Orion-pr-2009 - Astrophysics Research Institute
... Europe and on the U.S. Mainland. Tom Megeath, an astronomer from the University of Toledo, provided a catalogue of the positions of the very youngest stars – sources revealed only recently by the Spitzer Space Telescope. Thomas Stanke, a researcher based at the European Southern Observatory in Garch ...
... Europe and on the U.S. Mainland. Tom Megeath, an astronomer from the University of Toledo, provided a catalogue of the positions of the very youngest stars – sources revealed only recently by the Spitzer Space Telescope. Thomas Stanke, a researcher based at the European Southern Observatory in Garch ...
M WHITE DWAR F The WhiTe-hoT Core
... When a star has used up all its hydrogen fuel, it expands rapidly. Eventually, it collapses under its own gravity and becomes a white dwarf. Although it’s out of fuel, a white dwarf still shines brightly, like an electric burner that glows after you turn off the stove. Like the electric burner, a wh ...
... When a star has used up all its hydrogen fuel, it expands rapidly. Eventually, it collapses under its own gravity and becomes a white dwarf. Although it’s out of fuel, a white dwarf still shines brightly, like an electric burner that glows after you turn off the stove. Like the electric burner, a wh ...
2012 New York State Science Olympiad Astronomy
... Egregious and/or repeated violations of this rule will be dealt with strictly. 12. Do not be discouraged if you do not finish in the allotted time, as this test is designed to be very difficult, in order to differentiate between the top teams. 13. Please remove this front page before leaving the roo ...
... Egregious and/or repeated violations of this rule will be dealt with strictly. 12. Do not be discouraged if you do not finish in the allotted time, as this test is designed to be very difficult, in order to differentiate between the top teams. 13. Please remove this front page before leaving the roo ...
Problems_blackbody_spectra_hr
... Above are three spectral curves showing stars A, X, Y, Z. Star A is shown in all of the plots as a point of comparison. Assume that stars A and Y are the same size. 7. Between stars A and Y, which star looks redder? Explain your reasoning. ...
... Above are three spectral curves showing stars A, X, Y, Z. Star A is shown in all of the plots as a point of comparison. Assume that stars A and Y are the same size. 7. Between stars A and Y, which star looks redder? Explain your reasoning. ...
- Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope
... binaries were discovered to be strong x-ray emitters – 10 orders of magnitude greater! ...
... binaries were discovered to be strong x-ray emitters – 10 orders of magnitude greater! ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 12. Star C and star D are at the same distance from us, but star D is 10,000 times more luminous than star C. How do their brightness levels compare? Star D will appear brighter by a factor of 10,000 over star C. 13. How do the magnitudes of stars C and D in problem 4 compare? (Problem 4 synopsis: ...
... 12. Star C and star D are at the same distance from us, but star D is 10,000 times more luminous than star C. How do their brightness levels compare? Star D will appear brighter by a factor of 10,000 over star C. 13. How do the magnitudes of stars C and D in problem 4 compare? (Problem 4 synopsis: ...
b. - UW Canvas
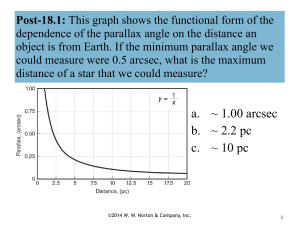
... Post-18.1: This graph shows the functional form of the dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? ...
... Post-18.1: This graph shows the functional form of the dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? ...
Similarities Between Electric and Gravitational Forces • Coulomb’s force: q F
... The End States of Stars • Ordinary stars sustain the thermal pressure • Heat flows from the star to the universe • Without nuclear-energy sources: the star will contract and get hotter • But violent or not, death is as inevitable • Astronomers belive four are possible: ...
... The End States of Stars • Ordinary stars sustain the thermal pressure • Heat flows from the star to the universe • Without nuclear-energy sources: the star will contract and get hotter • But violent or not, death is as inevitable • Astronomers belive four are possible: ...
stars and beyond - Math/Science Nucleus
... On this celestial globe the equator is 90° from the North Star. This does not correspond to the Earth’s equator, so it is called the celestial equator. From the celestial equator parallel lines are spaced north and south. These are the parallels of declination, which indicate the distance of a star ...
... On this celestial globe the equator is 90° from the North Star. This does not correspond to the Earth’s equator, so it is called the celestial equator. From the celestial equator parallel lines are spaced north and south. These are the parallels of declination, which indicate the distance of a star ...
Exam #2 Solutions
... the point on an HR diagram where conditions within the core of the star are sufficient to initiate fusion. ZAMS is an acronym for Zero Age Main Sequence. B. The five stars that appear in nearly a straight line in the lower left of the HR diagram are what type of objects? These five objects are white ...
... the point on an HR diagram where conditions within the core of the star are sufficient to initiate fusion. ZAMS is an acronym for Zero Age Main Sequence. B. The five stars that appear in nearly a straight line in the lower left of the HR diagram are what type of objects? These five objects are white ...
Section 4 Formation of the Universe Chapter 19
... • An instrument called a spectrograph is used to break a star’s light into a spectrum. The spectrum of a star will vary depending on which elements are present. ...
... • An instrument called a spectrograph is used to break a star’s light into a spectrum. The spectrum of a star will vary depending on which elements are present. ...
Presentation
... have such alignment, and the fraction decreases for planets with larger orbits. For a planet orbiting a sun-sized star at 1AU, the probability of a random alignment producing a transit is ...
... have such alignment, and the fraction decreases for planets with larger orbits. For a planet orbiting a sun-sized star at 1AU, the probability of a random alignment producing a transit is ...
