15 - Edmodo
... 1. Where did the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram come from? Why is it significant? (2 Marks) ...
... 1. Where did the Hertzsprung-Russell diagram come from? Why is it significant? (2 Marks) ...
AyC10 Fall 2007: Midterm 2 Review Sheet
... larger radius. Still, a red giant is not necessarily more massive than a red dwarf. As they evolve off the Main Sequence, stars do not gain mass. Therefore, a star that has one solar mass on the main sequence will evolve into a 1-solar-mass red giant. Do stars form by themselves, or in groups? Most ...
... larger radius. Still, a red giant is not necessarily more massive than a red dwarf. As they evolve off the Main Sequence, stars do not gain mass. Therefore, a star that has one solar mass on the main sequence will evolve into a 1-solar-mass red giant. Do stars form by themselves, or in groups? Most ...
PHYS 175 (2014) Final Examination Name: ___SOLUTION_____
... All questions are worth 1 pt., unless otherwise noted. Select the best answer for each question. Please answer discussion/description questions in complete sentences. Your may use your own handwritten notes, homework assignments and quizzes as references d ...
... All questions are worth 1 pt., unless otherwise noted. Select the best answer for each question. Please answer discussion/description questions in complete sentences. Your may use your own handwritten notes, homework assignments and quizzes as references d ...
Ch. 1 - University of Tennessee Department of Physics and Astronomy
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
... will destroy the integrity of the work and is not permitted. The work and materials from it should never be made available to students except by instructors using the accompanying text in their classes. All recipients of this work are expected to abide by these restrictions and to honor the intended ...
Stars, Galaxies & Universe
... closer to the stars. B. Satellite telescopes are able to see through solid objects. C. Satellite telescopes can detect wavelengths that are blocked by the atmosphere. D. Satellite telescopes have the ability to see the future. ...
... closer to the stars. B. Satellite telescopes are able to see through solid objects. C. Satellite telescopes can detect wavelengths that are blocked by the atmosphere. D. Satellite telescopes have the ability to see the future. ...
Galaxies - University of Iowa Astrophysics
... • Heber Curtis argued the Milky Way was just one of many galaxies – “island universes” • Held in the Smithsonian's Museum of Natural History – the auditorium still looks the same ...
... • Heber Curtis argued the Milky Way was just one of many galaxies – “island universes” • Held in the Smithsonian's Museum of Natural History – the auditorium still looks the same ...
Sun - TeacherWeb
... Elements from Helium (He) to iron (Fe) are made in stars by nuclear fusion. ...
... Elements from Helium (He) to iron (Fe) are made in stars by nuclear fusion. ...
Formation of Stars
... Star-forming regions are best studied using the infrared and radio portions of the spectrum. The dust in these regions absorbs most of the optical and UV light produced by the new stars, requiring observations at longer wavelengths. Infrared and radio waves pass through dust because their wavelength ...
... Star-forming regions are best studied using the infrared and radio portions of the spectrum. The dust in these regions absorbs most of the optical and UV light produced by the new stars, requiring observations at longer wavelengths. Infrared and radio waves pass through dust because their wavelength ...
RFS_multiple_choice_Dec8_Key
... A. Messier objects: astronomical objects catalogued by Charles Messier B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some ti ...
... A. Messier objects: astronomical objects catalogued by Charles Messier B. They are all objects for which the first detailed study was carried out by the Mauna Kea Observatory in Hawaii C. Objects which lie within 5 degrees on either side of the ecliptic, and are hence occulted by the moon at some ti ...
Lecture
... – O star: ~ 1 million years – G star (Sun): ~ 10 billion years – M star : ~ 5,000 billion years ...
... – O star: ~ 1 million years – G star (Sun): ~ 10 billion years – M star : ~ 5,000 billion years ...
FRAC TRIVIA I QUIZ - Flint River Astronomy Club
... 6. (8 pts.). Name eight Messier objects that are bright enough to be seen without binoculars or a telescope from a dark site in, say, Arizona. 7. (6 pts.). Three Messier objects are referred to as “Pinwheel Galaxy.” What are they, and what constellations are they in? 8. (5 pts.). Name the five types ...
... 6. (8 pts.). Name eight Messier objects that are bright enough to be seen without binoculars or a telescope from a dark site in, say, Arizona. 7. (6 pts.). Three Messier objects are referred to as “Pinwheel Galaxy.” What are they, and what constellations are they in? 8. (5 pts.). Name the five types ...
PARALLAX – IT`S SIMPLE! Abstract
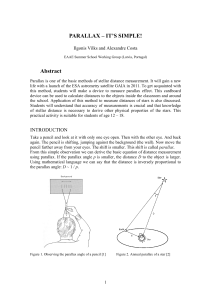
... Agency HIPPARCOS satellite went into orbit. Its catalogue, published in 1997, gave parallaxes of 120 thousand of stars with accuracy of 0.002 arcsecond and therefore it was possible to determine distances up to 500 parsecs (1 pc = 3,086×1016 m). Why astronomers need to know distances to the stars? L ...
... Agency HIPPARCOS satellite went into orbit. Its catalogue, published in 1997, gave parallaxes of 120 thousand of stars with accuracy of 0.002 arcsecond and therefore it was possible to determine distances up to 500 parsecs (1 pc = 3,086×1016 m). Why astronomers need to know distances to the stars? L ...
Last Year`s Exam, Section B
... What effect will this have on any stars which may subsequently form in the Orion Nebula? outer regions of star contain heavy elements made during star’s life and during supernova explosion ...
... What effect will this have on any stars which may subsequently form in the Orion Nebula? outer regions of star contain heavy elements made during star’s life and during supernova explosion ...
Astronomy and the Universe - Department of Physics and Astronomy
... What makes up our solar system? What are the stars? Do they last forever? What are galaxies? What do astronomers learn by studying them? How does measuring angles help astronomers learn about objects in the sky? What is powers-of-ten notation, and why is it useful in ...
... What makes up our solar system? What are the stars? Do they last forever? What are galaxies? What do astronomers learn by studying them? How does measuring angles help astronomers learn about objects in the sky? What is powers-of-ten notation, and why is it useful in ...
Conceptual Physics
... a. as massive as the Sun but only about as large in size as Jupiter b. as massive as the Sun but only about as large in size as Earth c. as large in diameter as the Sun but only about as massive as Earth d. about the same size and mass as the Sun but much hotter 23. What is the basic definition of a ...
... a. as massive as the Sun but only about as large in size as Jupiter b. as massive as the Sun but only about as large in size as Earth c. as large in diameter as the Sun but only about as massive as Earth d. about the same size and mass as the Sun but much hotter 23. What is the basic definition of a ...
Document
... object at the center of some galaxies that produces energy at a high rate- Quasar a neutron star that emits radio waves- Pulsar large celestial body that emits lights; Sun- Star the apparent shift in wavelength of light as the source moves away from or toward observer; Red and blue shifts- Doppler E ...
... object at the center of some galaxies that produces energy at a high rate- Quasar a neutron star that emits radio waves- Pulsar large celestial body that emits lights; Sun- Star the apparent shift in wavelength of light as the source moves away from or toward observer; Red and blue shifts- Doppler E ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.