giant Stage • Hydrogen burning migrates outward. The star’s outer envelope expands. • Its surface cools and becomes red. • The core collapses as helium is converted to carbon. Eventually all nuclear fuel is used and gravity squeezes the star. ...
... Red-Giant Stage • Hydrogen burning migrates outward. The star’s outer envelope expands. • Its surface cools and becomes red. • The core collapses as helium is converted to carbon. Eventually all nuclear fuel is used and gravity squeezes the star. ...
Stars I
... brightness changes as 1/distance2 The inverse square law describes how the brightness of a source light (a star!) diminishes with distance But how do we get the distances to stars whose brightness we DON’T know? ...
... brightness changes as 1/distance2 The inverse square law describes how the brightness of a source light (a star!) diminishes with distance But how do we get the distances to stars whose brightness we DON’T know? ...
astrocoursespring2012lec1-1-5
... -minor errata They point to the cross-over point of the analemma as the the equinox. This is not the case. The equinox occurs halfway between the most northern, and south excursion of the Sun ...
... -minor errata They point to the cross-over point of the analemma as the the equinox. This is not the case. The equinox occurs halfway between the most northern, and south excursion of the Sun ...
astrocoursespring2012lec5-1-1
... Astronomical Procedure: From Apparent Magnitudes of Variable Stars to their Distances Plot apparent magnitude values from observations at different times results in a light curve for a Cepheid in the Large Magellic Clouds – our closest extragalactic neighbour.Henrietta Leavitt did just that. ...
... Astronomical Procedure: From Apparent Magnitudes of Variable Stars to their Distances Plot apparent magnitude values from observations at different times results in a light curve for a Cepheid in the Large Magellic Clouds – our closest extragalactic neighbour.Henrietta Leavitt did just that. ...
Review Questions for Chp 2
... 47. How many types of electromagnetic radiation are there? 48. What was Newton’s most important contribution to astronomy? 49. Give an example of what Doppler radar is used for on Earth. 50. Define light year. 51. What does the Earth rotate around? 52. What is the main problem with a reflecting and ...
... 47. How many types of electromagnetic radiation are there? 48. What was Newton’s most important contribution to astronomy? 49. Give an example of what Doppler radar is used for on Earth. 50. Define light year. 51. What does the Earth rotate around? 52. What is the main problem with a reflecting and ...
SAMPLE TEST: Stars and Galaxies Multiple Choice Identify the letter
... a. the wavelength of light emitted by the star b. the color of the star c. the distance between the star and Earth d. binary star systems 4. Stars of which color have the coolest surface temperature? a. red c. yellow b. orange d. blue 5. A light-year is approximately ____. a. 9.5 trillion kilometers ...
... a. the wavelength of light emitted by the star b. the color of the star c. the distance between the star and Earth d. binary star systems 4. Stars of which color have the coolest surface temperature? a. red c. yellow b. orange d. blue 5. A light-year is approximately ____. a. 9.5 trillion kilometers ...
ASTRONOMY: WHAT DO YOU NEED TO KNOW
... What triggers star formation in an interstellar gas cloud? Shock waves from the explosions of nearby stars What is a protostar? A collapsing cloud of gas and dust destined to become a star but not yet glowing as a star What is a star cluster? Stars held together in a stable group by their common gra ...
... What triggers star formation in an interstellar gas cloud? Shock waves from the explosions of nearby stars What is a protostar? A collapsing cloud of gas and dust destined to become a star but not yet glowing as a star What is a star cluster? Stars held together in a stable group by their common gra ...
Life Cycle of Stars
... 2. If one of those clouds of dust and gas is massive enough, it’s own gravity causes it to start to collapse so it folds in on itself towards the center of that cloud it gets denser and denser and hotter and hotter 3. Eventually, the particles of that the gas and the dust are made of are brought so ...
... 2. If one of those clouds of dust and gas is massive enough, it’s own gravity causes it to start to collapse so it folds in on itself towards the center of that cloud it gets denser and denser and hotter and hotter 3. Eventually, the particles of that the gas and the dust are made of are brought so ...
Lab 6
... Using the index to figure out distance and age – the method of standard candles Astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, began to use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as a powerful tool to determine stellar properties. Initially, the method of standard candles for individual stars was applied to whole cl ...
... Using the index to figure out distance and age – the method of standard candles Astronomers, including Edwin Hubble, began to use the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram as a powerful tool to determine stellar properties. Initially, the method of standard candles for individual stars was applied to whole cl ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.