Lesson 6 - Magnitudes of Stars
... The “Distance Modulus” gives ratio of apparent brightness “light ratio” The difference between the apparent magnitude and the absolute magnitude. m - M = Distance Modulus 2.512m-M = “light ratio” Now can use our definition of apparent brightness in a useful way. ...
... The “Distance Modulus” gives ratio of apparent brightness “light ratio” The difference between the apparent magnitude and the absolute magnitude. m - M = Distance Modulus 2.512m-M = “light ratio” Now can use our definition of apparent brightness in a useful way. ...
Stars
... From this point on, the core cools down like an ordinary object. While it is still hot enough to be seen, such a core is known as a white dwarf star. Compared to other stars, white dwarfs are tiny. More remarkable is the way that the radius of a white dwarf depends on its mass. In normal main sequen ...
... From this point on, the core cools down like an ordinary object. While it is still hot enough to be seen, such a core is known as a white dwarf star. Compared to other stars, white dwarfs are tiny. More remarkable is the way that the radius of a white dwarf depends on its mass. In normal main sequen ...
Astrophysics notes - School
... sources is greater than λ/d the two sources can be resolved (we can see them as two separate sources). Where d is the diameter of the aperture and λ is the wavelength of the ...
... sources is greater than λ/d the two sources can be resolved (we can see them as two separate sources). Where d is the diameter of the aperture and λ is the wavelength of the ...
Star-S_Teacher_Guide - The University of Texas at Dallas
... A common misconception with students is that the stars are on fire, and burn just like fires on the Earth. If your students bring up such misconceptions during the introduction, gently guide them through the difficulties with this idea. Two major difficulties are the source of fuel and of oxygen to ...
... A common misconception with students is that the stars are on fire, and burn just like fires on the Earth. If your students bring up such misconceptions during the introduction, gently guide them through the difficulties with this idea. Two major difficulties are the source of fuel and of oxygen to ...
Magnitude Scale and Distance Measurements
... You will need to apply this later on, when we determine the distance to a star cluster by curve-fitting on the H-R Diagram. 1) The absolute magnitude of the Sun is +4.83, of Sirius A is + 1.45, and of Spica is .119. Using the apparent magnitudes given in part 1 of this review, find the distances to ...
... You will need to apply this later on, when we determine the distance to a star cluster by curve-fitting on the H-R Diagram. 1) The absolute magnitude of the Sun is +4.83, of Sirius A is + 1.45, and of Spica is .119. Using the apparent magnitudes given in part 1 of this review, find the distances to ...
Death of Stars notes
... cycle of exactly 1.3373011 seconds. • Some scientists speculated that this was evidence of an alien civilization’s communication system and dubbed the source LGM (Little Green ...
... cycle of exactly 1.3373011 seconds. • Some scientists speculated that this was evidence of an alien civilization’s communication system and dubbed the source LGM (Little Green ...
food for thought - Boulder Ensemble Theatre Company
... stars of the Small Magellanic Cloud. She then spent two years in Europe. Upon her return, she spent a few years with her family in Wisconsin before returning to a paid position at the Observatory in 1902, where she was paid 30 cents an hour for her analysis of variable stars. Leavitt is best known f ...
... stars of the Small Magellanic Cloud. She then spent two years in Europe. Upon her return, she spent a few years with her family in Wisconsin before returning to a paid position at the Observatory in 1902, where she was paid 30 cents an hour for her analysis of variable stars. Leavitt is best known f ...
AN ATTEMPT To prove the MOTION OF THE EARTH FROM
... Introductions enough for that purpose: But rather to furnish the Learned with an experimentum crucisto determine between the Tychonick and Copernican Hypotheses. That which hath hitherto continued the dispute hath been the plausibleness of some Arguments alledged by the one and the other party, with ...
... Introductions enough for that purpose: But rather to furnish the Learned with an experimentum crucisto determine between the Tychonick and Copernican Hypotheses. That which hath hitherto continued the dispute hath been the plausibleness of some Arguments alledged by the one and the other party, with ...
C:\Documents and Settings\Administrator\Desktop\Lecture 15.wpd
... MSun = -26.5 + 31.5 = +5 The Sun would be a dim star just visible in Cortland at 10 parsecs. Distance Distance can only be determined directly from a local group of stars near enough to have their parallax measured. ...
... MSun = -26.5 + 31.5 = +5 The Sun would be a dim star just visible in Cortland at 10 parsecs. Distance Distance can only be determined directly from a local group of stars near enough to have their parallax measured. ...
Hipparcos

Hipparcos was a scientific satellite of the European Space Agency (ESA), launched in 1989 and operated until 1993. It was the first space experiment devoted to precision astrometry, the accurate measurement of the positions of celestial objects on the sky. This permitted the accurate determination of proper motions and parallaxes of stars, allowing a determination of their distance and tangential velocity. When combined with radial-velocity measurements from spectroscopy, this pinpointed all six quantities needed to determine the motion of stars. The resulting Hipparcos Catalogue, a high-precision catalogue of more than 118,200 stars, was published in 1997. The lower-precision Tycho Catalogue of more than a million stars was published at the same time, while the enhanced Tycho-2 Catalogue of 2.5 million stars was published in 2000. Hipparcos ' follow-up mission, Gaia, was launched in 2013.The word ""Hipparcos"" is an acronym for High precision parallax collecting satellite and also a reference to the ancient Greek astronomer Hipparchus of Nicaea, who is noted for applications of trigonometry to astronomy and his discovery of the precession of the equinoxes.