* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download b. - UW Canvas
Cygnus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Corona Australis wikipedia , lookup
Perseus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Cassiopeia (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Reflecting instrument wikipedia , lookup
Aquarius (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Observational astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Canis Minor wikipedia , lookup
Corvus (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
Lunar theory wikipedia , lookup
Canis Major wikipedia , lookup
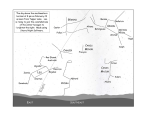
Timeline of astronomy wikipedia , lookup
Malmquist bias wikipedia , lookup
Dialogue Concerning the Two Chief World Systems wikipedia , lookup
Orion (constellation) wikipedia , lookup
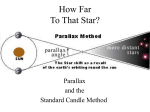
Cosmic distance ladder wikipedia , lookup
Post-18.1: This graph shows the functional form of the dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? a. ~ 1.00 arcsec b. ~ 2.2 pc c. ~ 10 pc ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 8 Post-18.1: This graph shows the functional form of the dependence of the parallax angle on the distance an object is from Earth. If the minimum parallax angle we could measure were 0.5 arcsec, what is the maximum distance of a star that we could measure? a. ~ 1.00 arcsec b. ~ 2.2 pc c. ~ 10 pc ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 9 Post-18.2: The Moon never stops in its orbit; however, it is possible to get an exact measurement of its parallax and thus its distance at any given moment. How would we get the parallax shift of the Moon? a. Take simultaneous measurements from two locations. b. Take two measurements at different times from one location. c. Take two measurements from the same location at the same phase of the Moon. ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 10 Post-18.2: The Moon never stops in its orbit; however, it is possible to get an exact measurement of its parallax and thus its distance at any given moment. How would we get the parallax shift of the Moon? a. Take simultaneous measurements from two locations. b. Take two measurements at different times from one location. c. Take two measurements from the same location at the same phase of the Moon. ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 11 Post-18.3: An equation in the form of y = 1/x governs the relationship between the parallax angle and the distance. In gravity, which equation states the proportionality between the force and the distance? a. 1 y= 2 x b. y =1 / x c. y=x ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 12 Post-18.3: An equation in the form of y = 1/x governs the relationship between the parallax angle and the distance. In gravity, which equation states the proportionality between the force and the distance? a. 1 y= 2 x b. y =1 / x c. y=x ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 13 Post-18.4: The table below lists the three stars of Orion’s belt. Which of the following ranks these stars from nearest to farthest? a. b. c. Mintaka, Alnilam, Alnitak Alnilam, Alnitak, Mintaka Mintaka, Alnitak, Alnilam ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 14 Post-18.4: The table below lists the three stars of Orion’s belt. Which of the following ranks these stars from nearest to farthest? a. b. Mintaka, Alnilam, Alnitak Alnilam, Alnitak, Mintaka c. Mintaka, Alnitak, Alnilam ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 15 Post-18.5: True or False: Alnilam is approximately three times farther away from us than Mintaka. a. true b. false ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 16 Post-18.5: True or False: Alnilam is approximately three times farther away from us than Mintaka. a. true b. false ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 17 Post-18.6: The parallax for the star Sirius, constellation Canis Major, is 0.379 arc seconds; the parallax for the star Rigel, constellation Orion, is 0.00378 arc seconds. Approximately how much farther away from us is Rigel than Sirius? a. 10 times farther b. 100 times farther c. 1000 times farther ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 18 Post-18.6: The parallax for the star Sirius, constellation Canis Major, is 0.379 arc seconds; the parallax for the star Rigel, constellation Orion, is 0.00378 arc seconds. Approximately how much farther away from us is Rigel than Sirius? a. 10 times farther b. 100 times farther c. 1000 times farther ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 19 This concludes Activity 18: Finding Distances to Stars Using Parallax Measurements ©2014 W. W. Norton & Company, Inc. 20