ppt - Astronomy & Physics
... The HR diagram allows us to define the evolution of stars in terms of tracks on a luminosity/temperature diagram’ Stars heavier than 2 solar masses don’t live long enough for intelligent life to evolve Even stars like the Sun are destined to expand through a supergiant phase which will eventually ma ...
... The HR diagram allows us to define the evolution of stars in terms of tracks on a luminosity/temperature diagram’ Stars heavier than 2 solar masses don’t live long enough for intelligent life to evolve Even stars like the Sun are destined to expand through a supergiant phase which will eventually ma ...
White Dwarf Stars
... • Recently, Joe Taylor and Russell Hulse won a Nobel Prize for their study of pulsars. • These objects act as cosmic clocks and are useful for probing the dynamics of stars. ...
... • Recently, Joe Taylor and Russell Hulse won a Nobel Prize for their study of pulsars. • These objects act as cosmic clocks and are useful for probing the dynamics of stars. ...
PARALLAX EXERCISE1 The goal of this exercise is to introduce the
... Determining distances to celestial objects is one of the most important and most difficult measurements in astronomy. Compare the Sun to another star in the sky. They look completely different, and it was once believed that they were different types of objects. In fact, the Sun was once considered a ...
... Determining distances to celestial objects is one of the most important and most difficult measurements in astronomy. Compare the Sun to another star in the sky. They look completely different, and it was once believed that they were different types of objects. In fact, the Sun was once considered a ...
parallax
... Determining distances to celestial objects is one of the most important and most difficult measurements in astronomy. Compare the Sun to another star in the sky. They look completely different, and it was once believed that they were different types of objects. In fact, the Sun was once considered a ...
... Determining distances to celestial objects is one of the most important and most difficult measurements in astronomy. Compare the Sun to another star in the sky. They look completely different, and it was once believed that they were different types of objects. In fact, the Sun was once considered a ...
Article Reference - Archive ouverte UNIGE
... (radial velocities or transits), the occurrence rate of hot Jupiters orbiting solar-type stars is low. It has been estimated to be as high as 1.5 ± 0.6% by Cumming et al. (2008) from radial velocity surveys, and as low as 0.5 ± 0.1% by Howard et al. (2012) from the Kepler results. Johnson et al. (20 ...
... (radial velocities or transits), the occurrence rate of hot Jupiters orbiting solar-type stars is low. It has been estimated to be as high as 1.5 ± 0.6% by Cumming et al. (2008) from radial velocity surveys, and as low as 0.5 ± 0.1% by Howard et al. (2012) from the Kepler results. Johnson et al. (20 ...
Stars - PAMS-Doyle
... Motion of Stars • They rotate on an axis • They may revolve around another star • They move toward or away from our solar system. • The Doppler Effect can determine their direction…works just like sound in the apparent shift because of motion! ...
... Motion of Stars • They rotate on an axis • They may revolve around another star • They move toward or away from our solar system. • The Doppler Effect can determine their direction…works just like sound in the apparent shift because of motion! ...
Chapter 17 Measuring the Stars
... in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect; th ...
... in Binary Stars In order to measure stellar masses in a binary star, the period and semimajor axis of the orbit must be measured. Once this is done, Kepler’s third law gives the sum of the masses of the two stars. Then the relative speeds of the two stars can be measured using the Doppler effect; th ...
Orion - CSIC
... Given a star chart without constellation figures marked on it (whether real star charts or made-up star patterns), students can invent their own constellations, looking for patterns in the stars that appeal to them. Students can then be asked to make up stories to go with their new constellations. O ...
... Given a star chart without constellation figures marked on it (whether real star charts or made-up star patterns), students can invent their own constellations, looking for patterns in the stars that appeal to them. Students can then be asked to make up stories to go with their new constellations. O ...
Stars and Constellations
... For the people in the Native American southwest, the sky is not something remote from Earth. Rather, it is a unifying whole, both a window into the universe and an instrument for understanding and measuring its rhythms. Indian people have been watching the sky for many generations and applying its s ...
... For the people in the Native American southwest, the sky is not something remote from Earth. Rather, it is a unifying whole, both a window into the universe and an instrument for understanding and measuring its rhythms. Indian people have been watching the sky for many generations and applying its s ...
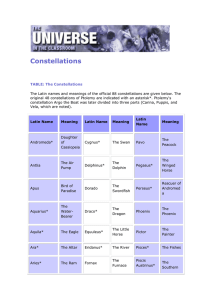
Constellations
... • Polaris (the North Star) doesn’t “move” due to the Earth’s rotation. • The angle of Polaris to the north horizon gives the observer’s latitude Polaris Location Latitude directly overhead ...
... • Polaris (the North Star) doesn’t “move” due to the Earth’s rotation. • The angle of Polaris to the north horizon gives the observer’s latitude Polaris Location Latitude directly overhead ...
13 The Family of Stars
... triangulation was done by Eratosthenes about 2300 years ago. He noticed that when the Sun was directly overhead in Syene, it was at an angle in Alexandria. By measuring the angle θ and the distance b between the cities he calculated the radius r = b/θ. ...
... triangulation was done by Eratosthenes about 2300 years ago. He noticed that when the Sun was directly overhead in Syene, it was at an angle in Alexandria. By measuring the angle θ and the distance b between the cities he calculated the radius r = b/θ. ...
Mr - White Plains Public Schools
... diagram, a star like Earth’s Sun will eventually (1) explode in a supernova (2) become a black hole (3) change to a white dwarf (4) become a neutron star 2. Stars like Earth’s Sun ...
... diagram, a star like Earth’s Sun will eventually (1) explode in a supernova (2) become a black hole (3) change to a white dwarf (4) become a neutron star 2. Stars like Earth’s Sun ...
Stars, Galaxies, and the Universe Section 1 Distances to Stars
... • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun causes the stars to appear to shift slightly to the w ...
... • The stars seem as though they are moving counterclockwise around a central star called Polaris, the North Star. Polaris is almost directly above the North Pole, and thus the star does not appear to move much. • Earth’s revolution around the sun causes the stars to appear to shift slightly to the w ...
Properties of Stars: The H
... Stellar Mass: Binary Systems • So for a single-lined SB we measure one component of the motion of one component of the binary system. (3b) Double-lined Spectroscopic Binary. Take a spectrum of an apparently single star and see two sets of absorption lines with each set of lines moving back and fort ...
... Stellar Mass: Binary Systems • So for a single-lined SB we measure one component of the motion of one component of the binary system. (3b) Double-lined Spectroscopic Binary. Take a spectrum of an apparently single star and see two sets of absorption lines with each set of lines moving back and fort ...
Star Birth
... – About 10 million years after its first appearance, a protostar (comparable in mass to our Sun) will become a true star. – It would have shrunk to about the size of our Sun (starting from about 10,000 times the size of our Sun) the contraction would raise the temperature to 10 million Kelvin - enou ...
... – About 10 million years after its first appearance, a protostar (comparable in mass to our Sun) will become a true star. – It would have shrunk to about the size of our Sun (starting from about 10,000 times the size of our Sun) the contraction would raise the temperature to 10 million Kelvin - enou ...
Two-Gyro Performance, Scheduling and Acquisitions
... – This problem was identified by the OTA SEs in some follow-on analysis of the previous problem’s test results. However, the cause of this problem is different. – Problem only occurs with Target-ReAcq style Acqs/ReAcqs where both PASS and the onboard ReAcq process are effectively accounting for a po ...
... – This problem was identified by the OTA SEs in some follow-on analysis of the previous problem’s test results. However, the cause of this problem is different. – Problem only occurs with Target-ReAcq style Acqs/ReAcqs where both PASS and the onboard ReAcq process are effectively accounting for a po ...
PDF Version
... galaxy, which are all about the same distance from us, to find the correlation between the period and the intrinsic brightness. They also measured the distances to the nearest Cepheid variables using the parallax method. While the parallax method is good for measuring distances only to a few hundred ...
... galaxy, which are all about the same distance from us, to find the correlation between the period and the intrinsic brightness. They also measured the distances to the nearest Cepheid variables using the parallax method. While the parallax method is good for measuring distances only to a few hundred ...
Milky Way
... variable stars” in some of them. • Cepheids are evolved supergiant stars that brighten and fade periodically as their size oscillates. Remember, these are standard candles. • If Cepheids appear faint, then they must be way outside the Milky Way Galaxy. • From the distance and angular size of spiral ...
... variable stars” in some of them. • Cepheids are evolved supergiant stars that brighten and fade periodically as their size oscillates. Remember, these are standard candles. • If Cepheids appear faint, then they must be way outside the Milky Way Galaxy. • From the distance and angular size of spiral ...
Johnathan - WordPress.com
... star in the night sky, with a visual magnitude of 0.13. Rigel is a triple star system. The primary star (Rigel A) is a bluewhite supergiant around 120,000 times as luminous as the Sun. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and swollen out to 79 times the Sun's radius. An Alpha Cygni variable, it puls ...
... star in the night sky, with a visual magnitude of 0.13. Rigel is a triple star system. The primary star (Rigel A) is a bluewhite supergiant around 120,000 times as luminous as the Sun. It has exhausted its core hydrogen and swollen out to 79 times the Sun's radius. An Alpha Cygni variable, it puls ...
The Swansong of Stars Orbiting Massive Black Holes
... orbital energy. Examples of dissipative processes are tidal heating, or gravitational wave emission. These processes are effective only when the star passes very close to the MBH. Inspiral starts when the star is scattered into a highly eccentric orbit, which brings it close to the MBH. Every orbit ...
... orbital energy. Examples of dissipative processes are tidal heating, or gravitational wave emission. These processes are effective only when the star passes very close to the MBH. Inspiral starts when the star is scattered into a highly eccentric orbit, which brings it close to the MBH. Every orbit ...
Starry Night¨ Times - October 2008
... lightyears from the back of your eyeball. It has about 25 bright stars spattered across a field about the size of a full moon; in reality, they're spread over an area 20 lightyears in width. Bright enough to be sometimes visible to the naked eye (Aristotle is said to have noticed it around 325 B.C.) ...
... lightyears from the back of your eyeball. It has about 25 bright stars spattered across a field about the size of a full moon; in reality, they're spread over an area 20 lightyears in width. Bright enough to be sometimes visible to the naked eye (Aristotle is said to have noticed it around 325 B.C.) ...
Figures I through VII in Section 1 on the following sheet
... Which spectrum would most likely have been produced by star B from figure X (_3_)? Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure II (_4_)? Why (_5_)? Of the stars labeled on figure X: Which two are the two hottest (_6_)? Which are the two brightest (_7_)? ...
... Which spectrum would most likely have been produced by star B from figure X (_3_)? Of stars C and E in figure X, which is more likely to have produced the spectrum in figure II (_4_)? Why (_5_)? Of the stars labeled on figure X: Which two are the two hottest (_6_)? Which are the two brightest (_7_)? ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.